Quality Issues Identified in High-Speed Railways and Subways
Lower Network Stability in Rural Areas Compared to Major Cities
According to the service quality inspection results for the three major mobile carriers, SK Telecom, LG Uplus, and KT ranked in that order for service stability in high-definition video streaming, which requires high speeds. When looking solely at 5G download speeds, SK Telecom, KT, and LG Uplus ranked in that order for fastest speeds.
The Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Information Society Agency (NIA) announced these findings in the results of the 2025 telecommunications service coverage inspection and quality evaluation on December 30.
 On the 12th, ahead of the re-vote on the impeachment motion against President Yoon Sukyeol, telecommunications workers are installing base stations near the National Assembly in Yeouido, Seoul to ensure smooth communication. Photo by Kang Jinhyung
On the 12th, ahead of the re-vote on the impeachment motion against President Yoon Sukyeol, telecommunications workers are installing base stations near the National Assembly in Yeouido, Seoul to ensure smooth communication. Photo by Kang Jinhyung
This year’s evaluation focused on reflecting the quality experienced by users and actual usage environments. The total number of evaluation sites increased by 200 compared to the previous year, and measurements were expanded in rural areas and indoor facilities. For outdoor areas, the evaluation focused on regions that received lower scores in the previous year, concentrating on areas where user inconvenience was expected.
In particular, the evaluation introduced the rate of meeting required speeds for major services, calculating the required speed for each service commonly used by consumers. Subsequently, the "rate of meeting required speeds"-the proportion of measurements exceeding the required speed-was announced. The previous quality evaluations averaged transmission speeds measured under optimal conditions, such as latest devices and fully charged batteries, which led to criticism that the results did not reflect the quality experienced by users.
The rate of meeting required speeds serves as an indicator of the stability of telecommunications services. Even if the average speed is the same, a higher rate of meeting required speeds indicates less variation in quality and a more stable service.
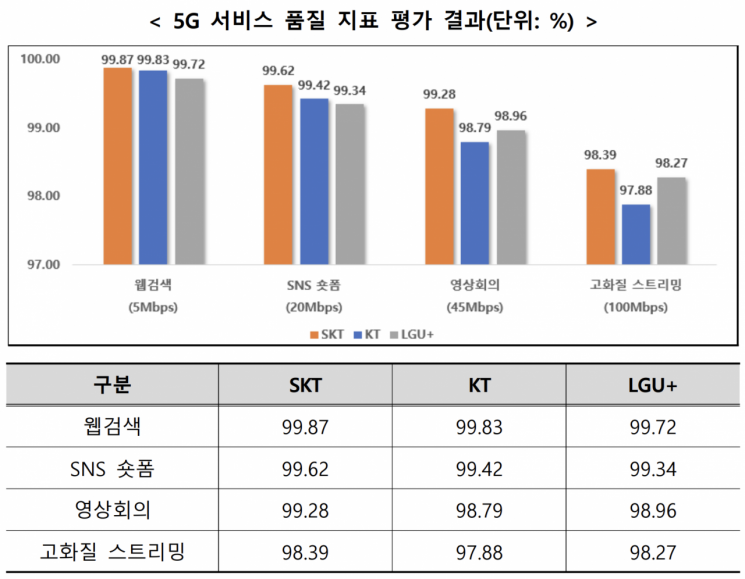 The Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Information Society Agency (NIA) announced on the 30th the results of the 2025 telecommunications service coverage inspection and quality evaluation. Satisfaction rates of required speeds by the three mobile carriers. Provided by the Ministry of Science and ICT
The Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Information Society Agency (NIA) announced on the 30th the results of the 2025 telecommunications service coverage inspection and quality evaluation. Satisfaction rates of required speeds by the three mobile carriers. Provided by the Ministry of Science and ICT
According to the survey, the nationwide rate of meeting required speeds for high-definition streaming (100Mbps) was 98.18%. By carrier, SK Telecom recorded 98.39%, LG Uplus 98.28%, and KT 97.88%.
Meanwhile, for web browsing requiring speeds of around 5Mbps (99.81%) and short-form social networking services (SNS) requiring 20Mbps (99.46%), the rate of meeting required speeds exceeded 99%, indicating stable quality for both services.
By region, the rate of meeting required speeds (for high-definition streaming) was as follows: outdoor areas 98.1%, indoor facilities 98.73%, subway 98.56%, expressways 97.12%, and high-speed railways 81.44%.
By city size, the rate of meeting required speeds was 99.08% in large cities and 96.05% in rural areas, showing that rural areas were 3.03 percentage points lower than large cities. In rural shared network areas jointly established by the three carriers, the rate of meeting required speeds was 96.94% for SK Telecom, 96.37% for LG Uplus, and 95.5% for KT. The rural shared network refers to the 5G network in rural areas, which is built and jointly used by the three carriers.
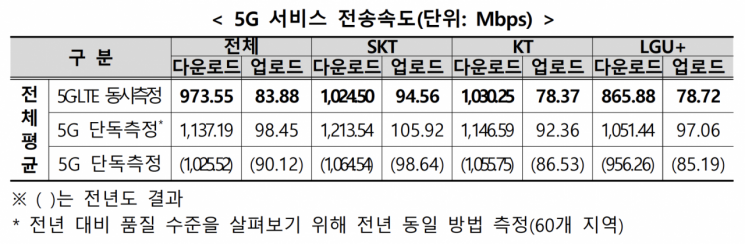 The Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Information Society Agency (NIA) announced on the 30th the results of the 2025 telecommunications service coverage inspection and quality evaluation. 5G speeds of the three mobile carriers. Provided by the Ministry of Science and ICT
The Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Information Society Agency (NIA) announced on the 30th the results of the 2025 telecommunications service coverage inspection and quality evaluation. 5G speeds of the three mobile carriers. Provided by the Ministry of Science and ICT
The nationwide average 5G download speed was 973.55Mbps, down about 52Mbps from the previous year (1025.52Mbps). However, the Ministry of Science and ICT explained that this was due to the simultaneous measurement of 5G and LTE devices. Unlike last year, when all 5G and LTE base station resources were fully utilized in the 5G Non-Standalone (NSA) mode, this year some LTE resources were allocated for LTE evaluation, making direct comparison difficult.
Download speeds on networks utilizing both 5G and LTE were measured at 1030.25Mbps for KT, 1024.5Mbps for SK Telecom, and 865.88Mbps for LG Uplus.
According to the 5G coverage inspection, the 5G access availability rate was 97.69%. Access availability was determined by measuring 5G signal strength, and if more than 10% of measurements fell below the standard signal strength, the area was classified as having insufficient access. Facilities with access availability rates below 90% totaled 27 locations (17 for LG Uplus, 14 for SK Telecom, 14 for KT, with some regional overlap among carriers).
There were 32 areas (5.3%) identified as having insufficient 5G quality, mainly in subway and high-speed railway sections. In particular, of the 19 high-speed railway sections previously identified as having poor quality last year, 14 showed improvement upon reinspection, but five sections-including KTX Cheonan-Asan to Osong to Daejeon to Gimcheon-Gumi-remained unimproved.
The Ministry of Science and ICT plans to apply Shared Network 2.0 technology to high-speed railway sections where quality issues are repeatedly reported. Through this, the government aims to improve the Gyeongbu and Honam lines by 2026, and enhance the quality of all high-speed railway sections by 2027.
The nationwide average LTE download speed was 96.18Mbps. By region type, the average LTE speeds were 97.56Mbps for indoor facilities, 90.81Mbps for outdoor areas, 123.16Mbps for subways, 113.80Mbps for expressways, and 116.16Mbps for high-speed railways.
In WiFi speed measurements, download speeds were 408.37Mbps for commercial WiFi, 426.88Mbps for open WiFi, and 400.48Mbps for public WiFi.
The Ministry of Science and ICT will release a list of areas with insufficient access and quality based on the evaluation results and will require carriers to make improvements, with follow-up inspections planned for the next evaluation.
Choi Woo-hyuk, Director General of Network Policy at the Ministry of Science and ICT, stated, "We will continue to enhance quality measurement and evaluation methods, focusing on vulnerable areas such as indoor, underground, transportation facilities, and rural regions. In addition, we will develop indicators and conduct evaluations in preparation for 5G Standalone (SA) mode in 2026 to promote the advancement of telecommunications infrastructure, while consistently driving improvements in user-perceived quality."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















