 The carbon dioxide removal catalyst developed by the research team this time, 'amorphous anatase-crystalline rutile titanium dioxide,' has a blue color.
The carbon dioxide removal catalyst developed by the research team this time, 'amorphous anatase-crystalline rutile titanium dioxide,' has a blue color.
[Asia Economy Reporter Junho Hwang] Domestic researchers have developed a catalyst that removes carbon dioxide using visible light. By utilizing this catalyst, indoor and outdoor carbon dioxide, fine dust, and pathogens can be eliminated. Additionally, carbon monoxide is produced as a byproduct of the catalyst, which can be used as an energy source, making it expected to be applied as a measure to improve air quality.
On the 20th, the Institute for Basic Science announced that Hyoyoung Lee, deputy director of the Nanostructure Physics Research Group, developed a catalyst that converts carbon dioxide into oxygen and carbon monoxide using visible light.
Removing Carbon Dioxide with Visible Light
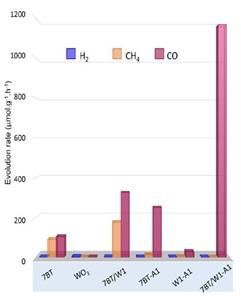 Comparison table of byproducts between conventional Blue Titanium Dioxide (7BT) catalysts and the newly developed Blue Titanium Dioxide catalyst. The far right column shows the results for the newly developed catalyst, indicating that only carbon monoxide is produced.
Comparison table of byproducts between conventional Blue Titanium Dioxide (7BT) catalysts and the newly developed Blue Titanium Dioxide catalyst. The far right column shows the results for the newly developed catalyst, indicating that only carbon monoxide is produced.
The research team created a new catalyst (Blue Titanium Dioxide) that reacts to visible light by doping tungsten oxide and silver into anatase-rutile titanium dioxide (TiO2). This activated charge generation and increased photoconversion efficiency.
The doped TiO2 utilized 34.8% of the absorbed light for catalytic conversion. This is three times higher photoconversion efficiency than existing materials. Also, during the carbon dioxide-to-oxygen conversion process, it was confirmed that 100% carbon monoxide was produced without methane. Notably, the amount of carbon monoxide generated was 200 times greater than that of conventional titanium dioxide catalysts and 15 times more than the best catalysts reported in academia. This process was synthesized in liquid phase at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, ensuring stability. Existing titanium dioxide processes handled gases at high temperature and pressure, posing significant risks.
TiO2 is a material used in ultraviolet blockers, deodorants, and sterilizers. More than 5 million tons are used annually. This material absorbs ultraviolet light and converts water and carbon dioxide into methane, carbon monoxide, and a large amount of oxygen. The scientific community has been focused on developing a catalyst that absorbs only ultraviolet light, is economically efficient, and removes carbon dioxide using this material.
Removing Fine Dust and Pathogens with Visible Light
Deputy Director Hyoyoung Lee stated, "We have secured the core technology for manufacturing Blue Titanium Dioxide that operates with visible light and developed a new visible light catalyst using it. The catalyst developed this time also showed excellent performance in removing fine dust and hospital pathogens." He added, "It is expected to be applied in various research fields and spread worldwide."
The research results were published on the 3rd in the chemistry and materials science journal 'Materials Today.'
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.

![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)














