The most delicate body part requires numerous components
Extremely complex calculations needed for control
Difficult to achieve human-like precision and rapid tactile response

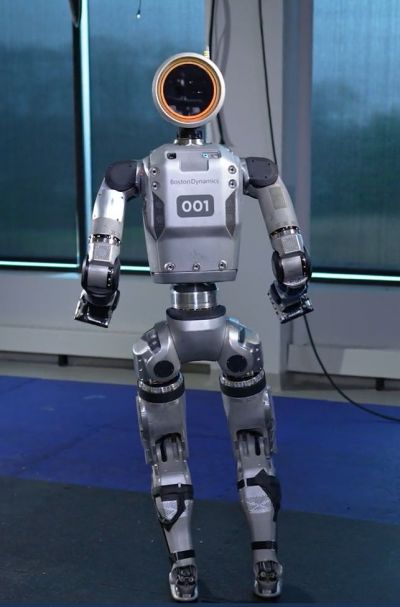
Elon Musk's Tesla and Boston Dynamics, a subsidiary of Hyundai Motor Group, have announced ambitious plans to deploy humanoid robots in automobile factories starting next year. Both Tesla's "Optimus" and Boston Dynamics' "Atlas" do not yet operate with the same precision as human hands. However, if humanoids are developed for household use in the future, robot hands that closely resemble human hands are likely to emerge as a core technology.
Among the various body parts of humanoid robots, the hand is considered the most difficult to replicate with human-like functionality. Even the world's leading humanoid companies are struggling to develop hands that move like those of humans. On October 2, Hyundai Motor Securities provided a detailed explanation of the reasons for this in its report, "The Core of Humanoids: Robot Hands."
'Human hands are too complex': Limitations of size, weight, and cost
First, there is the issue of structural complexity. The human hand contains more than 25 bones, over 30 joints, and numerous muscle tissues intricately connected. Even moving a single finger involves the subtle and simultaneous operation of several muscles and tendons.
To replicate these movements in a humanoid robot's hand, dozens of actuators (devices that move robot joints) are required. This inevitably leads to challenges related to size, weight, and cost. Although the number of companies focused solely on developing robot hands is increasing, the fact that the price can reach tens of millions of won demonstrates these issues.
Too many calculations required for control
Humans can intuitively control numerous body parts simultaneously through the brain and nervous system. For example, consider the command "Hold an egg without breaking it, but grip the cup next to it firmly." This is very easy for a human.
However, robots must calculate and control every joint through algorithms. For humanoids, it is not easy to grasp objects with varying levels of force depending on the situation and to calculate the exact amount of force being applied.
Difficult to sense tactile feedback as precisely as humans
The human hand contains thousands of tactile, pressure, and temperature receptors. This allows people to subconsciously detect subtle differences in texture. Tactile feedback is also transmitted to the brain through the nervous system, which immediately commands the hand to respond.
However, the tactile sensors installed in robot hands are limited. As a result, the speed and accuracy of data processing cannot be as advanced as those of humans. This technical limitation is why many humanoid robot developers still use gripper designs with only two or three fingers.
The capabilities of robot hands are becoming increasingly important
Many experts believe that five fingers are essential for humanoid robots to delicately grasp and manipulate fine objects such as needles, cables, or eggs. Since countless objects and tools in human society are designed for human hands, five-fingered robot hands are also necessary to use these items without additional equipment.
For robot hands to operate like human hands, it is essential to devise methods to sufficiently deploy actuators and sensors in the right places while also reducing costs. Park Junyoung, an analyst at Hyundai Motor Securities, explained, "Recently, there have been companies in Korea developing robot hands that achieve sufficient degrees of freedom while significantly lowering costs," adding, "In the future development of the humanoid industry, the ability to create advanced robot hands at a low cost will be crucial."
In the securities market, Robotis, Rainbow Robotics, and KNR Systems are cited as listed companies developing robot hands. In addition, HiZen R&M and Yujin Robot are listed companies that manufacture components for robot hands, such as actuators, reducers, sensors, and motors.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.