KITA Robotics Industry Analysis Report
Widening Global Competitiveness Gap Between Korea and Japan
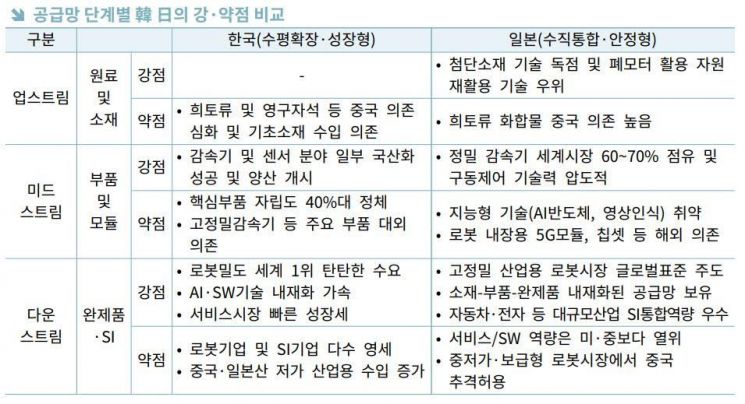
Dependence on China for Essential Materials, Localization Rate Stuck at 40%
Although Korea possesses strong capabilities in utilizing robots, an analysis has found that the country is structurally vulnerable to supply chain risks due to its high dependence on foreign sources for key materials and components.
According to the report "Changing Landscape of the Global Robotics Industry and Comparative Supply Chain Analysis of Korea and Japan," released by the Korea International Trade Association's Institute for International Trade and Commerce on January 25, Korea ranks fourth in the world for the number of industrial robots installed and first in robot density, maintaining a top global position in terms of robot utilization. However, 71.2% of total robot shipments in Korea are concentrated in the domestic market.
In contrast, Japan, which ranks second globally in industrial robot installations, exports more than 70% of its shipments overseas, highlighting a significant gap in global competitiveness between Korea and Japan.
 On the opening day of CES on the 6th (local time), a representative from Korean robotics company Robotis demonstrated a robot at the Las Vegas Convention Center (LVCC) in Nevada, USA, that mimics hand gestures recognized by a camera. This is unrelated to the article content. Photo by Yonhap News.
On the opening day of CES on the 6th (local time), a representative from Korean robotics company Robotis demonstrated a robot at the Las Vegas Convention Center (LVCC) in Nevada, USA, that mimics hand gestures recognized by a camera. This is unrelated to the article content. Photo by Yonhap News.
The report identified "structural differences in the supply chain"-spanning upstream (raw materials and materials), midstream (core components and modules), and downstream (finished products and system integration)-as the core reason for the gap between the two countries. Korea relies on China for 88.8% (as of 2025) of its permanent magnets, a material essential for robot operation, and Japan and China are also the largest importers for major components such as precision reducers and controllers. As a result, the localization rate for materials and components critical to robot functionality remains in the 40% range, leading to a situation where increased production of finished robots is structurally tied to increased imports of materials and components.
On the other hand, despite being a country with limited natural resources, Japan mitigates upstream supply chain shocks through resource recycling technologies that recover rare earth elements from discarded motors, as well as advanced material technologies such as specialty steel and precision magnets. In the midstream stage, global companies like Harmonic Drive (reducers) and Yaskawa (motors) hold 60-70% of the world market for key components, establishing a stable "vertically integrated" supply chain. Based on this component competitiveness, Japan is recognized as a leader in setting global standards in the high-precision industrial robot market.
The report proposed a two-track strategy for the continued growth of Korea's robotics industry: stabilizing the supply chain and leading new markets. At the corporate level, it emphasized the need to secure new markets based on a stable supply chain by ▲ strengthening joint research and development (R&D) between companies on the demand and supply sides of key materials and components, ▲ acquiring technologies to reduce reliance on rare earth elements, ▲ expanding exports of combined packages including robots, system integration, and after-sales service, and ▲ marketing "Clean Robots" based on security and reliability. At the government level, the report called for policy support such as ▲ sharing risks associated with localization and creating public sector demand, ▲ advancing urban mining-based resource recycling systems, ▲ supporting the creation of global references (track records) for the "K-Robot Package," and ▲ enhancing the alignment between domestic testing/certification systems and international standards.
Jinshil Mu, Senior Research Fellow, stated, "While Korea excels in robot utilization, there is a clear structural limitation due to high dependence on foreign sources for key materials and components," adding, "Rapidly shifting from a manufacturing- and utilization-focused strategy to a supply chain stabilization strategy will be crucial for the future competitiveness of the robotics industry."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)














