On July 31, a joint research team from Chosun University and Chungnam National University announced that they have developed a new interface-control-based material technology that can improve the initial irreversible capacity loss of lithium-ion batteries. A research paper on this technology was published in the July 2025 issue of the internationally renowned energy journal, International Journal of Energy Research.
This study was conducted by a joint research team led by Professor Lee Jeongsu of the Department of Life and Chemical Engineering at Chosun University, and Professors Song Woojin and Lim Jongcheol of Chungnam National University. The research demonstrated the potential to simultaneously improve both the efficiency and durability of lithium-ion batteries, which are widely used in electric vehicles, smartphones, and energy storage systems (ESS).
The team precisely controlled the surface structure of the graphite anode, which is one of the key materials in batteries, and combined it with a special liquid substance called an ionic liquid. Through this approach, they addressed the main causes of performance degradation.
They succeeded in reducing lithium loss (initial irreversible capacity loss) that occurs when a battery is used for the first time, and also decreased internal resistance that hinders current flow, thereby improving the overall performance of the battery.
The researchers introduced a chemical called 4-bromobenzoic acid to the edge of the graphite, and then applied an ionic liquid precursor in the form of a covalent bond. This effectively suppressed unnecessary reactions and resistance at the interface (boundary) where the electrode and electrolyte meet.
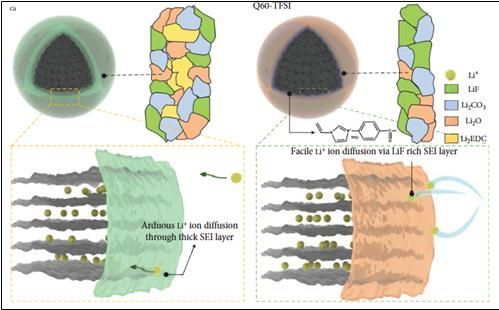 Schematic diagram of SEI layer formation mechanism on the surface of conventional graphite and modified graphite edges.
Schematic diagram of SEI layer formation mechanism on the surface of conventional graphite and modified graphite edges.
As a result, a thinner and more uniform solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) layer was formed, and it was confirmed that there was less performance degradation even after repeated charging and discharging. The battery also maintained high stability during fast charging and discharging.
This technology is a core advancement that can simultaneously enhance battery efficiency and durability. It is a key factor that can directly impact everyday life by increasing the driving range of electric vehicles, extending smartphone battery life, and ensuring stability during fast charging.
In the future, this technology is expected to reduce battery replacement cycles and increase energy efficiency, thereby improving consumer convenience. It is also anticipated to serve as a foundational technology for the development of next-generation high-performance batteries, contributing to the competitiveness of the domestic battery industry.
Professor Lee Jeongsu stated, "This research proves that it is possible to stably enhance performance by precisely controlling the structure of battery materials. It is a meaningful achievement that can serve as a foundation for the development of high-performance electricity in the future, and I hope it will be a study that benefits both daily life and the broader industry."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.

![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)














