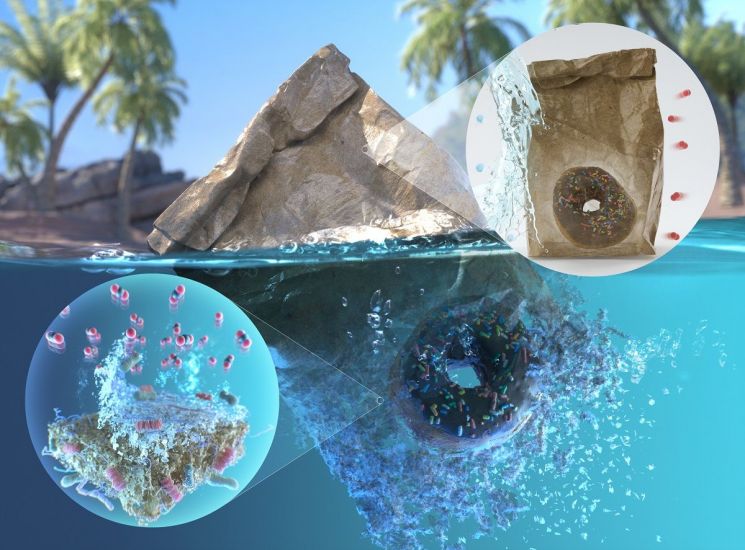
A paper coating agent that biodegrades most microplastics in the ocean, known as the most challenging environment for biodegradation, has been developed domestically.
Environmental pollution caused by plastics is a global challenge. In particular, microplastics smaller than 5 mm generated during the plastic degradation process float on the ocean surface and underwater for decades, polluting the marine environment, which has raised concerns. This is why the recent research results are attracting attention.
KAIST announced on the 17th that a joint research team consisting of Professor Jae-Wook Myung from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Professor Han-Seul Yang from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST, and Professor Jong-Chul Seo from the Department of Packaging and Logistics at Yonsei University developed a sustainable marine biodegradable high-performance paper coating agent.
 (From left) Professor Jae-Wook Myung, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, KAIST · PhD candidate Si-Hyung Choi · Professor Han-Seul Yang, Department of Life Sciences · Professor Jong-Cheol Seo, Department of Packaging and Logistics, Yonsei University · Integrated MS-PhD candidate Ki-Tae Park. Provided by KAIST
(From left) Professor Jae-Wook Myung, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, KAIST · PhD candidate Si-Hyung Choi · Professor Han-Seul Yang, Department of Life Sciences · Professor Jong-Cheol Seo, Department of Packaging and Logistics, Yonsei University · Integrated MS-PhD candidate Ki-Tae Park. Provided by KAIST
Paper packaging used in daily life is already recognized as an eco-friendly packaging material. However, it has significant limitations in moisture resistance, oxygen barrier properties, and strength.
To improve the low barrier properties of paper packaging, polyethylene (PE), ethylene vinyl alcohol (EVOH), and other materials are used as coating agents. However, these substances do not decompose easily and become major culprits in worsening plastic pollution when exposed to the natural environment.
To address these issues, many bio-based materials and biodegradable plastics have been developed as packaging materials, but there have been limitations in resolving the dilemma that increasing packaging performance lowers biodegradability.
To overcome this, the Yonsei University research team succeeded in producing a high-modulus film using biodegradable plastic polyvinyl alcohol and boric acid, coating it on paper to realize packaging materials with biodegradability, biocompatibility, high barrier properties, and high strength.
The developed coated paper showed excellent barrier properties against oxygen and water vapor while exhibiting high physical strength. In particular, it maintained high tensile strength even in humid environments, which the research team explained as a revolutionary overcoming of paper’s shortcomings.
The KAIST research team conducted in-depth verification of biodegradability and biocompatibility to evaluate the sustainability of the coated paper developed by the Yonsei University team.
In the laboratory, biodegradability of the coated paper was measured by simulating the marine environment, analyzing the degree to which the carbon components of the material mineralize into carbon dioxide over 111 days. The results confirmed that depending on the coating components, biodegradation ranged from as low as 59% to as high as 82%.
Additionally, using electron microscopy, the team observed marine microorganisms decomposing the coating material and confirmed the coating material’s low neurotoxicity. Biocompatibility of the coated paper was verified through in vivo biological response experiments using rats.
Professor Jae-Wook Myung of KAIST said, “This research is meaningful in that it proposed a coating strategy that overcomes the limitations of existing paper packaging, maintaining sustainability while enhancing packaging performance. The paper coating agent developed by the research team biodegrades in the natural environment without artificial intervention and is a low-toxicity substance, so even if unintentionally discarded, it does not exacerbate environmental pollution. This provides grounds to consider it a potentially sustainable alternative to plastic packaging.”
Professor Jong-Chul Seo of Yonsei University, who led the development of the high-performance paper coating, said, “Through this research, we developed an eco-friendly paper packaging technology that can replace hard-to-degrade plastic packaging. We hope that these research results can be applied in actual industrial fields.”
Meanwhile, this research was conducted with support from the National Research Foundation of Korea and the Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries. The research results were also published online in prestigious journals in the fields of eco-friendly sustainable science and technology and food science and technology, such as Green Chemistry and Food Chemistry.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.