Building AI-Based Microgrids
Maximizing Renewable Energy Utilization
Jeonnam Designated as a Specialized Region for Distributed Energy
Promoting Export Industry through Demonstration Projects
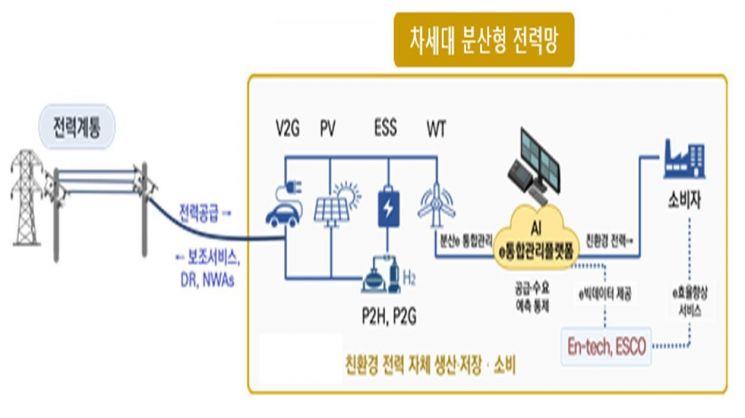
The government is set to launch the "Korean-style Next-Generation Power Grid" initiative. As the global renewable energy market expands and a 'supercycle' of power grid investments is underway worldwide, Korea is also planning to transition to a new power system based on regionally deployed intelligent power grids (microgrids).
According to the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy on July 31, the next-generation power grid is characterized by a 'bidirectional' system, where renewable energy generation such as solar power is managed primarily through the distribution network, and surplus electricity is sent back to the transmission grid. This marks a departure from the traditional 'generation-transmission-distribution' structure centered on large-scale power plants. Through microgrids, distributed renewable energy can be managed more efficiently, enhancing the stability of the power grid.
This initiative is aimed at keeping pace with the global expansion of renewable energy. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), in 2024, investments in renewable energy reached $760 billion, grid investments amounted to $388 billion, and investments in power storage facilities totaled $57 billion. The government intends to seize this global trend as an opportunity by building an intelligent power grid that integrates distributed energy resources, energy storage systems (ESS), and AI technology, thereby improving the efficiency of power generation, storage, and consumption.
The core of the next-generation power grid lies in its use of AI technology to forecast generation and demand, and to maximize the utilization of renewable energy by considering the available capacity of the grid. The government expects that this will reduce output controls and lay the groundwork for new business models in the power market.
The government will first launch a next-generation power grid demonstration project in Jeonnam. Jeonnam possesses the largest renewable energy resources in Korea, but frequent output controls occur due to grid limitations. Furthermore, the presence of related research institutes and public enterprises such as Korea Institute of Energy Technology (KENTECH), Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST), Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO), and Korea Power Exchange makes the region well-suited for large-scale demonstrations.
Jeonnam will be designated as a specialized region for distributed energy, with special regulatory exemptions applied under the Electricity Business Act and power market regulations. The government plans to allow direct power transactions between local generators and demand-side companies. By introducing customized electricity pricing schemes, the aim is to vitalize new power industry businesses.
Additionally, new core technology development projects will be established for long-duration ESS and microgrid technologies, expanding national research and development (R&D) investments. The government will open a renewable energy bidding market to activate virtual power plant (VPP) businesses and will build large-scale ESS in the distribution network to resolve the backlog of renewable energy connection requests.
Customized microgrids will also be built in industrial complexes, university campuses, airports, and military bases. In steel industrial complexes, the government is considering creating renewable energy clusters to produce green hydrogen from surplus electricity, which will be used in hydrogen-based steelmaking processes. In petrochemical complexes, pilot projects will install solar panels on unused factory rooftops and convert surplus electricity into heat or additional power.
The next-generation power grid industry encompasses not only equipment (solar, wind, ESS, inverters) but also networks such as optical communication networks and power line communication, operating systems, VPP platforms, and demand response services. The government aims to develop a track record through domestic demonstration projects and use this as a foundation to foster the industry as an export sector.
Korea Institute of Energy Technology (KENTECH) will operate as an 'open campus' for collaboration among companies, research institutes, and startups, and will pursue joint research, shared equipment use, and technology startup cooperation with Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology and Chonnam National University. Through these efforts, the government plans to support youth entrepreneurship and create the 'K-GRID Talent and Startup Valley,' where energy startups collaborate with companies and universities.
Given the need for power market system reform and cooperation among various industries and institutions, the government will also establish a "Next-Generation Power Grid Task Force" with participation from both the public and private sectors. The task force, led by Lee Hohyun, the Second Vice Minister of the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, will include relevant ministries, local governments, related organizations, industry representatives, and external experts to develop a roadmap and detailed implementation plans.
An official from the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy stated, "Distributed energy resources and AI-based power grid technology will be the key to expanding renewable energy and achieving energy transition," adding, "Based on domestic demonstration projects, we will create a new power grid industry that can lead the global market."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.