Competition in the biosimilar market is fierce worldwide. According to the Korea Bio Association, the global biosimilar market is expected to grow from $18.7 billion in 2021 to $74 billion by 2030.
Biosimilars refer to generic drugs recognized as equivalent in efficacy, effectiveness, and safety to existing biopharmaceuticals whose patent periods have expired. Biopharmaceuticals are developed using living cells and can only be approved after undergoing rigorous clinical trial processes.
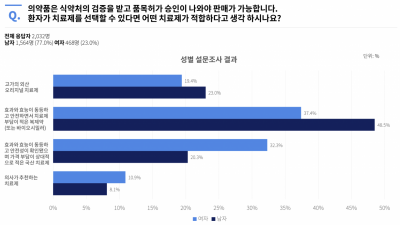
The mobile user survey platform 'Kratos' conducted a preference survey on biosimilars with 2,032 consumers. Seven out of ten respondents gave positive answers regarding biosimilars. This was interpreted as a low resistance to being prescribed biosimilars due to their lower price compared to original products.
Preference for domestic biosimilars was higher among women (32.3%) than men (20.3%). Men tended to prefer original drugs even if they were more expensive.
Interest in biosimilars was highest among people in their 40s (37.5%), followed by those in their 50s (28.5%) and 30s (18%).
The Ministry of Food and Drug Safety established evaluation guidelines and related regulations in 2009 and approved the first domestic biosimilar in 2012. At that time, Celltrion and Samsung Bioepis led the growth of the domestic biosimilar market.
Competition to develop biosimilars for biopharmaceuticals with patent exclusivity expiring by 2026 is intense. The Chinese patent for the obesity treatment drug Wegovy expires in 2026.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















