A next-generation graph-relational database (DB) system has been developed in South Korea. If this system is applied in industrial settings, artificial intelligence (AI) will be able to perform real-time inference on complex connections, going beyond simple searches, making it possible to implement AI services that are more advanced than existing ones.
KAIST announced on September 8 that Professor Minsu Kim's research team from the School of Computing has developed "Chimera," a DB system that fully integrates "relational DB" and "graph DB" to execute graph-relational queries more efficiently.
 (From left) Jeongho Park, Graphy Engineer; Geonho Lee, Doctoral Candidate; Minsu Kim, Professor. Courtesy of KAIST
(From left) Jeongho Park, Graphy Engineer; Geonho Lee, Doctoral Candidate; Minsu Kim, Professor. Courtesy of KAIST
Unlike traditional relational DBs, graph DBs represent data as vertices (nodes) and edges (connections), making them particularly effective for analyzing and inferring information that is intricately intertwined, such as people, events, places, and time. This characteristic is rapidly gaining traction in fields such as AI agents, social networking services (SNS), finance, and e-commerce.
In particular, as the demand for processing complex queries across relational DBs and graph DBs grows, there is increasing interest in "SQL/PGQ," a new standard language that extends relational query language (SQL) with graph query capabilities.
SQL/PGQ is a new standard language that adds graph traversal capabilities to the existing database language (SQL). It is designed to allow for simultaneous queries (searches) of tabular data and connection information, such as people, events, and places, making it much simpler to search for complex relationships like "Which company does a friend of this person's friend work at?" compared to previous methods.
However, until now, approaches have been limited to either forcibly simulating graph traversal through joins, or relying on pre-constructed graph views in memory.
For example, in the former case, performance drops sharply as the depth of traversal increases, while in the latter case, queries fail as data size grows due to memory shortages. Additionally, changes in the original data are not immediately reflected in the view, resulting in data staleness, and there is inefficiency in having to separately combine relational and graph results.
In contrast, Chimera fundamentally overcomes these limitations by redesigning both the storage layer and the query processing layer of the DB.
In this new design, the research team first introduced a "dual store architecture" that simultaneously operates a dedicated graph storage and a relational data storage.
They also applied a "traverse-join operator" that processes graph traversal and relational operations simultaneously, allowing complex operations to be executed efficiently within a single system. Through this, Chimera has become the world's first "graph-relational DB system" that integrates the entire process from data storage to query processing.
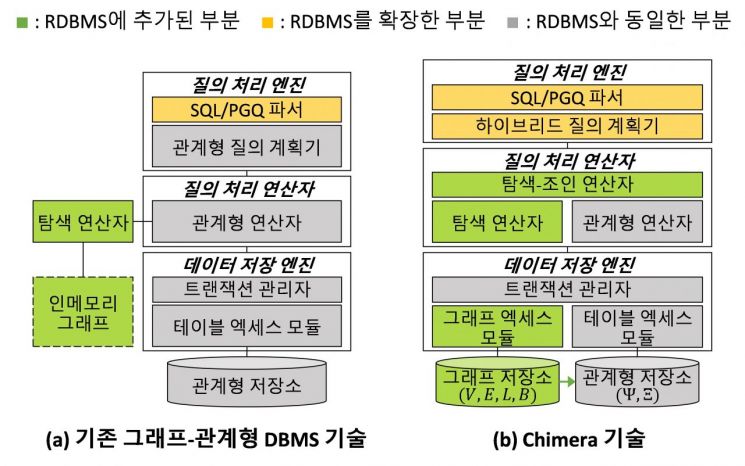 Comparison diagram of existing graph-relational technology and Chimera technology. Provided by KAIST
Comparison diagram of existing graph-relational technology and Chimera technology. Provided by KAIST
As a result, Chimera achieved performance that was 4 to 280 times faster than existing systems in the international performance benchmark "LDBC Social Network Benchmark (SNB)." Most notably, even as the scale of graph data increased dramatically, there were no query failures due to memory shortages, and since it does not use views, there were no delays in data freshness.
Professor Kim stated, "As the connections between data become more complex, the need for integrated technology that encompasses both graph and relational DBs inevitably increases. Chimera fundamentally solves these issues, and I expect it will be highly applicable in a variety of industries such as AI agents, finance, and e-commerce in the future."
Meanwhile, this research was conducted with Geonho Lee, a doctoral candidate in the School of Computing, as the first author; Jeongho Park, an engineer at Graphy Inc., as the second author; and Professor Kim as the corresponding author. The research results were presented at the international database conference VLDB on September 1.
The Chimera technology will be applied to "AkasicDB," a vector-graph-relational DB system to be launched by Graphy Inc., and is expected to serve as a core technology for implementing "high-performance AI agents based on RAG."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















