Comparison of Policy Proposals for the 20th and 21st Presidential Candidates
This Year's Proposals Emphasize 'Industrial Transformation'
SME Structural Reform Highlighted Amid Trends Like AI and Digital Transformation
Policies Include Regulatory Easing and Support for Business Recovery
The policy direction proposed by the small and medium-sized enterprises (SME) sector ahead of the presidential election has changed dramatically over the past three years. While the 20th presidential election in 2022 centered on an optimistic message of leveraging the recovery from the COVID-19 shock as an opportunity for growth, the current 21st presidential election, three years later, is dominated by a sense of crisis emphasizing the need to rebuild the stagnant industrial base.
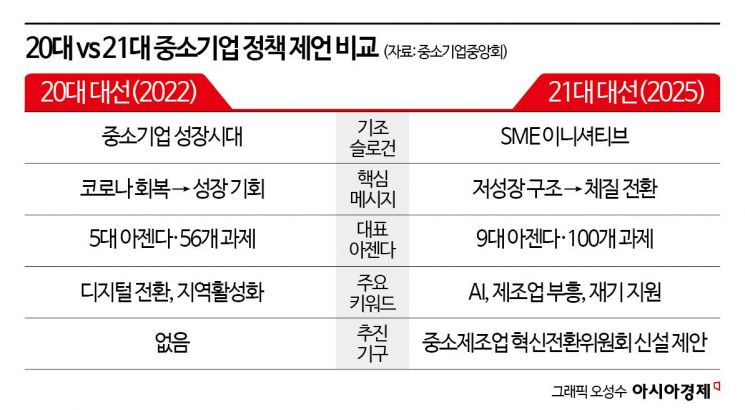
According to the SME sector on the 15th, the Korea Federation of SMEs (Kbiz) announced the 'SME Sector Proposals to the 21st Presidential Candidates' ahead of the upcoming presidential election in June. From the perspective of the 'SME Initiative,' Kbiz presented 9 major agendas and 100 policy tasks focusing on three key areas: sustainable jobs, manufacturing revival, and economic ecosystem circulation.
The core keyword is 'reconstruction.' The SME Council, which led the policy proposals, diagnosed in the proposal document that "the Korean economy, which has grown remarkably, is now facing low growth, polarization, and declining innovation." Specifically, the proposals include ▲establishing a 'Presidential Commission for SME Manufacturing Innovation and Transformation' ▲laying the groundwork for AI utilization by industry ▲support measures for the revival of small business owners by type. This reflects a sense of urgency that goes beyond mere expansion of support to a transformation into a new system.
The proposals released ahead of the 20th presidential election had a different direction. At that time, Kbiz requested that the recovery period from COVID-19 be used as a stepping stone for growth, creating policy opportunities for SMEs to take the lead in the economy through digital transformation and regional economic revitalization. The proposal contained 56 implementation tasks, about half the number of the current 100, based on five agendas: innovation transformation, growth promotion, infrastructure establishment, safety net expansion, and regional economic revitalization.
The reason for such a drastic change in the SME sector’s policy focus within just three years lies in the severely deteriorated business environment. Overlapping external risks such as rising raw material and energy prices, high interest rates, and high exchange rates have caused SME profitability to plummet. Added to this are policy burdens like minimum wage increases and carbon neutrality, labor shortages due to aging, and export uncertainties, creating a pervasive sense of crisis across the industry that "it is difficult to endure under the current system."
The SME business performance index also fell from 80.5 in December 2022 to 67.7 in December 2024. This means that the perceived economy has been significantly below the 'baseline' (100) for a prolonged period. Especially as new industry trends such as AI and digital transformation rapidly spread, the industry judges that it is no longer possible to overcome growth limits with the existing industrial structure. Accordingly, Kbiz newly emphasized regulatory reform to respond to new industries, easing entry barriers, and inter-industry linkage strategies in this proposal.
Lee Min-kyung, head of policy at Kbiz, said, "As Korea enters a low-growth phase, existing industries need to be properly restructured, and an environment must be created for new industries to enter smoothly. This proposal newly includes regulatory reforms related to new industries such as AI and Femtech, as well as soft-landing measures for small business owners to restart after closure."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)














