Installation of Facilities Using 4 Billion KRW Worth of Discharged Groundwater
3,000 Tons per Day of Discharged Groundwater Near KINTEX Station
Utilization for Improving Daehwacheon Water Quality and Creating Waterfront Spaces
Stepwise Expansion of Discharged Groundwater Use to Daegok Station
Goyang Special City, Gyeonggi Province (Mayor Lee Dong-hwan) plans to utilize the discharged groundwater occurring about 80 meters underground in the bedrock layer due to the development of GTX-A as an urban water resource. The city intends to efficiently use this water for managing public facilities such as KINTEX and Goyang Sports Complex, improving the water quality of Daehwa Stream, and introducing cooling & clean road systems, thereby contributing to budget savings and resource circulation.
 Lee Dong-hwan, Mayor of Goyang Special City, attending the GTX-A opening ceremony and test ride event. Photo by Goyang Special City
Lee Dong-hwan, Mayor of Goyang Special City, attending the GTX-A opening ceremony and test ride event. Photo by Goyang Special City
According to Goyang Special City on the 7th, this project was selected for the 2025 Ministry of Environment national subsidy project for installing discharged groundwater utilization facilities, receiving 2.035 billion KRW in national funding. The city will invest a total of 4.07 billion KRW (50% national, 50% city funds) to install discharged groundwater utilization facilities at ventilation shaft No. 4 of KINTEX Station. The Ministry of Environment revised the Groundwater Act in 2023 to establish administrative, technical, and financial support for promoting the use of discharged groundwater.
Previously, in July last year, Ilsanseo-gu confirmed flooding in the underpass box at the intersection of Miraero and Jungang-ro adjacent to Daehwa Stream. While investigating the cause of flooding, it was found that discharged groundwater from the GTX-A line was connected to the drainage channel. Subsequently, a dedicated pipeline was installed to divert the waterway to Daehwa Stream, and plans were made to utilize this water.
The discharged groundwater from ventilation shaft No. 4 amounts to about 3,000 tons per day, totaling 1,095,000 tons annually, which is 2.4 times the total capacity of Ilsan Lake Park. To efficiently utilize the groundwater, Ilsanseo-gu conducted on-site investigations and expert consultations in September last year. The results indicated that since the groundwater is drawn from the bedrock layer 70-80 meters deep, the possibility of soil erosion or ground subsidence (sinkholes) is minimal. Additionally, water quality tests showed no detection of harmful substances and met water quality standards, confirming suitability for 'domestic water use standards.'
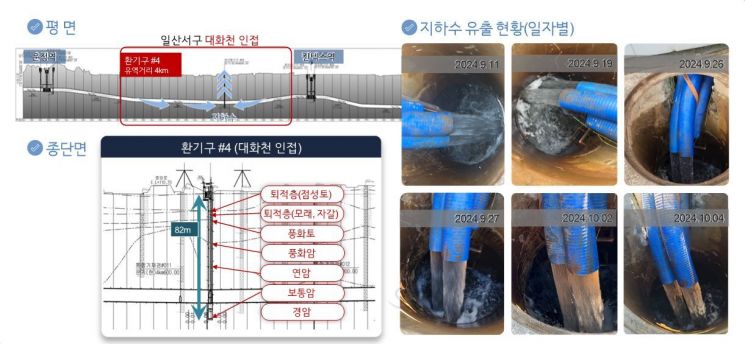 Status of groundwater discharge at ventilation shaft No. 4 on GTX-A line. Provided by Goyang Special City
Status of groundwater discharge at ventilation shaft No. 4 on GTX-A line. Provided by Goyang Special City
Ilsanseo-gu formed a dedicated TF team of 17 members, including five external experts, to devise plans for utilizing discharged groundwater. After discussions with related agencies and ministries, a utilization plan was established. The city then applied for the Ministry of Environment’s support project for installing discharged groundwater utilization facilities and was finally selected as a project site last month. Ilsanseo-gu plans to proceed with facility design this year and begin full-scale construction next year.
With large-scale underground space development actively progressing, such as urban infrastructure supply, the amount of discharged groundwater generated nationwide is steadily increasing every year. According to the Ministry of Environment, the total amount of discharged groundwater in Korea is about 380,000 tons per day (annual equivalent about 140 million tons per year based on reported discharged groundwater), which is approximately 60% of the Paldang Dam reservoir volume (240 million tons).
Only 11% of the total discharged groundwater is reused, while the remaining 124 million tons (89%) are discharged into sewage pipes or nearby rivers, highlighting the urgent need to establish an active utilization system for discharged groundwater. Last month, the Ministry of Environment added the utilization of discharged groundwater to the Korean Green Taxonomy (K-Taxonomy), which defines environmentally friendly economic activities.
 Calculation of groundwater discharge flow rate at ventilation shaft No. 4 on GTX-A line. Provided by Goyang Special City.
Calculation of groundwater discharge flow rate at ventilation shaft No. 4 on GTX-A line. Provided by Goyang Special City.
The city plans to utilize discharged groundwater for multiple purposes, including △introducing cooling & clean road systems along major roads such as Jungang-ro near Daehwa Station △landscaping and cleaning water for public facilities such as KINTEX, Goyang Sports Complex, baseball stadium, and park golf course △road environment improvement and maintenance △improving water quality of Daehwa Stream △supplying water for fire trucks and street cleaning vehicles through water supply equipment △creating cooling fog and artificial waterfalls to reduce fine dust and respond to heat waves.
Additionally, to secure clearer water and prepare for unspecified pollution situations, a separate water treatment system will be installed and managed. The city will also conduct monthly water quality tests on discharged groundwater for monitoring and review its applicability for each use.
 Utilization Plan for Groundwater Discharge from Ventilation Shaft No. 4 of GTX-A. Provided by Goyang Special City
Utilization Plan for Groundwater Discharge from Ventilation Shaft No. 4 of GTX-A. Provided by Goyang Special City
Goyang City plans to gradually expand the utilization range of discharged groundwater from ventilation shaft No. 4 near KINTEX Station to the area near Daegok Station.
To link with this public project, the city has applied for a national and local government-supported project to utilize about 300 tons per day of discharged groundwater from ventilation shaft No. 6 at KINTEX Station. Upon securing the budget, the city plans to design and construct a cooling & clean road system on surrounding roads. The approximately 6,500 tons per day of discharged groundwater from ventilation shafts No. 7 and 8 between KINTEX Station and Daegok Station is also being considered for future use in improving the water quality of Hallyu Stream and Ilsan Lake Park.
The Goyang Research Institute is conducting research to build a system that maximizes water resource utilization effects. In the future, the city plans to conduct periodic actual measurements through on-site maintenance services and establish an environmental monitoring system based on accumulated data, applying it to other discharge points.
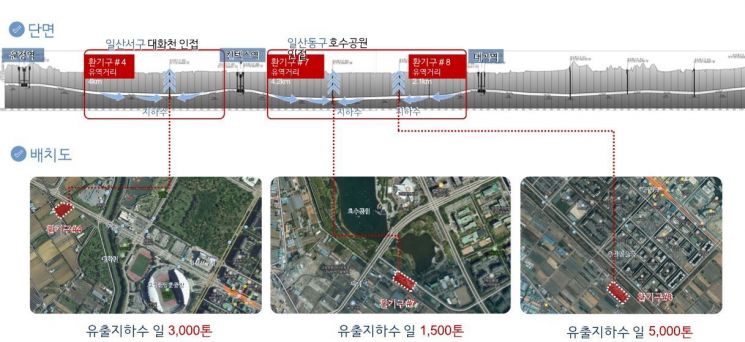 Status of Ventilation Shaft Groundwater Discharge by Section on GTX-A Line. Provided by Goyang Special City
Status of Ventilation Shaft Groundwater Discharge by Section on GTX-A Line. Provided by Goyang Special City
Furthermore, the city intends to combine clean groundwater from the bedrock layer with smart farm technology to cultivate specialized agricultural products such as wasabi and water parsley, which require demanding growing conditions, thereby contributing to regional agricultural development and revitalizing the tourism industry.
Mayor Lee Dong-hwan of Goyang City stated, “Near KINTEX Station on the GTX-A line, there are many public institutions, cultural and sports facilities such as Daehwa Stream, Goyang Sports Complex, and KINTEX, so it is expected to become a large-scale discharged groundwater utilization project. We will gradually expand the utilization of discharged groundwater to Daegok Station in the future to efficiently use limited water resources.”
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.