Major Chinese Players like Baidu Flock to Domestic Chips
NVIDIA Faces Fierce Pursuit... China's 'AI Chip Independence' Within Reach
"Supplying Domestic Firms... Important Message to the US"
The Wall Street Journal (WSJ) recently reported that "Chinese IT companies are unable to procure the latest AI chips like H20 from Nvidia due to U.S. export controls," and that "demand for Huawei's alternative 'Ascend 910B' chip has surged significantly." It is reported that Huawei has received orders for at least 5,000 chips from major domestic internet companies, including an agreement last year to supply 1,600 chips to Baidu.
Huawei's graphics processing unit (GPU) 'Ascend 910B' is gaining influence in the domestic market. As the supply of Nvidia's GPU A100, considered the biggest beneficiary of the AI era, has been blocked by sanctions against China, the Ascend 910B has rapidly attracted attention as an alternative. With increasing domestic demand, it is being evaluated as a symbol of "China's semiconductor self-sufficiency."
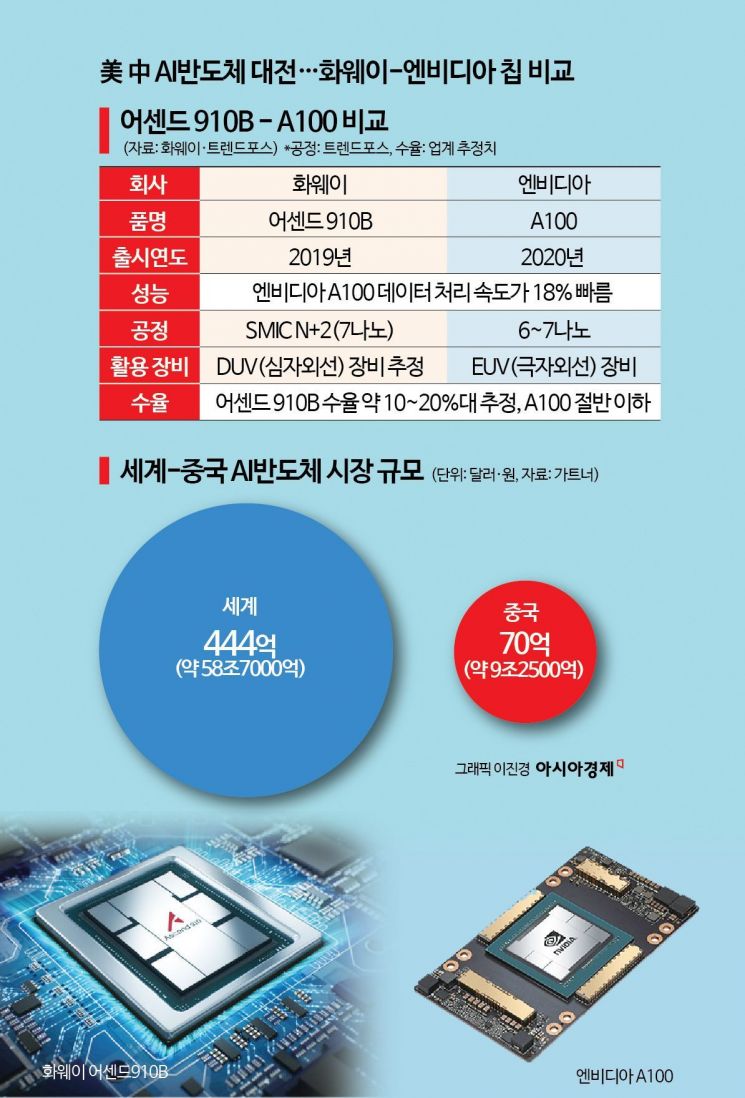
The Ascend 910B is an upgraded version of the 910 processor released in 2019 by Huawei's subsidiary HiSilicon. The 910 processor is based on Huawei's 'Da Vinci Architecture.' The Da Vinci Architecture is an AI computation neural processing unit (NPU) developed independently by Huawei. It is reported that while a conventional CPU performs one calculation at a time, this architecture can perform 4,090 calculations in the same time. The company's flagship chip 'Kirin 990,' which uses a 7nm (nanometer = one billionth of a meter) extreme ultraviolet (EUV) process, was also built on the same architecture.
The Ascend 910B began to attract serious attention starting in October 2022, when the export of Nvidia chips to China was blocked. At that time, the U.S. controlled exports of advanced AI chips such as Nvidia's A100 and H100 to China. Nvidia subsequently sold lower-spec chips like the A800 and H800, but a year later, in October last year, the U.S. government applied a new concept called 'performance density' to impose additional regulations, blocking exports of these chips as well. Nvidia's GPU 'RTX 4090D,' supplied to maintain its presence in the Chinese market, was rejected by Chinese customers. This chip is a downgraded version of the RTX 4090 to comply with U.S. export controls. This prompted Chinese IT companies to turn their attention to the Ascend 910B.
The main reason the Ascend 910B is regarded as a substitute for the A100 is that its manufacturing process technology is similar and its performance is not significantly inferior. Taiwanese market research firm TrendForce evaluated that this chip was likely manufactured using SMIC's (Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corporation) 'N+2' (7nm) or smaller process. The A100 uses a 6-7nm process. Comparing process levels, it is said that the Ascend 910B is by no means inferior.
Chip performance is also not significantly different. According to the Japanese media Asia AI Times, the Ascend 910B is 18% slower than the A100. Yeon Won-ho, head of the Economic Security Team at the Korea Institute for International Economic Policy, said, "If the report that it is 18% slower than Nvidia's chip is accurate, it means it is catching up to some extent in terms of performance."
Experts are paying close attention to the influence of the Ascend 910B, especially evaluating it as a threatening presence in economic security. There is ample possibility that the Chinese government is secretly utilizing this chip in security fields through Huawei. The Korea Institute for International Economic Policy believes the Ascend 910B could be used covertly for fake news production (information warfare), integration with robots and drones (lethal weapons), and assisting commanders' decision-making (enhancing operational capabilities).
However, there are criticisms that production efficiency is low due to outdated equipment, making it difficult to respond promptly to demand. Even if the Ascend 910B process level has reached 7nm, without EUV equipment, yield (ratio of good products) and performance decrease, and manufacturing time lengthens. China is currently dependent on DUV lithography equipment due to restrictions on importing EUV lithography equipment. Huawei's flagship chip Kirin 990 was manufactured using Taiwan's TSMC's EUV technology.
Experts estimate that the yield of the Ascend 910B made with DUV is less than half that of Nvidia's A100 made with EUV, and production costs are twice as high. Power consumption is also expected to be higher because it is difficult to efficiently draw circuit patterns. For the 7nm process, using EUV requires 28 exposure steps, but without the equipment, it must be done 54 times, twice as many. An industry insider estimated, "The yield of the Ascend 910B is likely in the 10-20% range."
Also, to improve the efficiency of AI semiconductors that process massive amounts of data, high-performance 'near memory' must be installed nearby. Major near memory semiconductor products include High Bandwidth Memory (HBM) and Graphics Double Data Rate (GDDR). Due to U.S. regulations, Huawei finds it difficult to secure products from major HBM suppliers such as Samsung Electronics, SK Hynix, and Micron.
Nevertheless, the dependence of Chinese IT companies on domestic chip makers is expected to increase as supplying advanced Nvidia chips becomes difficult. Huawei plans to launch a new high-end AI chip in the second half of this year, and Alibaba's chip subsidiary T-Head is also developing AI processors. WSJ reported that "state-owned telecom companies such as China Mobile and China Unicom have purchased large quantities of AI servers embedded with Huawei chips," and that "there is a demand to apply domestic chips in equipment." The Chinese AI semiconductor market is worth $7 billion (approximately 9.25 trillion KRW), and the possibility of it being filled with domestic chips is growing.
Yeon said, "Huawei supplying AI chips to domestic companies sends an important message to the U.S."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.

![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)














