Information Encryption Achieved with Simple Operation, No Power Supply Required
 Professor Nam Seungmin, Department of Electronic Engineering, Chosun University.
Professor Nam Seungmin, Department of Electronic Engineering, Chosun University.
Chosun University announced on May 8 that a research team led by Professor Nam Seungmin from the Department of Electronic Engineering has developed a "stretchable optical encryption film" that can encrypt and decrypt information simply by stretching the film, without the need for a power supply or additional electronic components.
This research was supported by the Samsung Electronics Future Technology Development Center, the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy’s Technology Innovation Development Project, the Samsung Electronics Research Support Program, and the National Research Foundation of Korea’s BK21 FOUR program. The results were published on March 26 in "Light: Science & Applications," a top international journal in the field of optics published by the global scientific publisher Springer Nature.
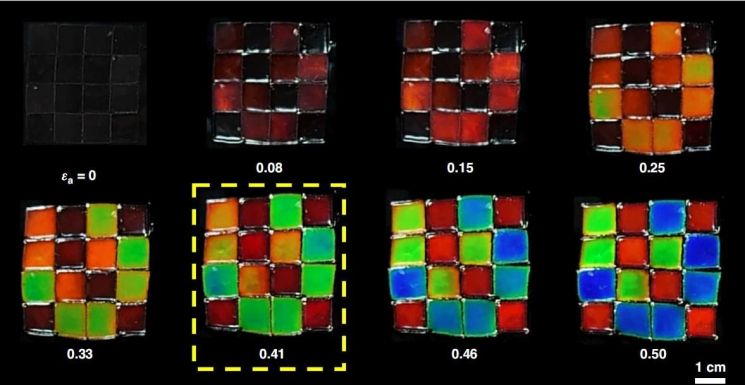 Stretchable Optical Encryption Film - The infrared region (encryption state) and visible light region (decryption state) appear sequentially before and after tension. Provided by Chosun University
Stretchable Optical Encryption Film - The infrared region (encryption state) and visible light region (decryption state) appear sequentially before and after tension. Provided by Chosun University
This technology is distinguished from conventional digital security technologies, which require complex computational devices or electrical and electronic stimulation, by enabling information encryption and decryption solely through mechanical stretching, without the need for a power supply or additional electronic components.
The research team also confirmed the film’s high durability, as its initial performance remained stable even after being stretched more than 100 times in repeated experiments. They demonstrated that complex security functions can be effectively implemented using only thin and flexible materials, similar to smartphone protective films.
Professor Nam Seungmin stated, "The stretchable optical encryption technology is highly practical and scalable, as it enables information security through a simple method that does not require a power supply. In the future, it could be utilized as a next-generation information protection device in various fields, including portable security tags and identification cards."
Meanwhile, Professor Nam Seungmin of Chosun University participated as the first author in this research. Joint authors include Park Jiyoon, a doctoral student, and Woo Seohyun, an integrated master’s and doctoral student, both from the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering at POSTECH. Professor Choi Sooseok from the same department at POSTECH participated as the corresponding author.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)














