6th After Germany, India, Sweden, UK, Thailand
Infected After Visiting East Africa
A variant of MPOX (formerly known as monkeypox) infection, spreading in Africa, has been reported in the United States following Europe.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announced on the 16th (local time) that a resident of California who recently traveled to East Africa was confirmed to be infected with the variant MPOX (clade I). The infected individual is currently isolated at their home in California, and state health authorities are checking for symptoms among those who had contact with them. The California Department of Public Health stated in a press release on the same day that there is no concern or evidence that the variant MPOX is spreading in California or elsewhere in the United States.
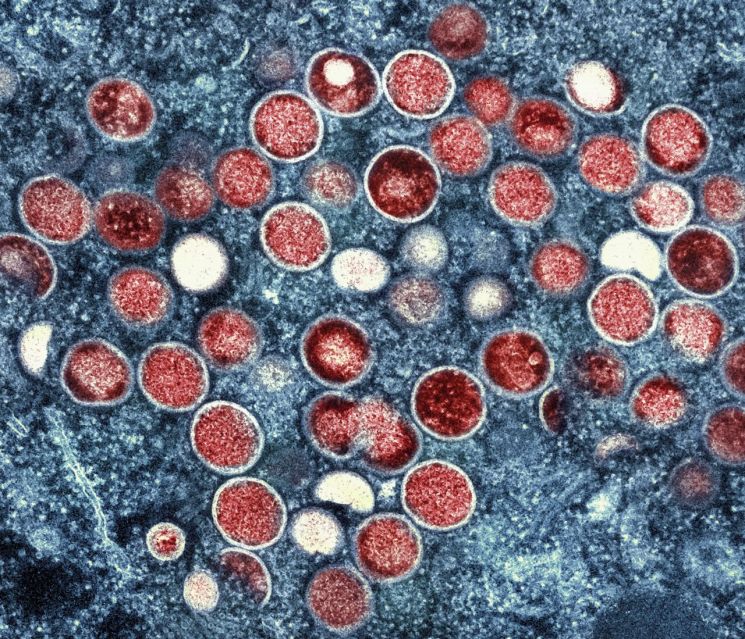 Electron microscope image of monkeypox virus particles (red). Provided by the U.S. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), Yonhap News Agency
Electron microscope image of monkeypox virus particles (red). Provided by the U.S. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), Yonhap News Agency
The World Health Organization (WHO) declared an international public health emergency (PHEIC) in August this year as the variant MPOX spread mainly in Africa. The new variant MPOX is known to have a high fatality rate and rapid transmission speed. Countries outside Africa where variant MPOX infection cases have been confirmed include Germany, India, Sweden, Thailand, and the United Kingdom, making the United States the sixth country outside Africa to confirm variant MPOX infection cases. The first country outside Africa to confirm variant MPOX infection cases was Sweden, where it was first detected in mid-August.
Meanwhile, suspected MPOX cases reported in the African continent this year have recently exceeded 50,000. On the 8th, the Africa Centers for Disease Control and Prevention announced that as of the 6th, an additional 2,532 cases were reported in the past week, bringing the total suspected MPOX cases reported in Africa this year to 50,840. Among these, confirmed cases number 10,741, with 1,083 deaths. Of the MPOX deaths in Africa, 99.4% are concentrated in Central Africa, including the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Among the 55 member countries of the African Union (AU), 19 countries have reported MPOX outbreaks this year. MPOX is an acute febrile rash illness caused by a viral infection, primarily transmitted through close physical contact. The incubation period averages 6 to 14 days, and symptoms such as headache, fever, and muscle pain appear during the initial days after infection. It also causes lesions filled with pus, and many cases result in scarring as the scabs fall off.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)














