Professor Kyungmin Jeong's Team Identifies the Impact of Electrode Curvature on Cylindrical Battery Performance
Curvature Optimization Enhances Battery Cell Stability
Published in Energy Storage Materials
A study has attracted attention by showing that simply designing electrodes considering the curvature of the battery can mitigate issues such as lithium metal deposition.
As global electric vehicle companies adopt cylindrical batteries, securing super-gap technology for cylindrical batteries has become urgent.
Professor Kyungmin Jeong's team from the Department of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST identified the impact of the curvature of cylindrical battery electrodes on electrochemical performance and proposed an optimized electrode design considering this factor.
 Research team. (From left) Researcher Jeon Byung-jin (first author), Professor Jung Kyung-min, Researcher Lee Young-hyun. Provided by UNIST
Research team. (From left) Researcher Jeon Byung-jin (first author), Professor Jung Kyung-min, Researcher Lee Young-hyun. Provided by UNIST
Cylindrical batteries are batteries in which the anode and cathode are stacked with separators in between and then rolled up. Considering the anode, separator, cathode, and separator as one set, typically 20 to 60 sets are rolled inside one cylindrical battery cell used in electric vehicles.
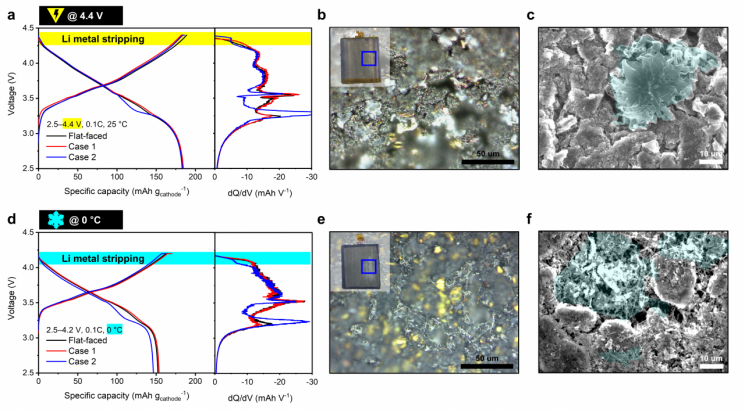
The research team started this study based on the observation that due to the curvature characteristics of cylindrical batteries, the contact area between the anode and cathode varies, which can cause the capacity ratio between the anode and cathode to deviate from the ideal design value. Generally, when designing batteries, the anode capacity is designed to be larger than the cathode capacity to prevent lithium metal deposition and enable fast charging.
By fabricating experimental curved single-layer cells simulating various curvature conditions and comparing them with commercial 21700 cylindrical batteries, it was confirmed that the capacity ratio of the electrodes varies depending on the electrode position.
In particular, in the central region with a large curvature, the risk of lithium metal deposition significantly increased during low-temperature or high-voltage charging. Lithium metal deposition causes short circuits. Moreover, this curvature sensitivity was greater in high-capacity high-nickel cathode materials.
To address this, the research team proposed a design strategy that adjusts the thickness of both sides of the electrode separately. This principle compensates for the capacity ratio changes caused by variations in the contact area ratio between the anode and cathode through thickness adjustment of the electrodes.
Byungjin Jeon, the first author of the study, explained, “We revealed that electrode curvature is an important design variable in cylindrical battery design,” adding, “This is significant in that an advanced research approach is needed that considers not only material characteristics but also electrode curvature for battery performance and stability.”
Professor Kyungmin Jeong emphasized, “This study confirmed the importance of an approach linking battery form factor and design/process technology,” and added, “In the intense global competitive environment, it is difficult to secure an advantage by research focused solely on improving the capacity of the materials themselves.”
This research was published online on the 20th of last month in the international energy journal Energy Storage Materials. The research was conducted through the industrial innovation infrastructure project ‘Establishment of a Performance Verification Platform for High-Power Secondary Battery Materials and Components’ supported by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE) and implemented by the Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology (KIAT).
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)














