"Stomach Cancer Burden Expected to Rise Among Younger Generation...
Need for Increased Prevention Investment"
A study has found that 15.6 million people born between 2008 and 2017 are expected to develop stomach cancer during their lifetime, and 76% of these cases are likely to be related to Helicobacter pylori infection.
On July 7, Yonhap News reported that a research team led by Dr. Park Jinyoung at the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), which operates under the World Health Organization (WHO), published the results of a study in the medical journal Nature Medicine. The study projected the future burden of stomach cancer among the younger generation born between 2008 and 2017, based on stomach cancer incidence data from 185 countries as of 2022 and United Nations demographic statistics.
Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped bacterium found in the gastric mucosa and is known to cause chronic gastritis, gastric ulcers, duodenal ulcers, and stomach cancer when it infects the human stomach.
The study found that, without additional stomach cancer prevention interventions, 15.6 million people born between 2008 and 2017 are expected to develop stomach cancer during their lifetime, and 76% of these cases are associated with chronic Helicobacter pylori infection.
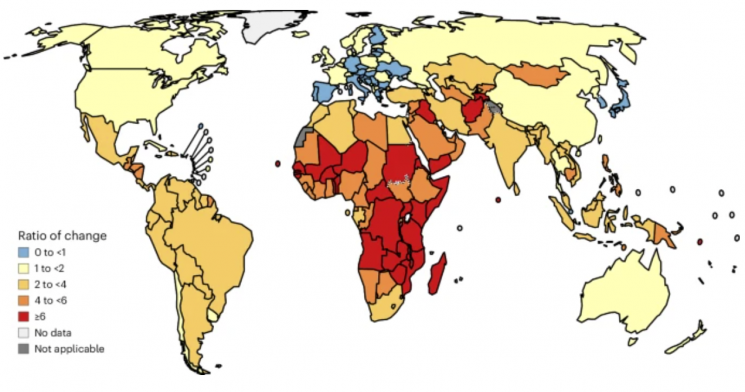 Map of stomach cancer burden change rates for those born between 2008 and 2017 compared to 2022. Blue (0 to <1): Expected decrease in stomach cancer cases compared to the present. Light blue to yellow (1 to <2): Slight increase in stomach cancer cases expected compared to the present. Orange to dark orange (2 to <4, 4 to <6): Possibility of 2 to 6 times increase in stomach cancer cases. Dark red (≥6): Stomach cancer burden expected to increase more than 6 times compared to the present.
Map of stomach cancer burden change rates for those born between 2008 and 2017 compared to 2022. Blue (0 to <1): Expected decrease in stomach cancer cases compared to the present. Light blue to yellow (1 to <2): Slight increase in stomach cancer cases expected compared to the present. Orange to dark orange (2 to <4, 4 to <6): Possibility of 2 to 6 times increase in stomach cancer cases. Dark red (≥6): Stomach cancer burden expected to increase more than 6 times compared to the present.
By region, it is estimated that two-thirds of all stomach cancer cases will occur in Asia, followed by approximately 1.97 million cases (13%) in the Americas, 1.73 million cases (11%) in Africa, 1.24 million cases (8%) in Europe, and about 67,000 cases (0.4%) in Oceania.
In particular, while 58% of all cases are expected to occur in traditionally high-risk regions, the remaining 42% are projected to arise in low-risk countries such as those in Africa due to changes in population structure. In sub-Saharan Africa, the possibility has been raised that the number of stomach cancer cases could be six times higher than the estimated figure for 2022.
The research team emphasized, "It is necessary to take an approach that considers the possibility of the younger generation developing stomach cancer in the future, depending on whether or not preventive strategies are in place," and added, "Investment in stomach cancer prevention should be expanded, including population-based Helicobacter pylori screening and treatment strategies (screen-and-treat)."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.

















