KDCA Announces '2023 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Results'
Chronic Diseases in 50s Worsen Over 10 Years
Alcohol Consumption Decreases in Men, Increases in Women
Last year, the smoking rate among adults in South Korea increased again, mainly among men in their 50s and women in their 20s. Although the obesity rate remained similar to the previous year, obesity increased among young people, including men in their 20s and women in their 20s and 30s.
The Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA) announced the results of the 9th National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) for the second year (2023) on the 3rd.
Since 1998, the NHANES has been conducted to understand the health and nutrition status of the population and to be used for establishing and evaluating health policies. Each year, about 10,000 people aged 19 and older are surveyed on smoking, drinking, physical activity, nutrition, chronic diseases, and more.
First, over the past 10 years (2014?2023), the prevalence of hypertension and diabetes among adults showed little change, but the prevalence of obesity and hypercholesterolemia increased.
Last year, the prevalence of obesity (body mass index of 25 or higher) among adults was 45.6% for men and 27.8% for women, with men decreasing by 2.1 percentage points and women increasing by 2.1 percentage points compared to the previous year.
The obesity prevalence among men showed a continuous increasing trend in their 20s (42.8% in 2022, 43.9% in 2023), while half of men in their 30s to 50s were still obese. The obesity prevalence among women in their 20s also increased by 3.9 percentage points to 22.1%, and in their 30s by 5.5 percentage points to 27.3% compared to the previous year.
The prevalence of hypertension was 23.4% for men and 16.5% for women, diabetes was 12.0% for men and 6.9% for women, and hypercholesterolemia was 19.9% for men and 21.4% for women, generally similar to or slightly lower than the previous year. When comparing the prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, and hypercholesterolemia by age, men showed a sharp increase in their 40s, and women in their 50s.
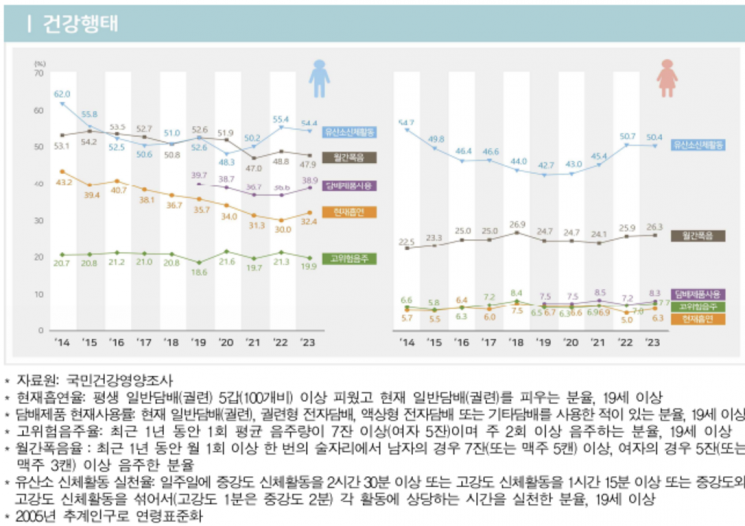
The smoking rate (based on conventional cigarettes) was 32.4% for men and 6.3% for women, increasing by 2.4 percentage points and 1.3 percentage points respectively compared to 2022. Looking at the past 10 years, the male smoking rate decreased from 43.2% in 2014 to 30.0% in 2022, then rose again. For women, it increased from 5.7% in 2014 to 7.5% in 2018, then decreased to 5.0% in 2022 before rising again.
Among men, the smoking rate for those in their 50s notably increased from 32.5% in 2022 to 42.1% last year, a 9.6 percentage point rise. For women in their 20s, the smoking rate rose from 5.8% to 12.1% during the same period, a 6.3 percentage point increase, showing a marked upward trend. The current use rate of tobacco products including e-cigarettes also rebounded, rising by 2.3 percentage points to 38.9% for men and by 1.1 percentage points to 8.3% for women compared to the previous year.
The 'high-risk drinking rate,' defined as adults who drink an average of 7 or more drinks per occasion (5 or more for women) or drink at least twice a week over the past year, was 19.9% for men, down from 21.3% the previous year, but increased from 7.0% to 7.7% for women.
The rate of practicing aerobic physical activity was 54.5% for men and 50.4% for women, slightly decreasing compared to the previous year.
In the survey item newly introduced last year, 'adequate health literacy level,' 60.4% scored 30 or higher out of 40 points. Health literacy was lower among older age groups and those with lower income levels.
In terms of diet, the trend of decreased intake of grains and fruits and increased intake of meat and beverages among the population aged 1 and older continued last year.
Last year, the daily fruit intake for men and women was 116.3g, down 7.3g from the previous year and 69.3g from 2014. Conversely, meat intake (129.0g) increased by 4.0g compared to the previous year and 22.3g compared to 2014, and beverage intake (274.6g) also rose significantly by 8.0g from the previous year and 97.0g from 2014.
The proportion of energy obtained from fat (26.3%) continued to increase, especially among women in their 20s (30.1%), approaching the upper limit of the recommended fat energy ratio in the Korean nutrient intake standards (30% for ages 19?29).
The KDCA analyzed that over the past 10 years, health behaviors and chronic disease indicators worsened among men and women in their 50s, and disparities by income level widened in male smoking rates, physical activity practice rates, and female obesity rates. For example, in 2014, the obesity rate among women in the 'low' income group was 10.0 percentage points higher than the 'high' group, but last year the gap widened to 14.6 percentage points.
Jiyoungmi, director of the KDCA, said, "In 2023, the health level of the population showed decreases in hypertension and hypercholesterolemia, but smoking increased, and drinking, physical activity, and obesity remained stagnant. We will strengthen the production of evidence for chronic disease prevention and management by introducing follow-up surveys to identify changes in health behaviors and causes of chronic diseases."
The statistical report containing the 2023 NHANES results will be published later this month and will also be made available on the KDCA National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey website.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.

![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)














