Complete Vaccination Rate for Two-Year-Olds in 2023 Reaches 93.6%
South Korea Maintains Higher Childhood Vaccination Rates Than Other Major Countries
The vaccination rates for major vaccines among children in South Korea remain significantly higher than those in other major countries.
According to the "2024 National Childhood Vaccination Coverage Status" released by the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency on July 28, the "complete vaccination rate"?meaning children who received all recommended vaccines according to the standard immunization schedule last year?was 93.3% for one-year-olds (born in 2023), 93.6% for two-year-olds (born in 2022), 88.7% for three-year-olds (born in 2021), and 89.4% for six-year-olds (born in 2018).
Compared to a year ago, the vaccination rate for two-year-olds increased slightly by 0.7 percentage points, while the rates for one-year-olds, three-year-olds, and six-year-olds decreased somewhat. In particular, the vaccination rate for one-year-olds dropped by 3.1 percentage points. This is interpreted as being due to the inclusion of the rotavirus vaccine in the national immunization program in 2023, which increased the number of required vaccinations for one-year-olds by two to three doses.
Excluding the rotavirus vaccine, the complete vaccination rate for one-year-olds was 96.2%, similar to the previous year's rate of 96.4%. The rotavirus vaccination rate for one-year-olds was 94.2%, which is more than 5.2 percentage points higher than the pre-introduction rate of the national immunization program (89.0%).
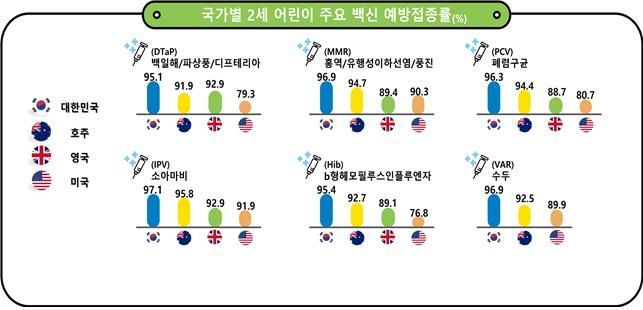
For six major vaccines?including pertussis·tetanus·diphtheria (DTaP), measles·mumps·rubella (MMR), and pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV)?the vaccination rates in South Korea were 1 to 19 percentage points higher than those in other major countries such as the United States, the United Kingdom, and Australia.
For two-year-olds, the DTaP vaccination rate was 95.1% in South Korea, compared to only 79.3% in the United States. For MMR, it was 96.9% in South Korea, while the United Kingdom recorded 89.4%. The PCV vaccination rate was 96.3% in South Korea, 80.7% in the United States, and the Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccination rate was 95.4% in South Korea and 76.8% in the United States, showing a significant difference.
Im Seungkwan, Commissioner of the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency, stated, "Vaccination is the most effective means of building immunity to prevent infectious diseases in children. I urge parents to ensure their children complete the recommended immunization schedule."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.