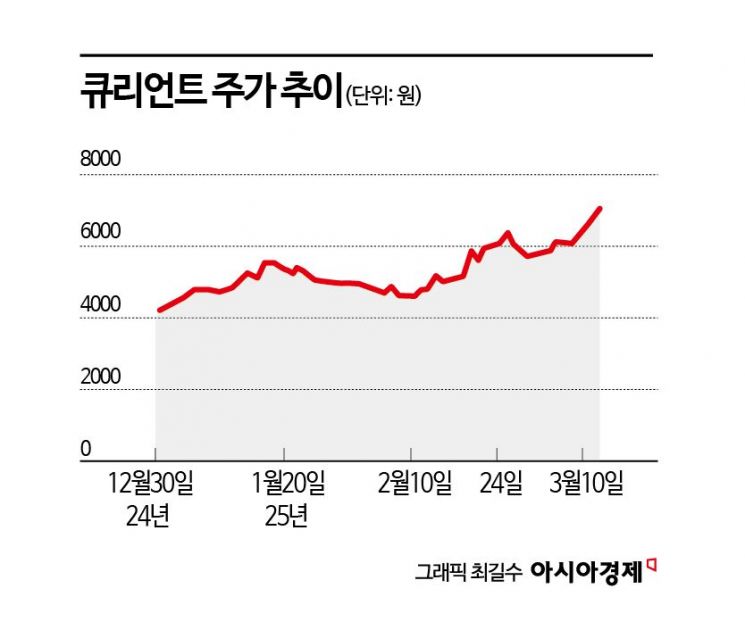
Stock Soars 64% This Year
Biotech Gains Attention as Tuberculosis Risk Grows
Securing PRV with FDA Approval
The corporate value of new drug developer Qurient is rapidly rising. As the importance of tuberculosis treatment drugs grows, expectations for the new drugs under development are spreading.
According to the financial investment industry on the 13th, Qurient has risen 64.1% this year. Considering that the KOSDAQ index rose 7.6% during the same period, the return rate compared to the market reaches 56.5 percentage points (P). The market capitalization has grown to 230 billion KRW.
Qurient is a clinical development specialized (NRDO) biotech. NRDO biotechs have a business model that conducts clinical trials on new drug candidates introduced from other bio ventures or research institutes, then increases the value of the pipeline and transfers the technology. This skips the research stage, reducing the new drug development period and risks. It can collaborate by sharing new drug development stages with multiple companies, allowing the pipeline’s value to be recognized early and invested funds to be recovered quickly.
In February 2023, Qurient signed a technology transfer contract with TB Alliance, an international organization for tuberculosis drug development, for Telacebec (Q203), a treatment for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB). TB Alliance assumes all development responsibilities for Telacebec, and Qurient secured the Priority Review Voucher (PRV) issued by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Qurient also receives a portion of the revenue generated from Telacebec as royalties. According to the global market research firm Market.us, the worldwide market for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis treatments is expected to grow at an average annual rate of 4.9%, from $1.1 billion in 2023 to $1.8 billion in 2033.
Phase 2A clinical trials have been completed in the United States and South Africa. Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis is tuberculosis resistant to both isoniazid and rifampicin, the two primary drugs for tuberculosis. It takes longer to treat than the standard 6-month treatment period for regular tuberculosis. There is increasing demand for effective and safe multidrug-resistant tuberculosis treatments for international public health.
Researcher Daewoong Yoo of Bukuk Securities explained, "We expect to start approval clinical trials within this year and possibly receive approval as early as next year," adding, "The potential increase in the value of the PRV is also a positive factor."
The fact that the U.S. government is effectively dismantling the international development agency USAID raises the global risk of tuberculosis spread, which could provide a favorable environment for developing tuberculosis treatments. Tuberculosis is one of the infectious diseases causing numerous deaths worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the number of patients diagnosed with tuberculosis in 2023 was 8.2 million, and the number of tuberculosis deaths reached 1.25 million.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)














