Record Number of Foreign Tourists Last Year, Led by China and the United States
Targeting 20 Million Foreign Tourists This Year
Qualitative Transformation Needed in Length of Stay and Consumption Structure
The South Korean tourism market, which has been showing signs of recovery since last year, is now entering a full-fledged growth phase. As demand is structurally shifting to include mid- and long-haul travelers, particularly from China and the United States, surpassing 20 million foreign tourists this year has emerged as a realistic goal. Experts now believe that the key challenge for Korean tourism is not simply increasing visitor numbers, but whether this growth can lead to qualitative changes in the length of stay and consumption patterns.
 On the afternoon of the 26th, when strong winds blew and severe cold returned, tourists were moving in thick clothing on Sejong-daero, Jongno-gu, Seoul. The Korea Meteorological Administration forecasted that temperatures would drop sharply from the afternoon, with the morning temperature tomorrow falling to minus 7 degrees Celsius, bringing severe cold. Photo by Jo Yongjun
On the afternoon of the 26th, when strong winds blew and severe cold returned, tourists were moving in thick clothing on Sejong-daero, Jongno-gu, Seoul. The Korea Meteorological Administration forecasted that temperatures would drop sharply from the afternoon, with the morning temperature tomorrow falling to minus 7 degrees Celsius, bringing severe cold. Photo by Jo Yongjun
China and the United States Lead Recovery of Foreign Tourist Arrivals... From 'Recovery' to 'Transformation'
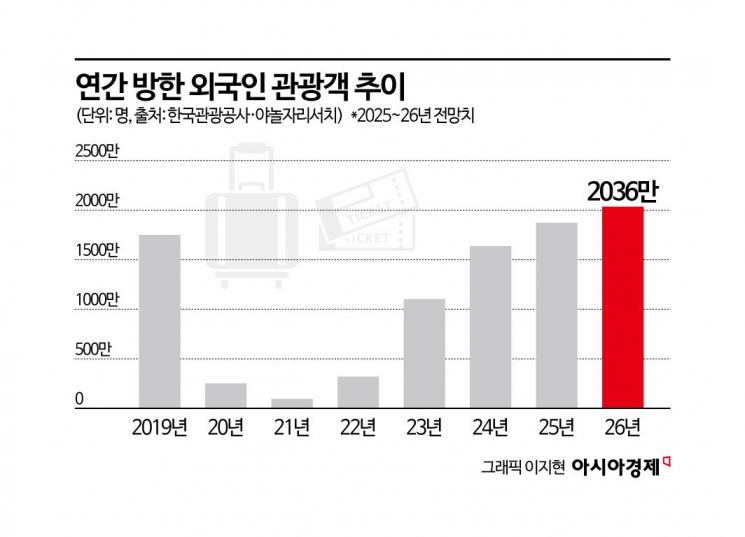
According to the Korea Tourism Organization on January 5, the number of foreign tourists visiting South Korea reached 17,418,270 as of November last year, an increase of 15.4% compared to the same period the previous year (15,098,766). This figure already exceeds the annual total of 16,370,000 visitors in 2024, and with December data yet to be added, it is expected to break the all-time record of 17,500,000 set in 2019. During the same period, the number of Koreans traveling overseas increased by only 3.2% to 26,803,084, meaning inbound recovery has significantly outpaced outbound growth.
By country, the rebound in the Chinese market was decisive. In November last year, the number of Chinese tourists reached 377,866, up 26.9% from the same month the previous year. The cumulative total for November was 5,087,135, an 18.4% increase, accounting for 29.2% of all foreign visitors and firmly reestablishing China as the largest core market. As Chinese tourist demand, which had been dispersed to Southeast Asia and Japan, returns to Korea, the very structure of the Korean tourism market is being reshaped.
This rebound is seen as the result of structural recovery, going beyond a simple base effect from the COVID-19 pandemic. The continued recovery of pent-up travel demand during the pandemic, combined with the restoration of mid- and long-haul routes to the Americas and Taiwan, normalization of airline capacity, and the global spread of K-content and major events, have all played a role. An industry insider explained, "Having moved past a recovery phase focused on short-haul travel, the Korean tourism market is now creating a new balance, with mid- and long-haul markets also coming back to life, surpassing the pre-pandemic structure."
In particular, the return of Chinese tourists symbolizes a structural shift in the market. Although it was widely expected that the share of Chinese tourists, which had plummeted after the THAAD dispute, would recover only slowly, double-digit monthly growth rates since the second half of last year have brought China back as a central pillar. In addition, recent external factors such as worsening China-Japan relations and changes in the foreign exchange environment have increased the likelihood that Korea will reemerge as an alternative destination for Northeast Asian tourism demand.
Possibility of Surpassing 20 Million Foreign Tourists for the First Time This Year
Based on these trends, there is growing confidence that the number of foreign tourists visiting Korea this year will exceed 20 million. With the figure already having recovered to the 17 million range by the end of last year, further increases in flights and continued recovery in key markets make surpassing 20 million a highly achievable scenario.
Industry experts cite China, the United States, and Taiwan as the three main growth engines. In the case of China, even though outbound demand has not fully normalized, Chinese tourists already account for nearly 30% of all foreign visitors, leaving significant room for further growth depending on policy changes. The U.S. market has also seen increased spending power due to a strong dollar, while Taiwan and Southeast Asia continue to show stable growth, especially in short-haul routes.
Hong Seokwon, Chief Researcher at Yanolja Research, noted, "During the THAAD dispute, 10-13% of Chinese tourist demand shifted to Japan. The recent deterioration in China-Japan relations could also provide a windfall for Korean tourism." He further projected, "If the 'balloon effect' caused by China-Japan tensions materializes, the number of Chinese tourists could increase to as many as 7 million, with the total annual number of visitors to Korea expanding to between 20.76 million and 21.26 million." This would exceed the 2019 record by more than 3 million in a single leap.
 On the 27th, when a heavy snowfall of up to 20cm fell in Seoul, a foreign tourist visiting the Namsan Observatory in Jung-gu, Seoul, is taking a commemorative photo. Photo by Jo Yongjun
On the 27th, when a heavy snowfall of up to 20cm fell in Seoul, a foreign tourist visiting the Namsan Observatory in Jung-gu, Seoul, is taking a commemorative photo. Photo by Jo Yongjun
The United States is also emerging as a key growth driver. With the strong dollar boosting Americans' overseas travel spending power, the number of American tourists visiting Korea is expected to increase by more than 60% compared to pre-pandemic levels. The fact that demand is recovering not only for short-haul but also for mid- and long-haul travel indicates that the Korean tourism market is making a qualitative leap forward.
However, it remains uncertain whether the increase in foreign tourists will immediately translate into an improved tourism balance. The number of Koreans traveling abroad is also expected to approach 30 million, meaning the gap between inbound and outbound travelers will likely remain at around 10 million for the time being. Without strategies to increase the length of stay and spending per foreign visitor, beyond simply boosting visitor numbers, growth may remain purely quantitative.
Industry stakeholders point to the activation of regional hub airports, development of interregional tourism products, and expansion of high value-added experiential content as key tasks that will determine the success of Korean tourism this year. An industry insider commented, "Up until now, the focus has been on how many people come, but from now on, the perspective needs to shift to how deeply they spend. If content, regions, transportation, and experiences are not organically connected, Korean tourism could fall back into a period of low growth."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















