Detailed Results of Nelmastovat Phase 1 Clinical Trial Presented at US SITC
Consistent Clinical Efficacy of BTN1A1 Antibody Therapy Demonstrated
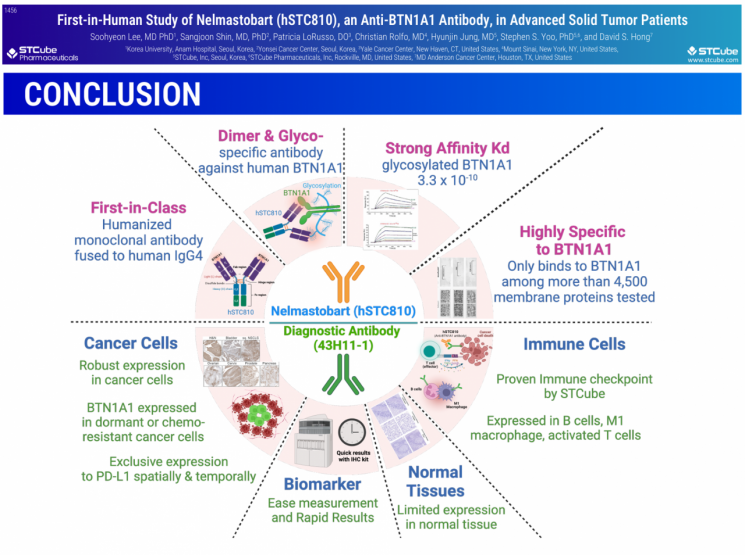
STCube demonstrated the excellent safety and efficacy of nelmastovate monotherapy in a Phase 1 clinical trial targeting patients with recurrent or progressive immune checkpoint inhibitor-resistant tumors (cold tumors). Following the validation of BTN1A1 as a novel biomarker for immune checkpoint inhibitors, nelmastovate, the world's first BTN1A1-targeting immune checkpoint inhibitor, received outstanding evaluations.
STCube announced on the 11th that it presented the final global Phase 1 clinical trial results of nelmastovate and research findings on the mechanism of BTN1A1 at the SITC (Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer) conference held in Houston, USA, from the 6th to the 10th.
The presentation topics were "The First-in-Human Clinical Study of BTN1A1 Antibody Nelmastovate in Advanced Solid Tumors" and "Spatial Biological Insights into Dual Targeting of BTN1A1 and YAP in Cancer: Enhanced Efficacy Results from 3D Cell Culture and Phase 1 and 1b Clinical Trials."
The poster presentation of the Phase 1 clinical trial results was led by the principal investigator, Professor Lee Suhyun of Korea University Anam Hospital. Newly disclosed were the efficacy analysis results of nelmastovate’s Phase 1 clinical trial evaluated by the independent central review committee (BICR).
This clinical trial was designed to evaluate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics (PK), and preliminary efficacy of nelmastovate monotherapy in patients with advanced solid tumors. Participants included patients with various solid tumors such as colorectal cancer, small cell lung cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, and ovarian cancer, who had failed an average of more than 3.7 prior treatments. A total of 47 patients were randomly assigned simultaneously in the USA and Korea, with dose escalation in six steps from 0.3 mg/kg to 15 mg/kg administered every 14 days.
Regarding the primary endpoint of safety evaluation, treatment-related adverse events (TRAE) occurred in 51.1% (24 patients), mostly mild grade 1 or 2 symptoms such as fatigue, headache, and drowsiness. Only one case of grade 3 or higher TRAE was reported, and no treatment-related deaths occurred. Dose-limiting toxicities (DLT) were not observed in any patient, and no clinically significant changes were noted in vital signs, electrocardiograms (ECG), or Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG PS), meeting the evaluation criteria.
According to the BICR efficacy evaluation, among 43 patients, partial response (PR) was observed in 3 patients (7%), and stable disease (SD) in 19 patients (44%). All three PR cases were colorectal cancer patients. The duration of treatment was confirmed to be 12.8 months. Unlike conventional chemotherapy used in third-line colorectal cancer treatment, where PR is often followed by a short treatment duration until disease progression (PD), survival was significantly improved. SD was observed in various cold tumors including small cell lung cancer, colorectal cancer, ovarian cancer, head and neck cancer, and thymic cancer, with one small cell lung cancer patient maintaining SD for over 22 months.
An STCube representative stated, "This presentation attracted significant attention as a meaningful achievement demonstrating the excellent safety and clinical benefits of BTN1A1-targeted therapy. The excellent safety and tolerability profile means it can be used not only as monotherapy but also in combination with other drugs without burden, allowing broad therapeutic applications."
They continued, "In terms of efficacy, a very high correlation was observed between BTN1A1 expression levels and nelmastovate treatment response, consistently proving the utility of BTN1A1 as a new biomarker for immune checkpoint therapy." They added, "Since BTN1A1 is expressed mutually exclusively with PD-(L)1 and shows very high expression intensity in cancer cells, utilizing BTN1A1 as a biomarker could further enhance the therapeutic effect of nelmastovate."
Furthermore, the potential as a treatment option to overcome the biggest challenges in cancer therapy?resistance and recurrence?was suggested. Clinical data reaffirmed that BTN1A1 and YAP (a protein inducing chemotherapy resistance) are co-expressed.
When resistance to anticancer drugs develops, YAP is overexpressed in cancer cells. Particularly in colorectal cancer, YAP expression indicates a poor prognosis. STCube retrospectively analyzed tumor tissues from colorectal cancer patients enrolled in the Phase 1 and investigator-initiated Phase 1b trials, dividing them into nelmastovate responders and non-responders.
The analysis demonstrated that the higher the proportion of cancer cells co-expressing BTN1A1 and YAP, the better the treatment outcomes with nelmastovate. This indicates that BTN1A1 and YAP serve as key biomarkers predicting treatment response to nelmastovate and could be reliable biomarkers to address chemotherapy resistance, especially in colorectal cancer treatment.
A company official said, "The best therapeutic effects of nelmastovate were observed when YAP was co-expressed in cancers with high BTN1A1 expression (patients resistant to chemotherapy). The same results were observed not only in the Phase 1 trial but also in the colorectal cancer investigator-initiated Phase 1b trial, and identical outcomes were obtained in 3D models reproduced in the laboratory, providing sufficient clinical evidence for the development of BTN1A1-targeted therapies."
Jung Hyunjin, CEO of STCube, introduced, "The Phase 1 trial involved patients with cold tumors who had failed previous cancer surgery, chemotherapy, and immune checkpoint inhibitor standard treatments, representing cancer types that are difficult to treat with immune checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy." He added, "Because BTN1A1 exhibits mutually exclusive expression with existing PD-L1, we expected clear anticancer efficacy. As a result, we were able to strategically plan subsequent clinical trials by demonstrating excellent safety, tolerability, and distinct anticancer efficacy."
CEO Jung emphasized, "Combining nelmastovate with existing chemotherapy and anti-PD-(L)1 immune checkpoint inhibitors is expected to produce strong synergistic effects in various cancers beyond small cell lung cancer and colorectal cancer. Based on these clinical results, we are pursuing multifaceted business strategies."
Currently, STCube is conducting global Phase 1b/2 clinical trials of nelmastovate combined with chemotherapy for relapsed/refractory extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC) and investigator-initiated Phase 1b/2 trials for third-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer patients who have failed standard anticancer therapies or are untreatable. In the colorectal cancer investigator-initiated trial, among 12 MSS colorectal cancer patients in Phase 1b, 2 achieved PR and 10 achieved SD, resulting in a disease control rate (DCR) of 100% and an objective response rate (ORR) of 16.7%.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)














