One of Only Three Successful De Novo Antibody Designs Worldwide...
Domestic Startup Galaxy's Achievement Stands Out
De novo is a Latin term meaning 'new and previously non-existent.' This unfamiliar expression has recently gained attention in the field of new drug development. This is because a 'de novo antibody design' technology has emerged that designs proteins not previously existing through AI. De novo antibody design is also a representative technology in the field of 'AI-based protein structure prediction and design,' which produced three Nobel Chemistry Prize winners last year.
If AI-based protein structure prediction and design technology becomes commercialized, it is expected to bring fundamental changes to the approach of new drug development. This is why pharmaceutical companies worldwide are paying attention to this technology. Protein structure prediction is one of the major challenges in the early stages of drug development. Currently, many proteins must be randomly tested until the desired protein for therapeutic development is found.
According to the bio industry on the 17th, the AI-based protein structure prediction and design field has only recently begun to yield significant results. Following the first successful case announced by the U.S. pharmaceutical company Nabla Bio in November last year, in December, Professor David Baker of the University of Washington, a Nobel Chemistry Prize winner last year, and the Korean AI drug development startup Galaxy succeeded in antibody design. So far, only these three places worldwide have succeeded in de novo antibody design.
Although still in the early research stage, the market outlook is bright. According to Global Insight Services (GIS), a global market research organization, the AI-based protein structure prediction and design market is expected to expand from $1.5 billion last year to $15.3 billion by 2034. The compound annual growth rate is about 26.1%.
One of the Three Successful De Novo Antibody Designs... Domestic Galaxy's Achievement Also Noteworthy
Galaxy, which has succeeded in antibody design very rarely worldwide and uniquely in Korea, is therefore attracting attention. Galaxy is an AI drug development startup founded in 2020, originating from the research lab of Professor Seok Cha-ok at Seoul National University. Currently, based on its technological capabilities, it is conducting joint drug development through strategic collaborations with pharmaceutical companies such as LG Chem and Y-Biologics. Professor Seok's lab has built an international reputation in the protein field by ranking among the top in international competitions such as CASP and CAPRI for over ten years.
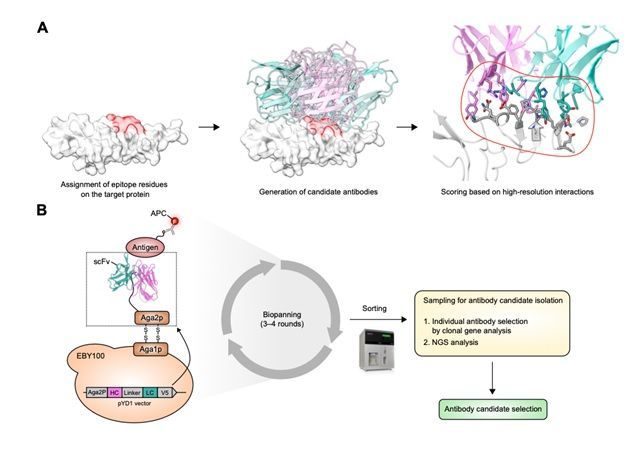
Galaxy's core technology is its independently developed protein design AI platform, 'GalaxyDesign.' GalaxyDesign was developed to teach AI the physical and chemical principles of protein folding and interactions, going beyond merely learning known data to find similar cases. It possesses precision and broad applicability that data-driven AI typically struggles to achieve.
This technological capability was confirmed to be versatile last month by successfully designing antibodies for various targets for the first time worldwide. The designed antibodies are known to have verified binding to therapeutic targets such as PD-L1, HER2, EGFR(S468R), ACVR2A/B, Fzd7, and ALK7.
In particular, the PD-L1 target antibody was confirmed to have similar functions compared to the commercially available antibody therapeutic atezolizumab. It recorded the highest binding affinity among AI-based antibody design cases announced so far, and also showed excellent results in thermal stability, productivity, and activity.
The antibody design for the target ALK7, whose structural information is not yet known, also draws attention. ALK7 is a receptor related to obesity and metabolic diseases. By using GalaxyDesign to predict the structure of ALK7 and designing antibodies that specifically bind to it, Galaxy demonstrated the potential for effective use in developing antibody therapeutics for targets whose structures have not yet been experimentally confirmed.
Galaxy plans to expand cooperation with global pharmaceutical companies in the future for AI-based protein structure design technology. A Galaxy representative said, "We believe that protein discovery and design in the early stages of AI-based drug development can fundamentally streamline the entire development process," adding, "We aim to contribute to effective therapeutic development through collaboration with global pharmaceutical companies and various partners."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.