12.9% of Restaurants Introduced Unmanned Ordering Devices Last Year
Kiosk Adoption on the Rise
Delivery App Usage Rate Reaches 31.7%... Upward Trend Continues
Monthly Delivery App Costs Exceed 300,000 Won Due to Increased Burden
Last year, one out of every ten domestic restaurants and cafes in South Korea adopted unmanned devices such as kiosks instead of employing staff. For the first time, the proportion of establishments receiving orders through delivery applications also exceeded 30%. However, the burden of costs associated with these changes remains significant.
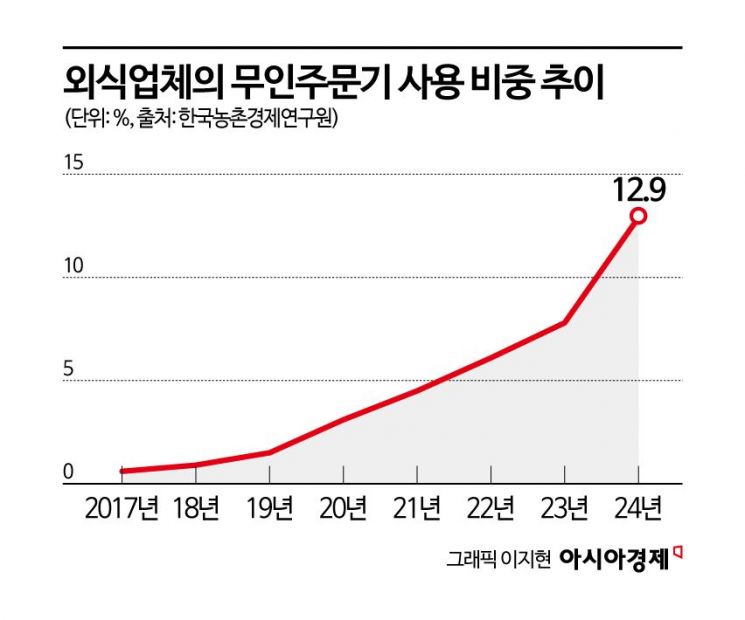
According to the "2024 Restaurant Management Status Survey" by the Korea Rural Economic Institute released on April 26, 2025, the proportion of unmanned ordering devices used in the domestic restaurant industry reached 12.9% last year, an increase of 12.3 percentage points from the previous year's 7.8%. The adoption rate of unmanned ordering devices in restaurants, which was only 0.6% in 2017, has continued to expand annually, surpassing 10% for the first time last year.

By business type, the adoption rate was higher in sectors other than general restaurants (16.6%) compared to general restaurants (9.4%). The highest adoption rate was seen in coffee and other non-alcoholic beverage shops at 30.2%, followed by hamburger, sandwich, and similar food service businesses at 27.9%. Among general restaurants, Japanese restaurants had a relatively high adoption rate at 18.3%, while Korean restaurants were lower at 7.7%. Across all sectors, pubs had the lowest adoption rate at 2.9%.
As of last year, kiosks accounted for more than half of the unmanned ordering devices used in restaurants, followed by customer mobile phones and tablet PCs. Compared to 2023, the proportion of kiosks decreased (from 67.0% to 54.8%), while the number of establishments adopting customer mobile phones (from 28.3% to 35.8%) and tablet PCs (from 4.0% to 9.2%) increased.
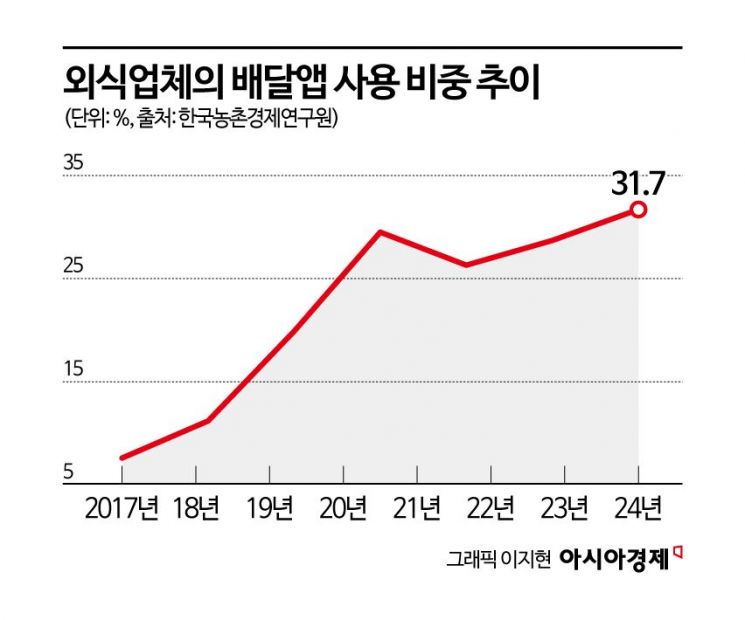
The use of delivery apps also surpassed 30% for the first time. The proportion of restaurants using delivery apps steadily increased from 7.6% in 2018 to 19.9% in 2020, and surged to 29.5% during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2021. Although it slightly declined to 26.3% in 2022 after the transition to endemic status, it rose again last year, increasing by 3.0 percentage points from the previous year to reach 31.7%.
However, as the use of delivery apps has increased, so has the burden of delivery app usage costs. The average monthly delivery app usage cost for restaurants, which had been rising every year, temporarily declined in 2021 when delivery fees were reduced to support businesses during the pandemic. However, costs began to rise again afterward, and last year, the average monthly cost was 303,000 won?a 22.7% decrease from the previous year, but still exceeding 300,000 won.
Park Sungjin, a research fellow at the Korea Rural Economic Institute, stated, "The growing costs associated with delivery apps are increasing the burden on restaurants, making it urgent to address the issue of delivery fees to stabilize restaurant management and alleviate financial pressure." He added, "It is necessary not only to actively promote the distribution and expansion of public delivery apps with lower fees, but also to devise aggressive promotional strategies to raise awareness of these public delivery apps."
On the other hand, the proportion of establishments that have adopted robots remains at 0.4%, indicating that the use of robots in restaurants is still in its early stages. The main reasons cited for not introducing robots were: "the tasks do not warrant robot adoption" (48.0%), "the business environment, such as space, is not suitable" (17.2%), and "there are no robots suitable for the tasks" (14.3%).
Researcher Park explained, "Given the characteristics of the restaurant industry, which includes many small business owners, the spread of food tech could positively impact profitability by reducing fixed costs. However, the initial investment burden and the lack of robot products suitable for the restaurant industry have hindered adoption." He advised, "To further expand food tech adoption in the future, efforts should be strengthened to develop and distribute robots tailored to the restaurant industry."
Meanwhile, the biggest management challenges faced by restaurants were found to be rising ingredient costs and intensified competition. Difficulties due to rising ingredient costs, which are directly linked to operating profits, were cited by 92.3% of respondents, followed by intensified competition (86.5%), rising rent (82.6%), rising labor costs (77.5%), and regulatory restrictions (75.6%). Additionally, a high proportion of respondents reported difficulties in hiring staff, with 54.2% citing kitchen staff shortages and 60.2% citing shortages in hall serving and counter staff, indicating that more than half of restaurants are struggling to secure enough personnel.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.