Samsung Life Insurance Yield 3.24%... Down 0.41 Percentage Points from Last Year
Insurance Companies' Yield Decline Continues for 10 Years... Sale of High-Interest Bonds
"High Proportion of Government and Special Bonds, Need to Expand Corporate Bond Holdings"
[Asia Economy Reporter Oh Hyung-gil] Although insurance companies have enjoyed windfall gains this year due to rising loss ratios amid the impact of the novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19), their asset management is on a worsening path. A vicious cycle is repeating where financial assets are disposed of, sacrificing future profits to make up for declining returns.
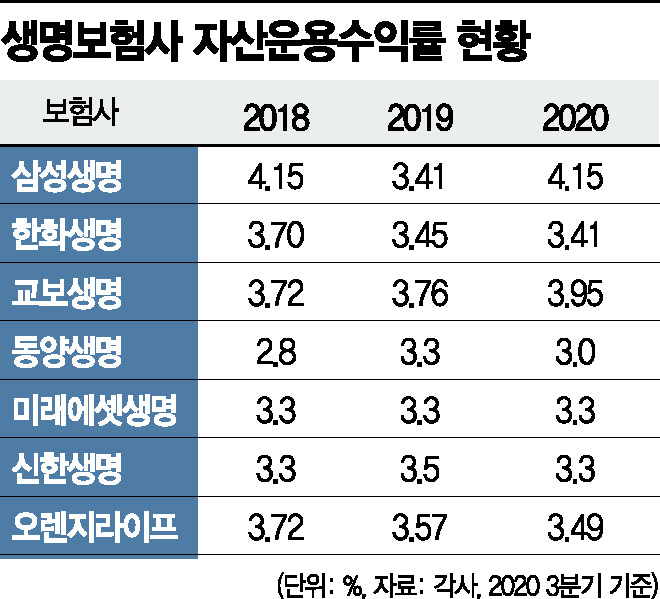
According to the insurance industry on the 19th, Samsung Life Insurance's Q3 quarterly report shows that its managed assets (as of the end of the period) amounted to KRW 238.15 trillion, with operating profits of KRW 5.63 trillion. The operating yield was 3.24%, down 0.41% from 3.65% in the same period last year. The annual operating yield, which reached 4.15% in 2018, also fell sharply to 3.41% last year.
This year, Samsung Life recorded returns exceeding 10% in real estate and other areas, but the yield on securities such as bonds, which make up the majority (76.8%) of its assets, was only 2.95%. Loans yielded a 3.89% return. However, this was insufficient to raise the overall yield.
Samsung Life managed KRW 74 trillion (40%) in government and public bonds among securities, KRW 33 trillion (18%) in special bonds, KRW 36 trillion (19%) in stocks, KRW 19 trillion (10%) in overseas foreign currency securities, and KRW 7 trillion (4%) in corporate bonds. Compared to the end of last year, it increased overseas foreign currency securities while reducing the proportions of special bonds and stocks.
Hanwha Life also saw its asset management yield fall by 0.04 percentage points from the end of last year to 3.41% in Q3. With managed assets nearing KRW 100 trillion, operating profits were only KRW 2.71 trillion.
Among the 'Big 3' life insurers, only Kyobo Life Insurance recorded an increase in yield by 0.19 percentage points from the end of last year to 3.95% (including non-operating assets). Medium-sized life insurers such as Tongyang Life (3.3% → 3.0%), Shinhan Life (3.5% → 3.3%), and Orange Life (3.57% → 3.49%) also had to endure declines in asset management yields.
The problem is that this decline in yields has continued over the past decade, but there are no immediate solutions. According to the Korea Insurance Research Institute, the average operating asset yield of life insurers has declined from 5.88% in 2010 to 3.50% last year.
If insurance companies fail to generate adequate returns from premiums paid by consumers, there is a growing concern that they may not be able to pay promised insurance benefits on time, leading to social issues. This could become more serious in the domestic insurance structure where losses from insurance operations are offset by profits from investment operations.
Ultimately, insurance companies are defending their performance by selling high-interest bonds. A study shows that excluding bond disposal gains from insurance companies' net profits last year, net profits for life insurers dropped sharply from KRW 3.1 trillion to KRW 1.2 trillion, and for non-life insurers from KRW 2.2 trillion to KRW 300 billion. The proportion of bond disposal gains in insurance companies is close to 62% for life insurers and 87% for non-life insurers.
Experts point out that while the value of held contracts can be improved through new contract sales, it is difficult to improve profitability due to the COVID-19-induced contraction in the business environment.
No Geon-yeop, a research fellow at the Korea Insurance Research Institute, suggested, "Compared to Europe, Korea has a higher proportion of government and special bonds and a lower proportion of financial and corporate bonds, so it is necessary to consider expanding the proportion of other assets such as corporate bonds." He added, "Among alternative investments, infrastructure stocks such as roads and ports have financially low risk coefficients, so their investment proportions should be increased."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.