Severe Intractable Diseases Managed as Chronic Conditions
Medication Interval Increased 7-Fold and Treatment Time Reduced by Up to 90%
"Replacing dozens of pills taken daily with an injection once every two months." Medications that were difficult to take or inject, resulting in ineffective treatment, are being improved for easier and more convenient administration. As a result, patients can now use medications much more comfortably while treating their diseases. Here are some representative cases of improved dosing convenience.
◆HIV: From dozens of pills a day to an injection once every two months= HIV is a disease that invades the human body, destroys immune cells, and weakens the immune system, leading to AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome). In the 1980s, AIDS caused by HIV infection was known as the "Black Death of the 20th century" due to its high mortality rate. However, with remarkable advances in treatment, HIV infection can now be managed from the early stages through continuous therapy, preventing progression to AIDS and allowing management similar to chronic diseases like diabetes or hypertension.
In the past, HIV treatment required taking dozens of pills daily, but with the development of single-tablet triple therapy, it is now possible to manage the disease with "one pill a day," similar to diabetes or hypertension. Recently, the world's first long-acting HIV injectable medication has emerged as a new treatment option. The long-acting HIV injectable (GSK Vocabria injection + Rekambys injection combination therapy) allows for both monthly and bi-monthly injection regimens. For the bi-monthly regimen, the initial induction therapy involves one injection per month for two months, followed by maintenance therapy with one injection every two months.
As a result, HIV-infected patients who previously took one oral pill daily have reduced their dosing frequency from 365 times a year to just 6 times. Large-scale clinical studies have confirmed that the long-acting HIV injectable shows viral suppression effects comparable to the existing triple oral therapy and has a safety profile similar to existing treatments. Vocabria was approved for use in South Korea in 2022 and is expected to be widely prescribed starting next year.
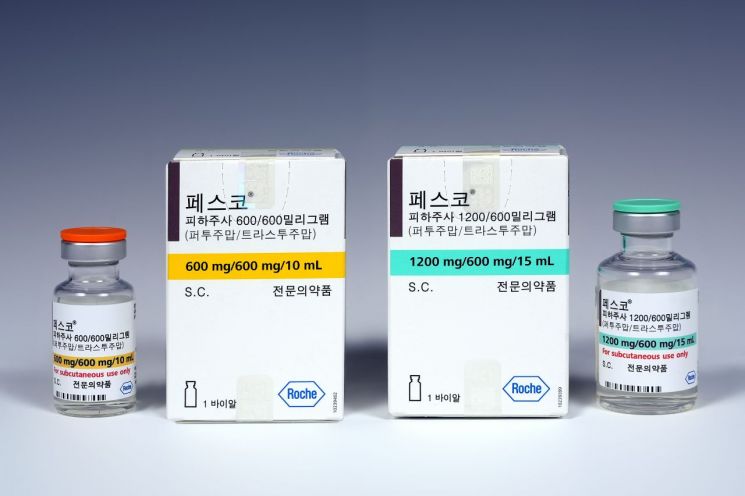
◆HER2-positive breast cancer subcutaneous injection PESCO reduces dosing time by 90%= HER2-positive breast cancer occurs in about 20% of all breast cancer patients. Anticancer drugs for HER2-positive breast cancer patients are administered via intravenous injection. Additionally, patients with veins that are difficult to locate or who are at risk of drug leakage from veins into surrounding tissues have a chemoport implanted for treatment. Each visit every three weeks requires a total of 4 hours and 30 minutes for one dose and observation.
However, the recently introduced subcutaneous injection drug "PESCO," which shortens dosing time and improves patient convenience, is gaining attention. PESCO requires only 20 minutes in total for one dose and observation, reducing dosing and post-dosing monitoring time by up to 90% compared to existing treatments. PESCO has been covered by health insurance since August this year. Consequently, patients who previously experienced long treatment times due to intravenous injections or physical discomfort from chemoport use are expected to benefit significantly.
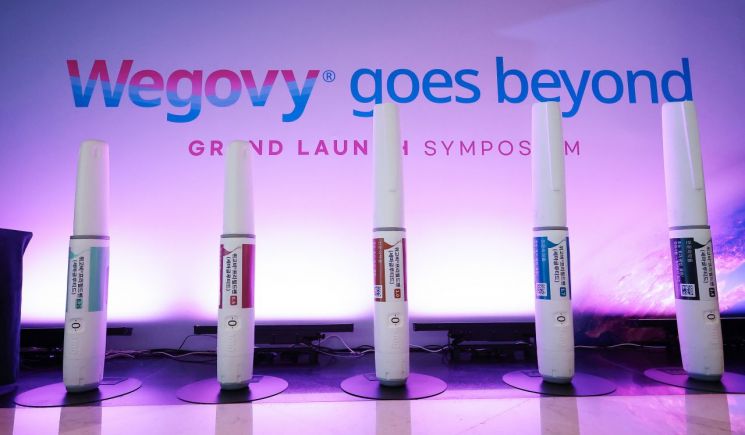
◆Obesity drug previously self-injected daily now once a week= This is a case where dosing convenience was greatly improved with Novo Nordisk's obesity treatment drug Wegovy. This drug significantly improved the cumbersome dosing method of the company's other obesity treatment drug, Saxenda. Saxenda requires self-injection under the skin of the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm once daily. Wegovy addresses this inconvenience by extending the injection interval from once daily to once weekly.
Korea Pfizer's "Engerla (Somatrogon)," a treatment for growth failure in children aged 3 years and older caused by pituitary growth hormone secretion disorder, has also dramatically extended its dosing interval. The previous once-daily dosing method has been extended to once weekly. Engerla is a product that meets the needs of drugs requiring long-term treatment and high treatment adherence. According to previous studies, among pediatric patients receiving daily growth hormone injections, 39% missed more than one weekly dose, and 23% missed more than two doses.
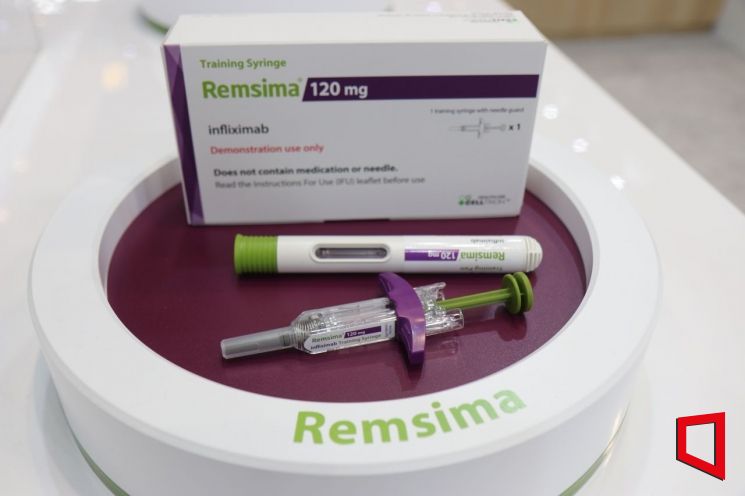
◆'The power of dosing convenience'... 'Remsima' aiming for annual sales of 1 trillion won= Remsima is a biosimilar of Johnson & Johnson's autoimmune disease treatment Remicade. It is used for diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease. Its cumulative sales in the third quarter reached 979.7 billion won, and annual sales are expected to reach 1.2 trillion won this year.
The biggest advantage of Remsima is that it is the only subcutaneous (SC) formulation among infliximab-based autoimmune disease treatments. Unlike intravenous injections (IV) that must be administered via infusion at a hospital, the SC formulation allows patients to self-inject at home. The drug is designed to be absorbed slowly in the body, reducing the frequency of administration. Thanks to this, Remsima has been recognized as a new drug in the United States.
Patient satisfaction with Remsima prescriptions is also high. According to a preference survey led by the University of Liverpool Hospital in the UK, released by Celltrion last May, the majority of patients who switched from infliximab IV formulations to Remsima preferred Remsima in terms of convenience and safety, with 77% expressing satisfaction.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.