June Industrial Activity Trends by Statistics Korea
Production up 1.2%, Consumption up 0.5%
Investment remains negative for four consecutive months
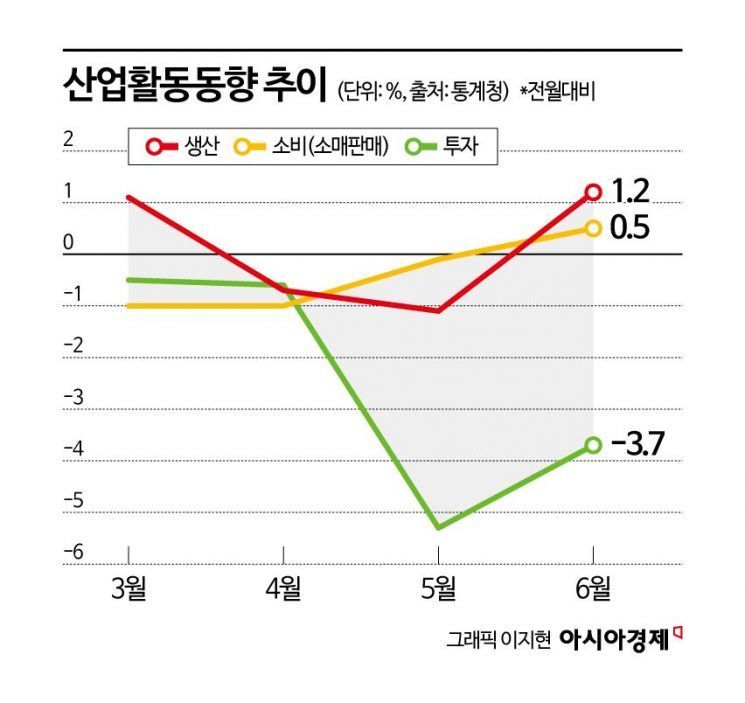
Driven by the automobile and semiconductor industries, total industrial production in June increased by 1.2% compared to the previous month, marking a slight uptick. Retail sales also turned positive for the first time in four months. However, facility investment declined for the fourth consecutive month. Although both production and retail sales increased, the growth rates remain low and investment continues to decline, indicating that the economic recovery is still weak.
According to the “June 2025 Industrial Activity Trends” released by Statistics Korea on July 31, total industrial production last month rose by 1.2% compared to the previous month. After two consecutive months of negative growth in April (-0.7%) and May (-1.1%), production increased slightly, reversing the downward trend.
Production of semiconductors, including DRAM, and automobiles rose by 6.6% and 4.2%, respectively, providing a modest boost to overall production. As a result, manufacturing output increased by 1.6% compared to the previous month. Despite a 25% tariff imposed on automobiles since April, production actually increased. Statistics Korea explained that this was due to a decrease in production in the previous month (-2.4%) and the launch of new hydrogen vehicles, both of which contributed to the rise in output. Production also increased in the service sector (0.5%), construction, and public administration.
In contrast, production of electronic components dropped sharply by 18.9%. Choi Changyun, Director of the Service Industry Trends Division at Statistics Korea, explained, “The downstream industry for electronic components is primarily smartphones. Due to tariff uncertainties in the downstream sector, manufacturers reduced production of smartphone components to adjust supply.” The decrease in electronic components was the largest in 16 years and six months since a 30.9% drop in December 2008.
The government stated that it was difficult to clearly identify the impact of U.S. tariffs in the June indicators. Although a 10% tariff has been imposed since April, performance has been better than expected. Cho Sungjoong, Director of Economic Analysis at the Ministry of Economy and Finance, said, “The expansion of our companies into alternative markets such as the EU, in addition to the U.S., may have played a role. Some companies also absorbed the tariff increase without raising prices, minimizing the impact on exports. In June, manufacturing output rebounded significantly, and the shipment index improved from -1.0% in May to 1.6% in June.”
Facility investment declines for four consecutive months... Longest drop in seven years
Investment indicators continued to deteriorate. Facility investment fell by 3.7% compared to the previous month, marking a fourth consecutive monthly decline. This is the longest period of decline in seven years, since the continuous decrease from February to June 2018. Investment in transportation equipment, such as aircraft, dropped sharply by 14.8% due to reduced imports, and although machinery investment increased by 1.7%, it was not enough to reverse the overall trend.
Director Choi explained, “There was a significant increase in semiconductor machinery investment in February, which created a base effect. However, on a year-on-year basis, facility investment has risen for five consecutive months, so the overall level is not necessarily bad.” On a monthly basis, facility investment decreased by 17.2% in January, then increased by 21.3% in February. On a year-on-year basis, after an 8.0% increase in February, facility investment has continued to rise for five consecutive months.
Retail sales, which reflect consumption trends, also saw only a modest increase. Sales of clothing and cosmetics rose, leading to a 0.5% increase compared to the previous month and turning positive for the first time in four months. Sales of durable goods such as passenger cars decreased by 1.6%, but sales of semi-durable goods (4.1%) and non-durable goods such as cosmetics (0.3%) increased, slightly boosting overall consumption. Statistics Korea noted that consumer sentiment is improving, and with the rollout of livelihood recovery consumption coupons included in the upcoming second supplementary budget, the trend of consumption improvement is likely to continue. Production in the service sector, which reflects service consumption, also increased by 0.5% compared to the previous month.
Construction sector turns positive compared to previous month, but...
Construction output, measured by constant construction completed, increased by 6.74%, turning positive from a 2.5% decrease in the previous month. This was mainly due to a significant increase in building construction (10.3%). Although civil engineering (-2.8%) declined, the expansion of both residential and non-residential building construction drove overall performance. However, Statistics Korea judged that it is still difficult to conclude that the construction market has begun to rebound. On a year-on-year basis, construction output continued to decrease for the 14th consecutive month, falling by 19.5% in May and by 11.9% in June.
The government highlighted that industrial activity indicators rebounded after the sluggish performance in April and May. The Ministry of Economy and Finance stated, “With improvements in domestic demand indicators, the effects of the second supplementary budget, including livelihood recovery consumption coupons, as well as recovering consumer sentiment and an active stock market, are expected to have a positive impact on the economy.” Director Cho also commented on the 15% tariff negotiations with the U.S. held that day, saying, “The resolution of uncertainties and the 10 percentage point reduction in mutual tariffs are expected to have a positive effect.”
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.