KAIST-US National Institute on Aging Joint Research Team
Korean researchers, in collaboration with American researchers, have created the world's first single-cell 3D epigenomic map of brain tissue affected by Parkinson's disease, a degenerative brain disorder, paving the way for new treatment approaches.
KAIST announced on the 8th that Professor Inkyung Jung's research team from the Department of Biological Sciences, in joint research with Professor Eliezer Masliah from the National Institute on Aging (NIA) under the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH), has created the world's first single-cell 3D epigenomic map of brain tissue affected by Parkinson's disease and, based on this, identified 656 new Parkinson's disease-associated genes.
Parkinson's disease is a common degenerative brain disorder affecting more than 1.2% of the population over 60 years old. Due to rapid population aging, its incidence is increasing worldwide. It is predicted that approximately 14.2 million patients will be affected by 2040. Currently, the various causes of Parkinson's disease have not been clearly identified.
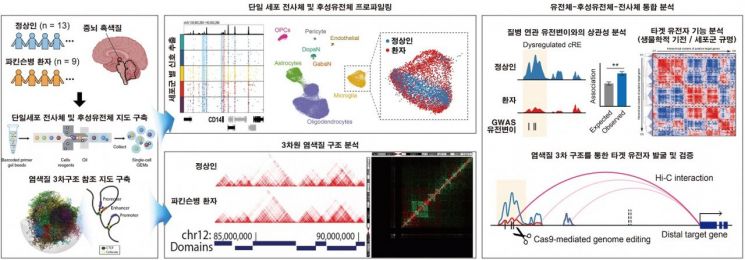 Identification of Parkinson's Disease-Associated Molecular Mechanisms through Single-Cell Epigenomic Map Analysis. Image source provided by KAIST.
Identification of Parkinson's Disease-Associated Molecular Mechanisms through Single-Cell Epigenomic Map Analysis. Image source provided by KAIST.
The research team was the first to confirm that abnormally occurring epigenetic features are involved in the onset of Parkinson's disease. By combining the latest single-cell genome technology with 3D epigenomic technology, they revealed that epigenetic changes in not only neurons but also glial cells?known to play a key role in maintaining the brain environment, such as oligodendrocytes and microglia?are involved in Parkinson's disease onset through 3D genome structures. These abnormal epigenetic features play a central role in regulating gene expression related to the cause or progression of Parkinson's disease. The results of this study are expected to provide important clues for future diagnostic and therapeutic research.
The research team stated, "Analyzing patient brain tissue at the single-cell level, this study goes beyond previous neuron-focused research by suggesting that glial cells may also play an important role in Parkinson's disease, marking a significant discovery. Since it demonstrated the importance of creating a 3D epigenomic map for identifying targets in degenerative brain diseases, it will be crucially utilized in future research on various complex genetic disorders."
This research was published on the 14th of last month in the international academic journal Science Advances (IF=14.14).
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.

![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)














