KDB Future Strategy Research Institute's 2026 Domestic Economic Outlook
"Purchasing Power to Rise on Recovery in Consumer Sentiment and Price Stability"
Construction Investment to Grow on Expanded SOC Budget
Facility Investment to See Modest Increase; Exports to Decline
Domestic Industries to Grow, Led by Semiconductors and Pharmaceuticals
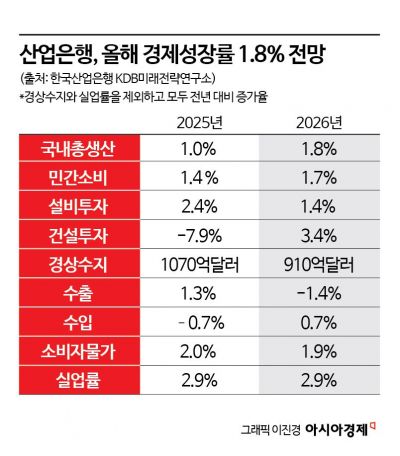
The Korea Development Bank (KDB) has forecast South Korea's economic growth rate for this year at 1.8%. This projection is in line with the estimates provided by the Bank of Korea, the International Monetary Fund (IMF), and the Korea Development Institute (KDI). KDB expects a gradual recovery across domestic industries, led by information technology (IT), pharmaceuticals, and construction. The bank also anticipates that conditions in sectors such as steel and general machinery, which struggled last year, will improve.
According to the financial sector on January 7, the KDB Future Strategy Research Institute stated in its recently published "2026 Domestic Economic Outlook" that "the domestic economy is expected to grow by 1.8% this year, higher than last year’s 1%, due to factors such as increased private consumption supported by policy measures like fiscal expansion, improvements in construction investment, and a base effect from last year’s low growth."
The report analyzed that private consumption is expected to gradually expand, based on the recovery in consumer sentiment that began in the second half of last year. In addition, consumer price stability and nominal wage growth outpacing inflation are projected to improve real purchasing power. However, the institute identified several factors that could constrain the recovery in consumption: the continued rise in household debt, the limited decline in lending rates and the resulting burden of principal and interest repayments, and persistently high living costs. Construction investment is expected to grow by 3.4% this year, rebounding from a 7.9% contraction last year. This positive outlook is attributed to improved order conditions since the second quarter of 2024 and an increase in the budget for social overhead capital (SOC).
Facility investment is projected to see only a modest increase of 1.4%, despite some improvement in investment conditions due to lower interest rates. This is because corporate investment sentiment remains sluggish and there is a possibility of increased direct investment in the United States. This growth rate is 1 percentage point lower than last year’s 2.4%. Exports are expected to decline by 1.4% year-on-year, despite continued growth in semiconductor exports. The decrease is attributed to the full impact of U.S. tariff policies and a slowdown in global trade growth due to U.S.-China trade tensions. As a result, the current account surplus is also expected to shrink compared to last year, mainly due to a reduction in the goods balance surplus.
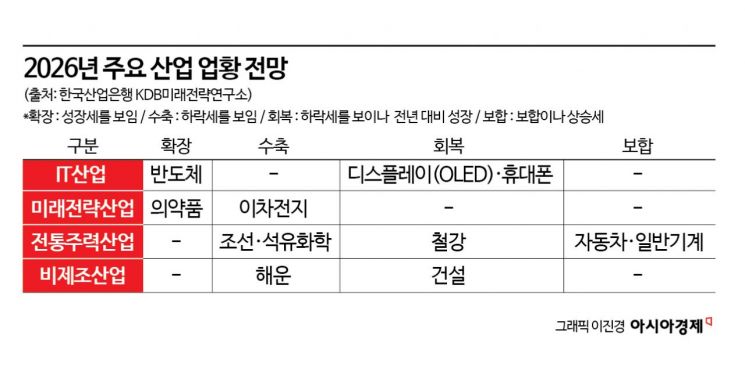
Regarding this year’s industrial outlook, the institute explained, "The IT industry, including semiconductors, displays, and mobile phones, is expected to grow, while government policy-driven improvements in the construction sector will help domestic industries such as general machinery and steel recover."
Specifically, semiconductors and pharmaceuticals were identified as industries expected to show pronounced growth. The semiconductor sector is projected to see increases in both production and exports, driven by expanded investment in artificial intelligence (AI) and greater demand for general server replacement. In the pharmaceutical sector, growth is expected to continue, particularly in the field of synthetic drugs, due to increased domestic demand resulting from an aging society and the expansion of the generic drug market. KDB also anticipates that pharmaceutical exports will rise as global market entry for products such as biosimilars and plasma-derived therapeutics expands.
Industries expected to grow year-on-year despite overall sluggish conditions include displays, mobile phones, steel, and construction. For displays, the increase in global shipments of organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) and the expansion of new demand markets are seen as positive factors. For mobile phones, rising demand for premium products is expected to have a favorable impact. Steel is expected to benefit from increased exports to emerging markets such as ASEAN countries, while construction is projected to be positively influenced by government policies and expanded SOC investment.
In contrast, the general machinery and automobile industries are expected to see growth similar to last year or only limited expansion. For general machinery, even though demand is rising due to AI and a recovery in construction investment, the trend toward protectionism is likely to limit growth. For automobiles, the positive impact of increased demand resulting from lower interest rates is likely to be partially offset by the effects of U.S. tariffs. The secondary battery, shipbuilding, petrochemical, and shipping industries are all expected to continue facing unfavorable business conditions. The secondary battery sector is burdened by slowing electric vehicle demand and oversupply from China; the petrochemical and shipping sectors are constrained by continued oversupply; and shipbuilding is limited by a stagnation in orders from global shipping companies.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.