KAIST has developed an artificial intelligence framework that automatically extracts biological pathway information. Biological pathway images representing information such as genes, proteins, and metabolites contain important research findings, but research on extracting information from images has been insufficient until now. This aspect adds significance to the current study.
On the 28th, KAIST announced that the research team led by Professor Hyunwook Kim of the Department of Bio and Chemical Engineering developed a machine learning-based ‘Extraction of Biological Pathway Information (EBPI)’ framework that automatically extracts gene and metabolite information from biological pathway images.
 (From left) Kwon Moonsoo, PhD candidate, Department of Bio and Chemical Engineering, KAIST; Lee Jungyu, PhD candidate; Kim Hyunwook, Professor. Provided by KAIST
(From left) Kwon Moonsoo, PhD candidate, Department of Bio and Chemical Engineering, KAIST; Lee Jungyu, PhD candidate; Kim Hyunwook, Professor. Provided by KAIST
EBPI recognizes arrows and text in images extracted from literature and reconstructs biological pathways into editable table formats based on this information. Using machine learning models such as object detection, it detects the position and direction of arrows within pathway images and classifies the text in the images into genes, proteins, or metabolites. Additionally, EBPI’s main function is to integrate the extracted information and provide pathway data in table form.
The research team validated EBPI’s performance by comparing biological pathway images extracted from 74,853 papers with manually curated pathway maps. The results confirmed that biological pathway information was automatically extracted with high accuracy.
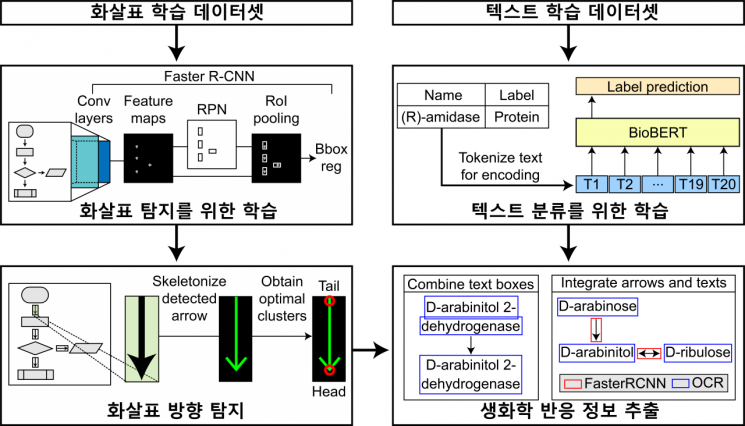 Schematic diagram of EBPI automatically extracting biochemical reaction information from bio pathway images. Provided by KAIST
Schematic diagram of EBPI automatically extracting biochemical reaction information from bio pathway images. Provided by KAIST
In particular, EBPI succeeded in extracting biochemical reaction information not included in representative biological pathway databases from a large volume of biological pathway images in the literature. When analyzing literature related to the biosynthesis of industrially valuable metabolites using EBPI, biochemical reactions reported in the literature but missing from existing databases were identified.
Professor Hyunwook Kim, who led the research, said, “EBPI will be an important tool in the analysis of large-scale literature data. This is the first case of analyzing biological pathway images with artificial intelligence in the fields of biotechnology, metabolic engineering, and synthetic biology, and it is expected to be usefully applied in experimental design and analysis in related research.”
Meanwhile, the research was conducted with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Agricultural Microbiology Project Group of the Rural Development Administration.
Dr. Munsu Kwon and Dr. Jungyu Lee, doctoral candidates in the Department of Bio and Chemical Engineering at KAIST, participated as co-first authors. This study was published in the November issue of ‘Metabolic Engineering,’ a leading international journal in the fields of metabolic engineering and synthetic biology.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















