Contributed to the Discovery and Analysis of the Novel Mitophagy-Promoting Compound PDE701
The Korea Institute of Ocean Science and Technology (KIOST), led by President Lee Heeseung, in collaboration with Professor Yoon Jin Ho's research team from the College of Medicine at Dong-A University, has identified that reduced activation of mitophagy is a key cause in the development of diabetic kidney disease through research using a fruit fly model. The team also succeeded in verifying the therapeutic efficacy of a newly discovered mitophagy-promoting compound derived from marine organisms.
The related research findings were published online in the world-renowned journal "Experimental & Molecular Medicine."
Mitophagy is a mechanism that selectively removes damaged or unnecessary mitochondria. Recently, it has been found to be closely associated with the onset of various diseases, drawing attention as a novel therapeutic strategy.
The title of the paper published in "Experimental & Molecular Medicine" is "Exploring mitophagy levels in Drosophila Malpighian tubules unveils the pivotal role of mitophagy in kidney function and diabetic kidney disease." The study, authored by Lee Heeseung, Lee Jihoon, and Lee Yeonju from KIOST, as well as Professor Yoon Jin Ho from Dong-A University College of Medicine, was published on October 23, 2025.
KIOST researchers, including Dr. Lee Heeseung, Dr. Lee Jihoon, and Dr. Lee Yeonju, secured and analyzed a variety of marine biological resources from the waters surrounding the "Pacific Ocean Marine Science Base," KIOST's overseas research outpost in the tropical Pacific, in their quest to discover new mitophagy-promoting compounds.
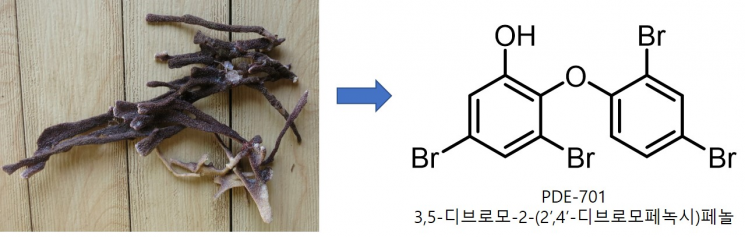
As a result, a brominated phenol-type marine natural product (3,5-dibromo-2-(2',4'-dibromophenoxy)-phenol (PDE701)) was discovered from a tropical sponge and provided to Professor Yoon Jin Ho's research team for physiological activity evaluation.
Professor Yoon Jin Ho's team analyzed their proprietary fruit fly mitophagy model and confirmed that mitophagy activation is essential for maintaining kidney function. Notably, they demonstrated that in the diabetic kidney disease model, mitophagy activation decreases even before a decline in kidney secretion or morphological abnormalities appear, thus proving that reduced mitophagy activation is a causal factor in the development of diabetic kidney disease.
Furthermore, the research team administered the newly developed mitophagy-promoting compound PDE701, confirming that it restores mitophagy activation in the diabetic kidney disease model and repairs damaged mitochondrial function.
In addition, they found that it also recovers impaired kidney function and extends lifespan. Follow-up studies are planned to further develop mitophagy-based therapeutics for kidney disease.
In 2000, KIOST established the "Pacific Ocean Marine Science Base" in the tropical Pacific, an area with the world's highest biodiversity. Since its opening, the base has conducted research on securing source organisms for marine biological resource utilization, biodiversity studies, marine ecological and environmental research, and exploration of tropical Pacific marine biological resources.
In particular, KIOST has established a foundation for the stable acquisition of valuable biological resources and the development and commercialization of marine bio-materials derived from these resources.
KIOST stated that it will continue to actively utilize marine biological resources secured through its infrastructure, strengthen joint research with leading universities and institutions, and further enhance its research capabilities to contribute to the growth of the marine bioindustry.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.

![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)














