Kia Initiates Seniority-Based Wage System Reform
Introduces Base Salary Performance Linkage for General Staff
Domestic Companies' Seniority System Usage Hits 16-Year Low
Government's 'Labor Reform Top Priority,' Expands Job and Performance-Based Pay System Adoption
Kia, a leading heavyweight company in Korea, has initiated the introduction of a job- and performance-based pay system. By linking personnel evaluations to the criteria for general staff base salary increases, the company aims to boost productivity and open the way to securing outstanding talent through active incentive offerings.
According to a comprehensive report by Asia Economy on the 25th, Kia's labor and management recently agreed to implement this year's wage negotiation plan, which passed a vote before the Chuseok holiday. In the previous tentative agreement vote, the Kia labor union approved the wage agreement but rejected the collective agreement.
However, some union members opposed accepting the wage agreement, including the 'general staff performance-linked system.' The Metal Workers' Union, the higher organization of the Kia labor union, also opposed and did not approve it. Nevertheless, the consensus inside and outside the labor-management circles is that it is difficult to renegotiate the agreement once a vote has been completed.
◆ Kia embarks on reforming the seniority-based wage system= The introduction of the performance pay system at Kia is significant in that it partially breaks down the long-standing barrier of the traditional industry's 'seniority-based pay system.' In this year's wage negotiations, Kia's labor and management agreed to change the compensation system to include personnel evaluations as a criterion for calculating the base salary of general staff. Until now, general staff at the assistant and deputy levels have received the same base salary increases, performance bonuses, and various allowances based on the seniority system. However, from now on, the additional base salary increase will be set differently according to individual performance, which can be seen as a broad relaxation of the 'seniority system.'
Kia has established a separate compensation system through allowances for production and sales staff. Among production staff, jobs with higher difficulty levels such as assembly (bodywork), chassis, and painting received higher allowance increase rates. Earlier, Hyundai Motor Company discussed abolishing the seniority system for research and general staff in this year's wage negotiations but faced union opposition and failed. Unlike Hyundai, which aimed to eliminate the seniority system table altogether, Kia kept the seniority system intact and found a compromise with the union by first discussing additional base salary reforms.
The business community views Kia's introduction of the performance-linked system as a signal for reforming the traditional industrial wage system. Since Kia's union, a representative male- and production-worker-centered large company union, agreed to differentiated compensation based on job and performance, it is seen as the first step toward revising the outdated seniority-based wage system.
◆ Reasons for the debate over job- and performance-based systems= The job- and performance-based pay system has been gradually spreading recently. From the management's perspective, differentiated pay based on job and individual evaluations is inevitable to secure outstanding talent and improve corporate productivity. The MZ generation also considers fair individual performance distribution a key factor in choosing jobs and recruitment.
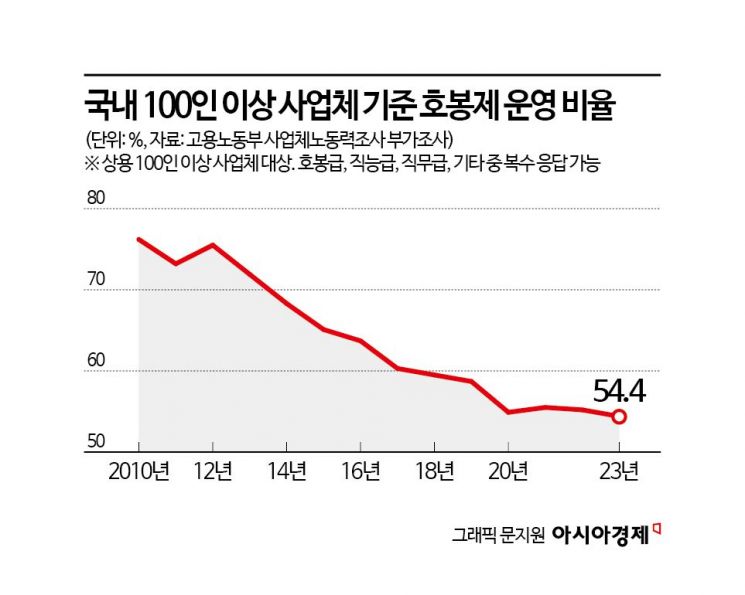
This can be confirmed by objective data. Last year, the operation rate of the seniority system in domestic companies hit its lowest point in 16 years. According to the Ministry of Employment and Labor's business labor force survey, as of the first half of last year, the operation rate of the seniority system among businesses with 100 or more employees was 54.4%, the lowest since 2007 (50.5%). It peaked at 76.2% in 2010 but has steadily declined, maintaining the 50% range since 2018. The reduction in companies operating the seniority system is influenced by the spread of performance-based pay systems, especially in the electrical, electronics, IT industries, and startups.
The government is persuading heavyweight large corporations, such as those in steel and shipbuilding, to reform the seniority-based wage system. The Future Labor Market Research Group, an expert panel on labor reform, pointed out that "the seniority-based wage system deepens the dual structure of the labor market" and "causes wage gaps between large and small businesses and between men and women."
In May, the Ministry of Employment and Labor selected consulting firms to assist in reforming wage systems by industry and is currently recruiting small and medium-sized enterprises in three industries for consulting. Professor Park Woo-sung of Kyung Hee University's Department of Business Administration said, "The reason why performance-oriented wage system reforms have not been achieved so far is due to a lack of momentum for change," adding, "If companies with high acceptance and suitability for job- and performance-centered wage systems lead the reform, it will create momentum for the wage system reform to spread throughout the labor market."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.

![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)














