Joint Study Reveals Link Between Financial Capability and Well-being Among Young People
Investment Product Ownership Varies by Capability
Young People Possess Knowledge, But Struggle to Take Action
"Introduction of 'Basic Finance' Concept Needed for Practical Financial Education"
A study has found that young people’s investment behaviors differ depending on their financial capability. According to the research, young people with higher financial literacy tend to prefer formal financial products such as savings accounts or stocks. Those who have more worries about the future and struggle to manage their spending are more likely to hold virtual assets such as cryptocurrencies. The study also examined the financial capabilities of young people themselves. Although they possess a certain level of financial knowledge, they find it difficult to put this knowledge into practice, highlighting the need for action-oriented financial education.
According to the financial sector on May 12, the non-profit organization Finance and Happiness Network and the youth policy platform ‘Yeolgodakki’ announced these findings in their joint report, ‘Youth Financial Capability and Financial Well-being,’ conducted in March. Out of 300 respondents under the age of 39, data from 259 participants were used after excluding responses with errors.
Financial capability consists of financial knowledge, financial behavior, and financial attitude. Financial knowledge refers to understanding financial concepts or principles. Financial attitude describes the values or beliefs about finance, or how one perceives money. Financial behavior refers to how one actually manages money based on their knowledge and attitude. Financial well-being is a concept that includes psychological stability regarding finances, expectations for the future, and self-efficacy in financial decision-making. Among these, financial security refers to a subjective perception of current and future financial stability. Financial satisfaction indicates overall satisfaction with one’s current financial life, while financial confidence refers to trust in one’s own ability to make financial decisions.
"A Study Empirically Analyzing the Relationship Between Financial Capability and Well-being"
There have been several studies on the financial behaviors of young people in Korea. The Bank of Korea and the Financial Supervisory Service release a national financial literacy survey every two years. The Korea Inclusive Finance Agency conducted a youth financial status survey in 2016 and then again in 2023, marking the first youth-focused financial survey in seven years. The agency conducted the same survey again last year. However, there are criticisms that the Bank of Korea and Financial Supervisory Service surveys target the entire population, while the Korea Inclusive Finance Agency’s survey is limited to a simple status report.
The scale used to measure capability and well-being in this survey was developed by the Finance and Happiness Network. It was tailored to the financial realities of Korean youth by referencing the OECD financial literacy questionnaire, and this is the first time it has been used in an actual survey. This research also empirically analyzed whether financial capability affects actual financial well-being, meaning subjective satisfaction with one’s financial status.
"Young People Investing in Cryptocurrency Seek Quick Riches"... High Financial Knowledge Does Not Always Lead to Action
First, the study analyzed the impact of financial capability and well-being on whether young people hold investment products. Financial knowledge had a positive effect on holding demand deposits, bonds, and stocks. In contrast, it had a negative effect on informal saving behaviors, such as entrusting investments to family members. In other words, the higher the financial knowledge, the more likely young people are to prefer formal financial products. Financial attitude did not have a statistically significant effect on holding most investment products. In the case of financial behavior, it had a positive effect not only on stocks but also on alternative investments such as gold and real estate. This means that young people who are more inclined to make actual financial decisions and take action beyond knowledge tend to engage in a wider range of investment activities. Lower financial security and higher financial satisfaction were both found to have a positive effect on holding cryptocurrencies. That is, those who have less control over their spending but still feel satisfied with their current financial life are more likely to invest in cryptocurrencies. The report interpreted this as “a sign that young people are either trying to escape real-world anxieties or are seeking opportunities for quick riches.”
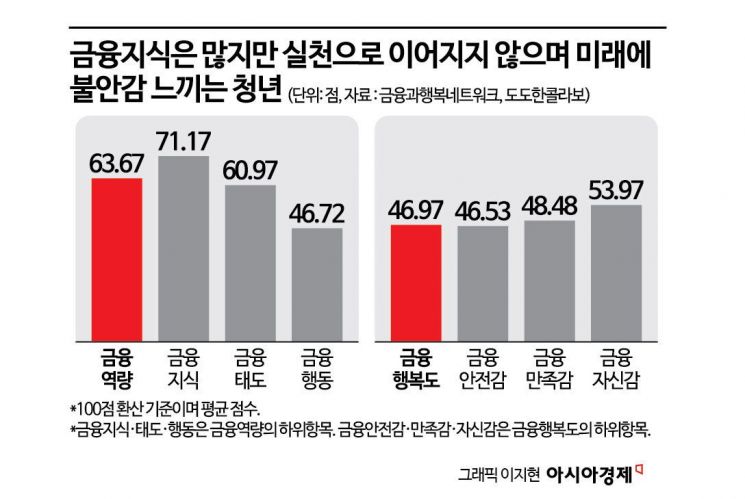
There was also an in-depth study on financial capability and financial well-being. According to the analysis, the average financial capability score for young people was 63.67 out of 100. They scored 71.17 in financial knowledge, but only 46.72 in financial behavior. This indicates that while young people possess financial knowledge, they struggle to translate it into action. In particular, their ability to carry out everyday financial practices, such as making long-term financial plans and keeping spending records, was found to be weak. The average financial well-being score was 46.97, with financial security (46.53) being the lowest among its components.
'Basic Finance' Concept Needed... Action-oriented Financial Education Should Be Combined
This study also revealed the relationship between financial capability and financial well-being. Financial knowledge showed only a weak correlation with well-being. In contrast, higher levels of financial behavior led to significant increases in overall well-being, including confidence, satisfaction, and security. The report explained that this demonstrates the need for action-oriented education that encourages behavior, rather than simply teaching financial knowledge.
The study also confirmed differences in well-being according to income level. Young people with monthly incomes of 3 million won or more had higher overall financial well-being than those with lower incomes. This suggests that financial instability among young people directly affects their subjective sense of financial security.
Jung Unyoung, chairman of the Finance and Happiness Network, suggested that financial education should focus on enabling young people to put their financial knowledge into action. For example, programs that help develop proper income and spending habits and attitudes. He also argued for the introduction of the ‘basic finance’ concept and the establishment of policy systems to support it. Jung said, “Today, finance is not just a tool but the foundation of life. We need ‘basic finance’ that can become a part of everyone’s daily life, not just a complex system. We must support young people so that their financial capability leads to real asset formation and improved quality of life.”
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.


![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)














