Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency Releases National Health and Nutrition Survey Results
Half of Men in Their 30s to 50s Remain Obese
High-Risk Drinking Rate Among Women in Their 30s Reaches 16.3%
3 Out of 10 Elderly Women Suffer from Osteoporosis
While the overall smoking rate among adults in Korea is declining, the use of electronic cigarettes continues to rise. The prevalence rates of hypertension, diabetes, and hypercholesterolemia have increased in both men and women, with the increase being more pronounced among men.
The Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency announced the results of the "2024 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey" on September 30.
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey has been conducted since 1998 to assess the health and nutritional status of Koreans. It surveys smoking, alcohol consumption, physical activity, nutrition, and chronic diseases among approximately 10,000 people from 4,800 households across 192 regions nationwide. Since last year, in preparation for a super-aged society, the survey has included additional items related to elderly health such as osteoporosis, sarcopenia, and daily living functions, and the release date has been moved up from December to September.
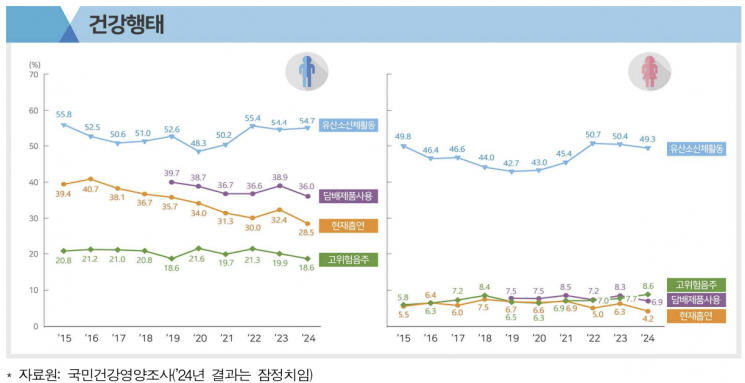
Increase in 'E-cigarette' Use Among Men, and 'High-risk Drinking Rate' Among Women in Their 30s
According to last year's survey, the current usage rate of tobacco products among adults aged 19 and older was 36.0% for men and 6.9% for women, down by 2.9 percentage points and 1.4 percentage points, respectively, compared to 2023.
By tobacco type, the current smoking rate (cigarettes) was 28.5% for men and 4.2% for women, both decreasing from the previous year. However, the current usage rates for electronic cigarettes (liquid: 4.9%, heated: 7.2%) showed a slight increase. The current usage rate of liquid electronic cigarettes was 7.9% for men and 1.7% for women, while the rate for heated electronic cigarettes was 11.2% for men and 3.1% for women. Notably, among men in their 50s, the current usage rate of liquid electronic cigarettes rose to 4.6% (up 3.0 percentage points), and among men in their 40s, the current usage rate of heated electronic cigarettes increased to 17.7% (up 6.9 percentage points).
The "high-risk drinking rate," defined as the proportion of adults who drink an average of seven or more drinks (five or more for women) at a time or drink at least twice a week over the past year, was 13.6% in 2024 overall. This rate decreased by 1.3 percentage points among men but increased by 0.9 percentage points among women. In particular, among men in their 20s, the high-risk drinking rate fell by 5.7 percentage points to 9.7%, while among women in their 30s, it rose by 3.1 percentage points to 16.3%.
The rate of practicing aerobic physical activity (at least 2 hours and 30 minutes of moderate-intensity activity per week, or at least 1 hour and 15 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity, or a mix of both) was 52.1% overall, with the highest rates among people in their 20s for both men and women.
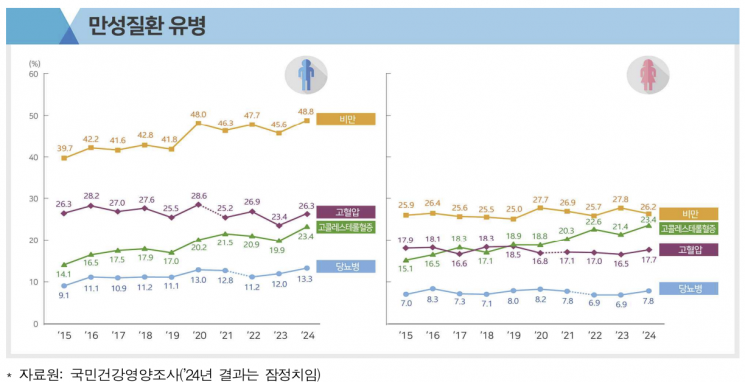
Prevalence of Chronic Diseases Increases, but Management Indicators Improve
Last year, the prevalence of obesity (body mass index of 25 kg/m² or higher) among adults was 48.8% for men and 26.2% for women. This represented a 3.2 percentage point increase for men and a 1.6 percentage point decrease for women compared to the previous year. Notably, about half of men in their 30s to 50s were obese.
The prevalence rates of hypertension, diabetes, and hypercholesterolemia all increased for both men and women compared to the previous year. The prevalence of hypertension was 26.3% for men and 17.7% for women, up by 2.9 percentage points and 1.2 percentage points, respectively. The prevalence of diabetes was 13.3% for men and 7.8% for women, up by 1.3 percentage points and 0.9 percentage points, respectively. The prevalence of hypercholesterolemia was 23.4% for both men and women, increasing by 3.5 percentage points and 2.0 percentage points, respectively. In particular, men in their 40s showed an upward trend in both obesity and chronic disease prevalence.
However, from 2022 to 2024, awareness, treatment, and control rates (among those receiving treatment) for chronic diseases improved significantly for both men and women compared to 2019 to 2021. Except for the treatment rate of hypercholesterolemia (64.8%) and the control rate of diabetes (40.5%), all management indicators exceeded 70%, with substantial improvements seen among people in their 30s and 40s.
In terms of dietary habits, the overall population (aged 1 and older) showed decreased intake of fruits and sodium but increased intake of meat, beverages, and fats. Last year, the average daily fruit intake was 110.5g, down 5.8g from the previous year. In contrast, meat intake rose by 5.7g to 134.7g, with significant increases among men in their 30s (21.7g), 40s (25.0g), and 50s (29.3g).
Total energy intake was 1,865 kcal, similar to 2023, but increased by more than 100 kcal among men in their 30s and 50s. The proportion of energy intake from fat continued to rise, and for men in their 30s, it reached 30.2%, which is at the upper limit of the recommended fat energy ratio (30%) for Koreans.
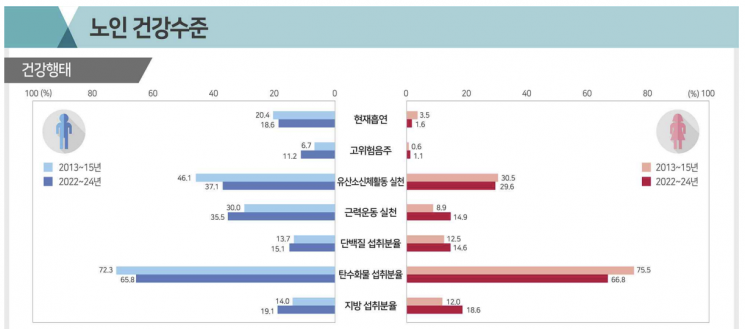
2 Out of 10 Elderly Men Still Smoke
Looking at health behaviors among seniors aged 65 and older over the past decade (2013-2015 and 2022-2024), the current smoking rate (cigarettes) among men decreased by 1.8 percentage points, but 2 out of 10 elderly men were still smokers. The high-risk drinking rate increased by 4.5 percentage points, while the rate of practicing aerobic physical activity dropped by 9.0 percentage points. However, the rate of practicing strength training increased for both men and women.
For both men and women, the proportion of energy intake from protein and fat increased, while the proportion from carbohydrates decreased, approaching the recommended energy distribution (protein 7-20%, fat 15-30%, carbohydrates 55-65%). The prevalence rates of obesity, diabetes, and hypertension increased among men but decreased among women, while the prevalence of hypercholesterolemia increased for both. Awareness, treatment, and control rates for chronic diseases improved significantly for both men and women.
Since last year's survey, the prevalence of osteoporosis among those aged 65 and older was 18.0% (3.8% for men, 31.6% for women), and the prevalence of sarcopenia was 9.4% (9.5% for men, 9.3% for women). The average score for the Elderly Daily Living Function Scale was 85.9 points (92.1 for men, 80.9 for women). Among the different domains, daily living had the highest score, followed by social activities, upper limb function, and lower limb function. Those with osteoporosis or sarcopenia had lower scores on the Elderly Daily Living Function Scale compared to those without these conditions, and reported the greatest difficulty in actions such as "bending, squatting, or kneeling" and "climbing a flight of stairs without resting."
Im Seungkwan, Commissioner of the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency, stated, "Among elderly men, health behaviors such as smoking and drinking have not improved, while 3 out of 10 women are affected by osteoporosis. This calls for more proactive management to improve quality of life in old age and to prevent chronic diseases from becoming more severe. We will continue to conduct surveys related to elderly health in preparation for the super-aged era, and strengthen the evidence base for chronic disease prevention and management through follow-up studies to understand long-term health changes and the causal relationships of disease occurrence."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.

![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)














