 [From left, Hyunjun Son Researcher, Geonho Kim Professor, Sejong Kim Researcher, Ssanggu Cho Professor]
[From left, Hyunjun Son Researcher, Geonho Kim Professor, Sejong Kim Researcher, Ssanggu Cho Professor]
The joint research team from License Medical Co., Ltd. and StemExoOne Co., Ltd. has developed a needle-free drug delivery system, offering new possibilities for the treatment of intractable skin diseases.
This achievement was made through collaborative research between License Medical, led by Professor Geonho Kim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering at UNIST, and StemExoOne, led by Professor Ssanggu Cho of the Department of Stem Cell and Regenerative Engineering at Konkuk University’s Advanced Biotechnology Division. The team announced the development of a "picoliter ice particle-based transdermal drug delivery technology using supersonic cryogenic jets."
The study was introduced in the "People Who Light Up Korea" section (Hanbitsa) of the Biological Research Information Center (BRIC), and was published in the prestigious pharmacology journal, Journal of Controlled Release (impact factor: 11.5, top 3.3% in pharmacology), under the title "Picoliter ice particles by supersonic cryogenic jets for transdermal drug delivery: Extracellular vesicle application for skin diseases." This publication attests to the academic value of the research.
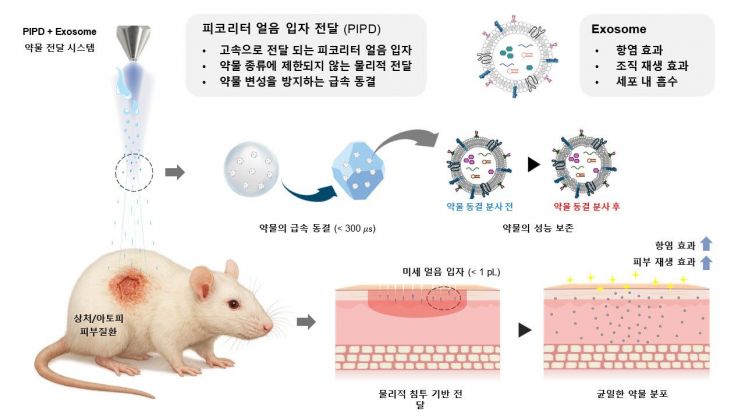
The "Picoliter Ice Particle Delivery (PIPD)" technology developed by the research team works by injecting liquid drugs with a supersonic cryogenic jet, which instantly atomizes and rapidly freezes the drug into fine ice particles. These frozen drug particles, despite their picoliter-scale volume, exhibit high penetration performance, allowing them to pass through the skin barrier without pain or damage and deliver drugs effectively into the tissue.
Using this technology, the team administered highly functional extracellular vesicles (EVs)-extracted from stem cells using a proprietary 4D culture method-to animal models of atopic dermatitis and skin wounds. The results showed that the therapeutic effect was comparable to or even better than conventional injection methods, and significantly superior to simple topical application. Notably, drugs delivered via PIPD were distributed uniformly across multiple layers of the skin, overcoming the issue of uneven distribution that has been a limitation of existing drug delivery methods.
The core of this research is the ability to safely deliver sensitive protein or cell-based biopharmaceuticals without denaturation. The process of forming drug ice particles is completed in less than 300 microseconds, preserving the drug’s structure and function. In fact, even after the PIPD process, the extracellular vesicles maintained their original size and shape, and the expression rates of surface protein markers (CD9, CD63, CD81) remained above 98%, confirming their integrity.
Professor Geonho Kim of UNIST stated, "This study is a good example of solving the challenges of conventional drug delivery technologies by integrating precision mechanical engineering and biotechnology. We plan to further develop this as a platform technology applicable not only to skin diseases but also to other body tissues."
Professor Ssanggu Cho of Konkuk University commented, "PIPD technology is an innovative method that can maximize the efficacy of next-generation biopharmaceuticals such as stem cell exosomes. It will offer new hope to patients suffering from chronic inflammatory diseases such as atopic dermatitis."
Based on these achievements, the research team expects that PIPD technology will reduce the treatment burden for patients, expand the range of drugs that were previously limited in use, and contribute to the treatment of various intractable diseases. License Medical has developed VetEase, a veterinary medical device applying the precision cryogenic cooling technology presented in this study, which is being distributed in Korea in collaboration with Yuhan Corporation. StemExoOne has also commercialized and supplies VexoHeal, a wound dressing for animals, to the market.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















