First National Survey on Health Information Literacy Conducted in Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Six out of ten Koreans have been found to possess adequate ability to understand and evaluate information or medical services related to health.
The Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA) announced on August 7 that it had published the results of its assessment of the public's health information literacy and identification of vulnerable groups with low health information literacy in the Korean Society of Epidemiology’s journal, 'Epidemiology & Health.'
Health information literacy refers to the ability to find, understand, and utilize health information or services necessary for making health-related decisions. As a key determinant of health, its importance is increasingly being emphasized.
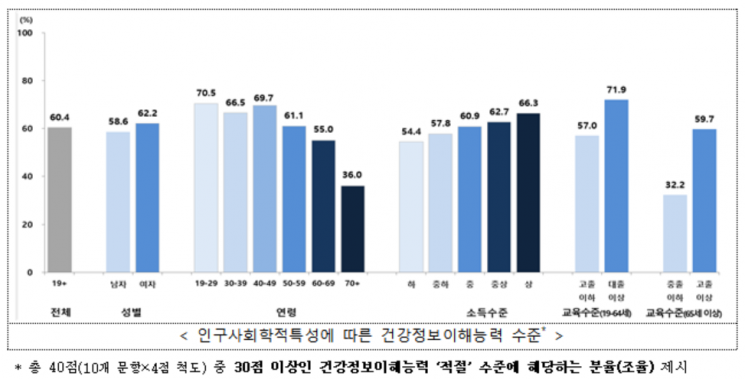
According to an analysis of data from 5,906 adults who participated in the 2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 60.4% of Korean adults were found to have an 'adequate level of health information literacy.'
By category, understanding explanations from doctors or pharmacists and patient education materials showed the highest level of comprehension in the health management area. In contrast, the resource utilization area, which involves disease prevention and evaluating and using acquired information, showed lower levels of understanding.
Additionally, women (62.2%) exhibited higher health information literacy than men (58.6%). Younger age groups showed higher levels of literacy, with those in their 20s demonstrating a health information literacy rate of 70.5%, which is nearly twice as high as those aged 70 and older (36.0%). Higher income and education levels were also associated with higher health information literacy.
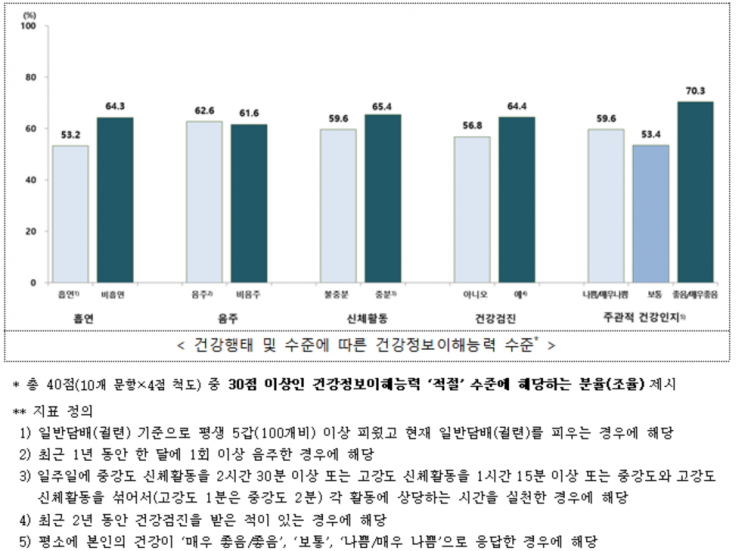
In terms of health behavior characteristics, individuals who practiced healthy lifestyles?such as non-smoking, sufficient physical activity, and participation in health check-ups?tended to have higher levels of health information literacy compared to those who did not.
Previously, the government designated the enhancement of health information literacy as a key task in the 5th National Health Promotion Comprehensive Plan (HP2030). The government is making efforts to regularly assess the public's health information literacy and, based on these findings, to establish systems for providing and utilizing health information.
To this end, the KDCA developed a measurement tool suitable for Korea’s circumstances in 2022 to monitor health information literacy at the national level and to provide evidence. This tool was introduced in the 2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, targeting adults. The health information literacy measurement tool used in the survey consists of 10 questions, divided into disease prevention (3 questions), health promotion (1 question), health management (4 questions), and resource utilization (2 questions). A total score of 30 or higher out of 40 (with each question scored on a 4-point scale) was considered an 'adequate level of health information literacy.'
Im Seungkwan, Commissioner of the KDCA, stated, "This survey is significant in that it systematically identified the public's level of health information literacy and related factors. We will work to improve the public’s health and health equity by revamping the National Health Information Portal and developing customized health information, so that all citizens, including vulnerable groups such as the elderly and those with lower education levels, can easily access and utilize health information."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.