[Hyundai Motor, Over the Mobility] (36)
The Icon of Innovation That Redefined the Automobile
A Smartphone on Wheels, a Moving Computer
Pioneering Manufacturing Methods Driving the Popularization of Electric Vehicles
Shifting the Core of Its Bu
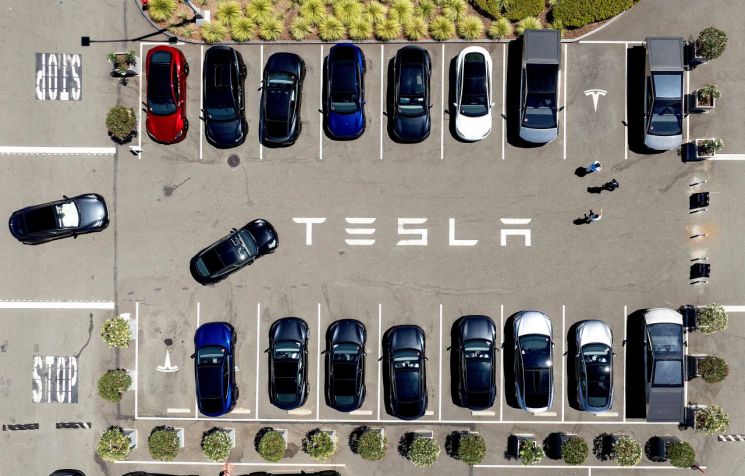 Tesla vehicles are lined up in the company factory parking lot in Fremont, California. Photo by AP/The Yonhap News Agency
Tesla vehicles are lined up in the company factory parking lot in Fremont, California. Photo by AP/The Yonhap News Agency
Tesla is not just a car brand. It has evolved beyond electric vehicle manufacturing into a comprehensive energy solutions company, encompassing autonomous driving, batteries, artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, data centers, and even space exploration. By breaking down the traditional boundaries of the automotive industry, Tesla is redesigning the entire landscape of technology, manufacturing, and business.
The issues Tesla once raised have now become industry standards. The innovative manufacturing methods introduced by Tesla triggered the popularization of electric vehicles. By developing its own batteries and semiconductor chips, Tesla gained control over production and development while simultaneously reducing costs. The ultra-large casting method known as "Giga Casting" has become a symbol of manufacturing innovation, simplifying production processes and increasing automation rates.
Tesla has also redefined the very concept of the automobile. Much like the nicknames "smartphone on wheels" or "moving computer," Tesla has created cars that continuously evolve. To achieve this, Tesla built a Software-Defined Vehicle (SDV) platform and introduced over-the-air (OTA) software update technology. As a result, consumers can now keep their cars up to date by downloading the latest software, without having to purchase a new vehicle.
In 2012, Tesla became the first in the industry to introduce OTA functionality with the Model S. OTA eliminated the need for customers to visit service centers for every repair. When concerns arose about the possibility of battery fires in the Model S, Tesla remotely modified and distributed software to adjust the vehicle's ride height, resolving the issue immediately.
Then, in 2019, Tesla ushered in the era of SDVs by introducing a centralized electrical/electronic (E/E) architecture with the Model 3. This system integrates the previously dispersed electronic control units (ECUs) throughout the vehicle, allowing a single high-performance central computer to control the car. While traditional internal combustion engine vehicles contained more than 100 ECUs, Tesla reduced this number to just four. This significantly decreased wiring length and the number of components, reducing both vehicle weight and manufacturing costs. This architecture has since become the standard model for the electric vehicle industry as a whole. Hyundai Motor is also developing a similar structure to transition to SDVs by 2026, and Chinese electric vehicle makers such as BYD have rapidly adopted this approach since 2023.
Recently, Tesla has been intensively developing its "Full Self-Driving (FSD)" system, which uses AI to learn from vast amounts of driving data. Thanks to its rapidly established SDV platform, Tesla is considered a frontrunner in the autonomous driving technology race. The moment people sit in the driver's seat of a Tesla, they are not just driving a car-they are subscribing to the future.
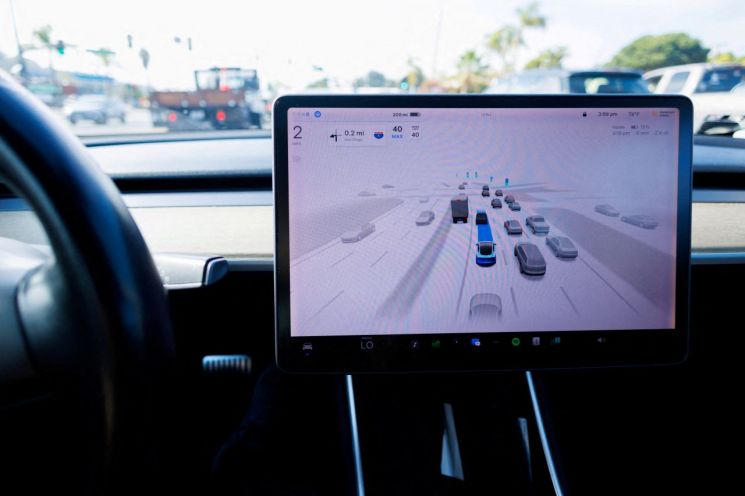 A Tesla Model 3 vehicle driving using the Full Self-Driving (FSD) system in Encinitas, California, USA. Photo by Reuters/Yonhap News
A Tesla Model 3 vehicle driving using the Full Self-Driving (FSD) system in Encinitas, California, USA. Photo by Reuters/Yonhap News
Putting Wheels on Smart Devices
Tesla's brand philosophy starts from a different place than traditional automakers. Rather than aiming to "make affordable and high-quality cars," Tesla chose electric vehicles as a means to address climate change. Founder Elon Musk is an engineer-entrepreneur with deep knowledge of physics and software. His perspective on electric vehicles began with the idea of "putting wheels on smart devices." Choosing electricity as the vehicle's power source was both an eco-friendly strategy and an inevitable decision to maximize the efficiency of IT devices.
So how did Tesla succeed with the "smart car" where the world's top IT company, Apple, failed? The answer lies in Tesla's unique spirit of "experimentalism." Tesla transplanted the development culture of the IT industry-fixing software bugs and continuously updating-directly into the automotive sector. Tesla prioritized rapid experimentation and market feedback over perfect products, opting for an open beta-style innovation of "release first and constantly improve." For Tesla, defects were not a brand risk but a part of innovation.
In contrast, Apple became trapped by its title as "the world's best" and its perfectionism. The "Titan Project" to create the Apple Car was pursued for over a decade, but in 2024, Apple ultimately announced its abandonment. The initial goal was set too high: a Level 5 fully autonomous vehicle. Despite being a group of the world's best engineers, and high expectations that Apple could build the best "smartphone on wheels," the company could not overcome the barriers of reality.
They failed to understand the entirely different autonomous driving ecosystem that combines IT software and mechanical hardware. Setting a goal of winning a gold medal before even learning to walk made success impossible. There was also criticism that there was no leader to break through the many unprecedented challenges in this new domain. Some have even said, "If Steve Jobs were alive, the Apple Car would have succeeded."
Elon Musk's leadership is fundamentally different. With relentless tenacity, he dragged Tesla from a laboratory curiosity to the center of the industry. During the early development of electric vehicles, Musk engaged in intense debates with engineers. A prime example was the early battery design for the Model S: Musk wanted to lower the body for design reasons, while engineers insisted on maintaining thickness for safety. Ultimately, this debate led to a structural innovation where the battery pack was integrated with the vehicle body. While Musk's management style is sometimes seen as harsh, in terms of project outcomes, his leadership has been the most powerful engine driving Tesla forward.
 Elon Musk, CEO of Tesla. Provided by The Asia Business Daily database.
Elon Musk, CEO of Tesla. Provided by The Asia Business Daily database.
Manufacturing Innovation: The Key to Popularizing Electric Vehicles
Tesla's innovation is also evident in its production methods. The company has established a vertically integrated supply chain, developing its own battery cells and packs, electric motors, software, and semiconductors. By building technology as an internal asset rather than outsourcing, Tesla has secured control over both costs and quality.
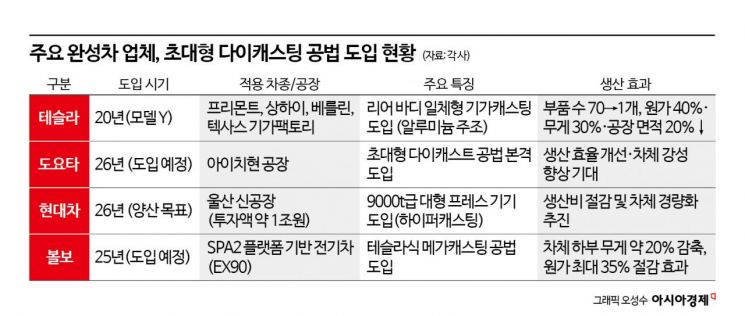
In 2020, the Model Y became the first in the world to use the ultra-large die-casting (Giga Casting) method. The rear body, previously made of over 70 separate parts, was combined into a single cast piece-produced "in one shot." This reduced costs by 40% and weight by 30%. With the disappearance of conveyor belts, factory floor space was reduced by 20%. The fundamental principle of Tesla's manufacturing is to minimize human touch, thereby reducing labor costs and lowering overall expenses. The Shanghai Gigafactory boasts an automation rate of 95%, with robots and AI control systems handling most processes.
These changes are part of a strategy to lower costs and accelerate the mass adoption of electric vehicles. Through productivity innovation, Tesla has made "reasonably priced electric vehicles" a reality. This model has become the standard for the entire automotive industry. Toyota has announced plans to introduce Giga Casting at its Aichi plant by 2026, and Hyundai Motor is building a factory in Ulsan with a 1 trillion won investment, aiming for mass production using the same method by 2026.
Competing with Hyundai Motor in Innovation Methods
While Tesla focuses on maximizing the efficiency of mass production, Hyundai Motor is striving to enhance manufacturing efficiency in small-batch, multi-model production. At the Hyundai Motor Group Innovation Center in Singapore (HMGICS), Hyundai Motor is experimenting with various production methods, such as a cell-based flexible manufacturing system, the integration of robots into manufacturing processes, and digital twins, all aimed at increasing flexibility and efficiency.
However, given that Hyundai Motor has built world-class automotive hardware capabilities, it is not easy to fully break away from a "quality-focused, perfectionist" framework. As a company that has grown on a long tradition of manufacturing, technological innovation is important, but a culture prioritizing completeness runs deep. Now, as the era of autonomous driving based on SDV platforms arrives, a shift in mindset seems necessary. The initial model of Hyundai Motor's seventh-generation Grandeur, released in 2022, faced much controversy over software defects, but it continues to enjoy strong demand in Korea. In 2024 alone, 110,000 units were sold, and cumulative sales are expected to surpass 200,000 this year. This may indicate that consumers now expect innovation, rather than perfection, from Hyundai Motor.
Unlike Tesla, which pursues full internalization, Hyundai Motor has built a strategic collaboration model. It jointly develops batteries with LG Energy Solution and SK On, and enhances competitiveness through strategic alliances with leading domestic companies such as Samsung Electronics for semiconductor cooperation. In contrast, Tesla controls every aspect of its technology from start to finish, accelerating the pace of innovation. Although the two companies have different approaches, their ultimate goal is the same: innovation. Ultimately, their competition is not about car design or specs, but about how they innovate.
Tesla's Transformation into an AI Company
This year, the core of Tesla's business is shifting from "electric vehicles" to "AI." Whereas Tesla previously positioned itself as a company championing carbon neutrality through electric vehicles, it now aims to directly transform human life through AI. A prime example is the strategy of turning the car itself into a "wheeled AI robot."
Through the beta version of its Full Self-Driving (FSD) software, Tesla has accumulated vast driving data in North America. As of March this year, Tesla announced that the cumulative mileage driven with FSD had reached 3.6 billion miles (about 5.8 billion kilometers). Tesla is virtually the only company in the industry to disclose such figures in detail and on a regular basis. In the autonomous driving industry, where AI is leveraged, the amount of accumulated data is the core technological asset. One key feature of Tesla's latest autonomous driving system is the application of an "end-to-end" neural network structure that learns and processes all at once. This means that even if remote communication networks with the outside are interrupted, the AI inside the vehicle can independently perform recognition, judgment, and control.
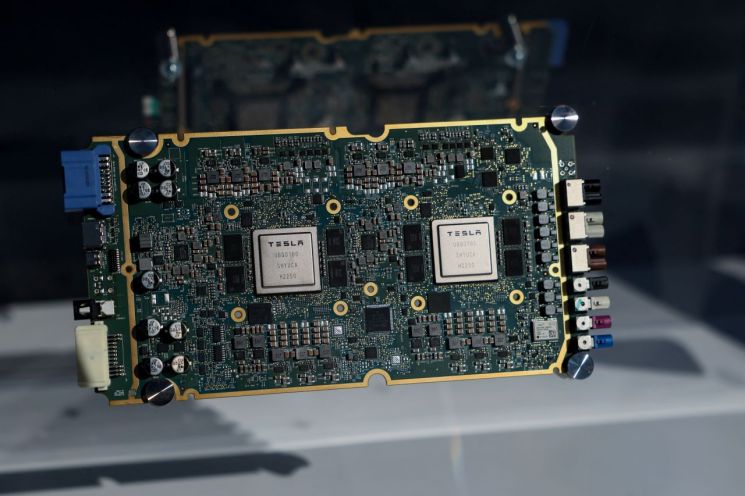 Tesla's autonomous driving chip is displayed at a dealership in Manhattan, New York, USA, on October 2, 2025. Photo by Reuters/Yonhap News
Tesla's autonomous driving chip is displayed at a dealership in Manhattan, New York, USA, on October 2, 2025. Photo by Reuters/Yonhap News
Tesla's revenue model is also changing. The company is shifting its business focus to FSD subscriptions and robotaxi services. Elon Musk has even set a concrete goal: by the end of 2025, more than half of the U.S. population will be able to use Tesla's robotaxi service.
Changes are also evident in Tesla's AI infrastructure. Since the early 2020s, Tesla has been developing the "Dojo" supercomputer project for autonomous driving AI training. Although the company has recently shifted somewhat toward an external cloud collaboration model, it remains committed to investing in its own data centers. Tesla is focusing on developing its own AI semiconductor chips (AI5 and AI6), a strategy intended to reduce dependence on external suppliers such as Nvidia.
The area where Tesla's AI technology is expected to most directly permeate our daily lives is robotics. Elon Musk has declared that the humanoid robot "Optimus," currently under development, will eventually account for 80% of Tesla's corporate value. Optimus is a robot designed with AI vision and control technology at its core. The concept is to transfer the way autonomous vehicles recognize, judge, and control themselves on the road to a "walking robot." While autonomous driving has changed the paradigm of mobility itself, Optimus aims to expand that technology into the broader physical world, including homes, industries, and logistics.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.


![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















