Hankyung Association, Survey on Hiring Trends and Perceptions of Top 500 Companies
Nearly Double Increase Compared to Last Year
"Cost and Time Savings, Improved Efficiency"
This year, the number of companies that have utilized or plan to utilize artificial intelligence (AI) in their talent recruitment processes has significantly increased.
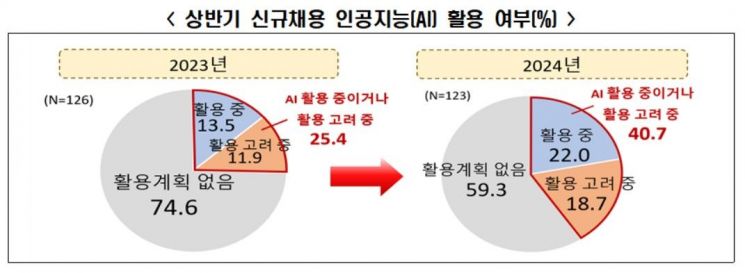 Survey results on the use of AI in new hires during the first half of this year. Graph provided by the Korea Employers Federation.
Survey results on the use of AI in new hires during the first half of this year. Graph provided by the Korea Employers Federation.
On the 28th, the Korea Economic Association (KEA) conducted a 'Recruitment Trends and Perception Survey' targeting the top 500 companies by sales (123 companies responded). Among all respondents, 40.7% said they have used or plan to use AI in recruitment during the first half of the year. Specifically, 22.0% of companies are currently using AI, while 18.7% are considering its use. This figure is nearly double compared to the first half of last year (25.4%).
Regarding which stage of the recruitment process companies are using or considering AI, 62.3% of all respondents answered the document screening stage. This was followed by the practical interview and discussion stage (29.5%) and executive interviews (8.2%).
The KEA stated, "Non-face-to-face recruitment using AI technology can reduce costs and time, thereby improving efficiency," adding, "It appears to enhance fairness and effectiveness in selection by objectively and deeply analyzing applicants' job suitability based on big data."
The proportion of companies planning to use on-demand recruitment methods rather than open recruitment also increased. Six out of ten companies (58.5%) said they would use on-demand recruitment for new university graduate hires in the first half of this year. This is a 1.4 percentage point increase compared to the response rate in the first half of last year (57.1%).
Companies cited "difficulty in finding suitable talent" (27.2%) as the biggest challenge related to new recruitment. This was followed by "early resignation after hiring" (24.9%) and "dropouts during the recruitment process" (21.1%).
The labor shortage in large companies showed a growing trend. Last year, the number of unfilled positions in workplaces with 300 or more employees was 23,000, nearly double the 13,000 in 2020.
It was also confirmed that 25.7% of new university graduate hires last year were "experienced new hires" who already had work experience. This is a 3.6 percentage point increase from 22.1% in 2022. The average career length of these experienced new hires was 1 year and 4 months.
Among new hires with experience, those with 1 to 2 years of experience accounted for 52.6%, more than half. This was followed by 6 months to 1 year (32.8%), 2 to 3 years (6%), over 3 years (5.2%), and less than 6 months (3.4%).
As policy tasks to promote new recruitment, companies answered that "inducing corporate investment and employment expansion through deregulation" (35%) is the most necessary. This was followed by "expanding incentives for companies that increase employment" (31.6%) and "supporting companies in new industry growth sectors" (9.8%).
Lee Sang-ho, Head of the Economic and Industrial Division at KEA, said, "Companies are strengthening efforts to secure suitable talent by expanding on-demand recruitment, increasing experienced new hires, and adopting AI technology," adding, "It is necessary to expand corporate incentives to increase employment capacity and focus on nurturing talent suitable for the field."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)














