Advancing Next-Generation Image Recognition Technology
The research team at Ajou University has developed a novel device that can be used in intelligent machine vision technology, enabling machines to recognize and interpret visual information in a manner similar to humans. This new sensor system operates at a faster speed and consumes less energy compared to existing systems, and is expected to see widespread application in the field of imaging in the future.
 Professor Hyungtak Seo's research team at Ajou University has developed a neuromorphic optical sensor for AI machine vision capable of intelligent image processing. Ajou University
Professor Hyungtak Seo's research team at Ajou University has developed a neuromorphic optical sensor for AI machine vision capable of intelligent image processing. Ajou University
On October 28, Ajou University announced that Professor Hyungtak Seo (Department of Advanced Materials Science and Engineering, Graduate School of Energy Systems) and his research team have developed a neuromorphic optical sensor for AI machine vision capable of intelligent image processing.
Machine vision is a technology that enables machines to recognize, collect, and analyze visual information in a way similar to the human eye by utilizing cameras, image processing software, and artificial intelligence (AI). While it has traditionally been used in industrial settings to measure products and identify defects in place of humans, it is now rapidly expanding into specialized fields such as autonomous driving, robotics, military, and medical applications based on AI advancements.
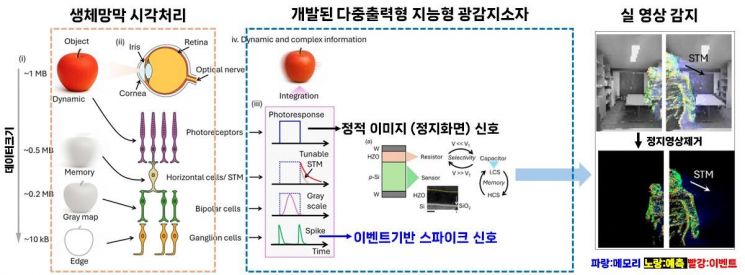
The optical sensing memory sensor developed by the research team was designed by mimicking the horizontal cells of the human retina. By utilizing hafnium-zirconium composite oxide, a material widely developed at the nanoscale for its ferroelectric properties, the team created a new sensor. As a result, the speed of the single-chip device was improved by a factor of 200, while power consumption was reduced by a factor of 1,000 compared to conventional sensors.
Professor Seo stated, "This research is the first case of implementing event-based image encoding and memory-based intelligent processing on a single chip to overcome the data bottleneck limitations of existing machine vision systems. By realizing a silicon junction structure for the device, it is possible to apply this technology to mass production processes."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















