Samsung's Market Share Drops to 7% Range, Gap with SMIC Narrows to 1 Percentage Point
Despite Leading Technology, Struggles with Yield and Reliability
Limitations Exposed in Mid-Range Process and Production Base Response
SMIC Grows on Domestic Demand, Threatening Samsung's Second Place
Samsung Seeks Rebound by Expanding Automotive Semiconductor Partnerships
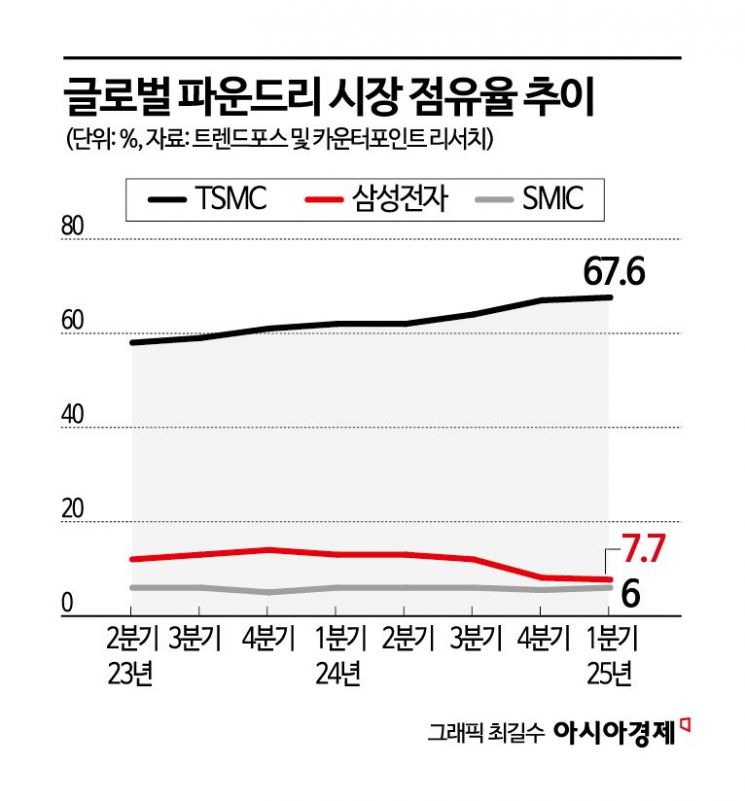
Samsung Electronics' market share in the semiconductor foundry (contract manufacturing) sector is showing a clear decline. While Samsung maintained a double-digit share two years ago, its share has recently dropped to the 7% range, falling to a level similar to that of China's SMIC (Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corporation). In contrast, Taiwan's TSMC is strengthening its dominance in the market with a share approaching 70%. In this situation, Samsung is seeking a turnaround by securing new customers in the automotive semiconductor sector.
According to market research firm TrendForce on June 10, TSMC's market share in the first quarter of this year was 67.6%, an increase of 9.6 percentage points (p) from 58% in the second quarter of 2023. During the same period, Samsung's share fell from 12% to 7.7%, a decrease of 4.3 percentage points, while SMIC maintained a 6% share, narrowing the gap with Samsung to 1.7 percentage points. Just a year ago, the gap was more than twice as wide.
Until the first quarter of last year, Samsung led SMIC by a wide margin with a 13% share, but from the fourth quarter of 2024, its decline became pronounced, and this year, the gap has narrowed to around 1 percentage point. In contrast, SMIC has stably maintained a 5-6% market share.
Experts point to Samsung's lack of response to both strategic issues and changes in the external environment as reasons for its underperformance. Although Samsung is a leader in technology, having introduced 3-nanometer ultra-fine processes and extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography early on, it is taking time to achieve stable yields and mass production reliability. There are few customers capable of utilizing advanced processes, and even those customers are mostly choosing TSMC.
While Samsung has focused on advanced processes, there is still significant demand for mid-range processes in the overall market. TSMC has expanded its customer base by offering both advanced and mature processes, whereas Samsung has been less proactive in diversifying its options.
From a production base perspective, TSMC is expanding into the United States, Japan, and Germany to meet the distributed demand of its customers. However, Samsung remains concentrated in South Korea and parts of the United States, exposing it to geopolitical risks.
On the other hand, although SMIC lags in technological capability, it is rapidly increasing its market share based on strong support from the Chinese government and domestic demand. While U.S. export controls make it difficult to secure advanced equipment, subsidies, tax benefits, and government-driven demand creation are positively impacting its performance.
The industry believes that if this trend continues, Samsung's position as the second-largest foundry could also be at risk. However, there are also reports that internal efforts are underway to restore competitiveness, such as stabilizing yields and recovering technological capabilities. A semiconductor industry official said, "Although Samsung Electronics' declining market share is drawing attention, internally, the foundry division is quietly enhancing its competitiveness by focusing on restoring technological capabilities and stabilizing yields. It will take time, but I believe there is potential for a rebound in the mid to long term."
Meanwhile, it has been reported that Autotalks, an Israeli semiconductor design company recently acquired by Qualcomm, visited Samsung's Austin foundry in the United States to conduct quality verification (PPAP) procedures. This process is a preliminary step for the production of automotive communication chips, adding weight to the possibility that cooperation with Qualcomm could expand beyond mobile to the automotive sector.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)














