Professor Lee Kyubin's Team Analyzes Quadruple Boundary Error
 Research team led by Professor Kyubin Lee from the Department of AI Convergence, Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology. Provided by Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology
Research team led by Professor Kyubin Lee from the Department of AI Convergence, Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology. Provided by Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology
Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) announced on the 14th that the research team led by Professor Lee Kyubin of the Department of AI Convergence has developed an AI technology that refines recognition results of untrained objects through error estimation.
This technology is equipped with the ability to delete or add misdetected objects in real time. It is expected to further enhance the visual perception capabilities of robots.
Existing AI vision technologies have limitations, such as only being able to recognize pre-trained objects and lacking the ability to distinguish new objects. To address this, technologies that correct errors based on images and initial prediction data have been developed.
To solve these issues, the research team developed the 'QuBER' model, which applies fast and accurate error correction technology. The QuBER model utilizes RGB-D images and initial prediction data to analyze 'Quadruple Boundary Error,' thereby increasing the accuracy of object recognition.
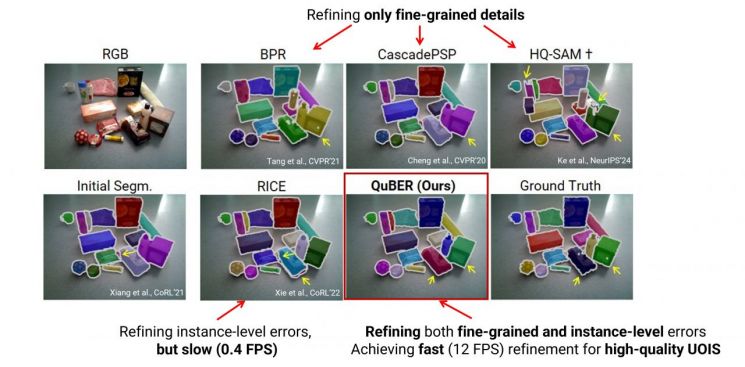 Comparison between QuBER developed by the GIST research team and existing models. Photo by Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology
Comparison between QuBER developed by the GIST research team and existing models. Photo by Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology
Quadruple Boundary Error is attracting attention as a key technique for improving the accuracy of AI vision technology. This technology analyzes the difference between the AI's initial predictions and the actual data (Ground Truth) based on four boundary criteria: ▲True Positive boundary (correctly detected boundary) ▲False Negative boundary (missed boundary that should have been detected) ▲False Positive boundary (incorrectly detected boundary) ▲True Negative boundary (correctly undetected boundary that should not be detected), efficiently correcting errors in object recognition.
The QuBER model developed by the research team demonstrated fast and accurate segmentation capabilities and achieved world-class accuracy, even in situations where recognition is difficult due to many occluded objects.
Professor Lee Kyubin said, "Through this research, we have confirmed the possibility that robots can accurately and efficiently recognize objects they encounter for the first time," adding, "This technology will play a significant role in the development of robots that operate reliably in new environments by being applied to various robotic tasks."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
















