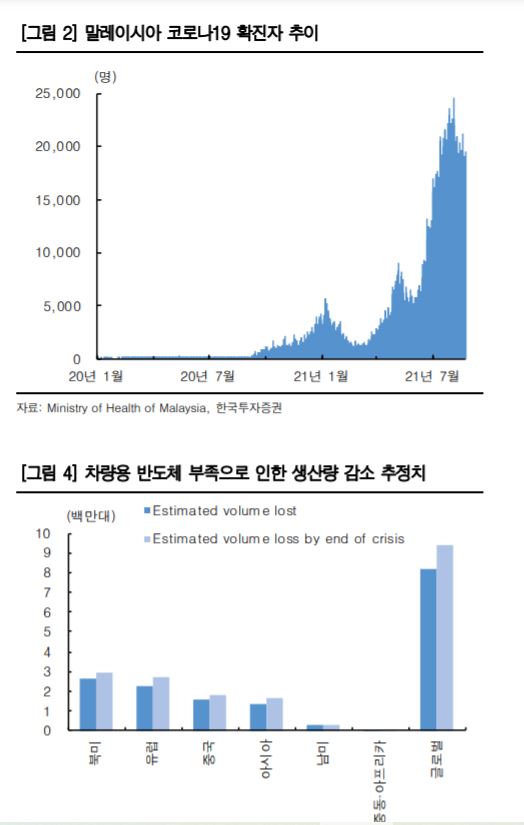
[Asia Economy Reporter Ji Yeon-jin] Attention is focused on how the resurgence of the vehicle semiconductor shortage will affect automobile stock prices.
According to the financial investment industry on the 21st, sales in the European region in August decreased by 18%, and the United States saw a 17% decline. This is analyzed to be due to supply disruptions rather than a drop in demand. Jinwoo Kim, a researcher at Korea Investment & Securities, said, "Even Toyota, which relatively well managed the vehicle semiconductor shortage in the first half of the year, is now undergoing consecutive production cuts," adding, "Toyota announced in August that it would reduce its September production target by 360,000 units, and recently further cut its production targets for September and October by 70,000 and 330,000 units respectively, lowering its annual production target by 3%."
This is due to the spread of COVID-19 in the Southeast Asian region, which has again impacted the supply chain. Semiconductors for brakes are mainly produced in Malaysia, and wiring harnesses are manufactured in Vietnam.
Production disruptions among major global companies are expanding, but the impact of these disruptions may vary depending on the degree of reliance on production bases in Southeast Asia. Looking only at the final assembly value chain of finished vehicles, Japanese companies are mainly affected, but most automobile companies depend on parts of the semiconductor supply chain in Southeast Asia. Also, major semiconductor foundries such as TSMC are expanding vehicle semiconductor production, but uncertainties are increasing ahead of the peak season in the fourth quarter due to the resurgence of COVID-19 in Southeast Asia.
Domestic companies are also expected to be inevitably affected. Hyundai Motor is estimated to be experiencing about a 10% production disruption in August and about 20% in September compared to the original plan. Kia is also facing disruptions mainly at its profitable domestic plants. Although inventory sales in the second quarter helped defend overall sales volume, concerns are emerging that production disruptions in the third quarter could directly translate into sales disruptions since inventory sales cannot be expected.
Rising raw material costs and freight prices are also burdensome. Finished car manufacturers are defending profitability through reduced incentives and selective production, but parts suppliers had expected increased operating rates in the third quarter due to deferred demand and in the fourth quarter due to seasonality; however, the resurgence of COVID-19 and semiconductor shortages have made inventory accumulation uncertain. Researcher Kim said, "If the COVID-19 resurgence in Southeast Asia subsides, the vehicle semiconductor shortage is expected to gradually ease thanks to production expansion and process transitions by foundry companies."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.