"North Korean hackers have emerged as the biggest threat to the virtual asset industry and have become a major source of revenue for the Kim Jong-un regime."
As diagnosed by the British publication The Economist, the activities of North Korean hacking groups in recent years have become a serious threat to international security. Their attacks have evolved beyond simple information theft to include financial system paralysis, attacks on national infrastructure, and hacking of cryptocurrency exchanges. The funds stolen through cybercrime are used to overcome North Korea's economic difficulties caused by sanctions and blockades, and to develop missiles and nuclear weapons.
Bybit Ethereum Disappears... Behind It, North Korea, the Largest Heist in History
On February 21, Ben Zhou, CEO of Bybit, had an ordinary day like any other?at least until the incident occurred. Before going to bed, he approved a fund transfer between company accounts. This was a routine procedure carried out while serving over 60 million users worldwide. Thirty minutes later, he received a call from Bybit's CFO. "Ben, there's a problem." His voice was trembling. "It seems we've been hacked. All the Ethereum is gone."
The U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) immediately launched an investigation and identified North Korea as behind the hacking incident involving approximately $1.5 billion (2.1742 trillion KRW). According to Reuters and The Guardian, the FBI attributed the attack to the North Korean hacking group Lazarus and stated that they used the 'TraderTraitor' method. TraderTraitor is a hacking technique that tricks victims into downloading cryptocurrency applications containing malware by disguising them as high-paying job offers and other lures.
The British newspaper The Independent described the Bybit incident as the largest 'robbery' in history, noting that the amount is comparable to North Korea's annual defense budget (1.47 billion USD as of 2023). Fortune magazine explained, "It surpassed the $1 billion that Saddam Hussein, the dictator of Iraq, embezzled from his country's central bank before the 2003 U.S.-Iraq war."
Since the incident, Bybit has tracked and frozen transactions amounting to $40 million but failed to prevent some cash-outs. The British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) reported, "Of the $1.46 billion in Ethereum stolen by North Korea's Lazarus group from the cryptocurrency exchange Bybit, at least $300 million has been cashed out."
Kim Jong-un Values Cyberwarfare Almost as Much as Nuclear Weapons... North Korea Responsible for 60% of Global Virtual Asset Theft
"North Korea brings in the best minds and can command them to do anything," said Kim Seung-joo, professor at Korea University's Graduate School of Information Security. Starting computer science education in the 1980s, North Korea recognized the military importance of network technology during the Gulf War and began actively nurturing related talents at the national level. Students with exceptional mathematical abilities were selected and sent to special schools, where they were exempted from annual forced labor. The hacking skills and cryptocurrency laundering techniques honed by these individuals are known to be top-tier. In the 2019 International Collegiate Programming Contest (ICPC), the North Korean team ranked 8th, surpassing Harvard, Oxford, and Stanford. Jenny Jeon, former assistant professor at Georgia Institute of Technology, cited boldness as a characteristic of North Korean hackers, analyzing that "while most countries act cautiously to avoid diplomatic repercussions, North Korea is not afraid to stand out."
From the mid-2010s, North Korea shifted from espionage sabotage (destruction) to cybercrime. Demonstrating how deeply North Korea is engrossed in cyberwarfare, Kim Jong-un mentioned early in his rule that "cyberwarfare is an all-purpose sword guaranteeing the ruthless striking power of the People's Army alongside nuclear weapons and missiles."
The COVID-19 pandemic is a background factor that allowed North Korean cybercrime to flourish. With international economic sanctions and the pandemic combined, North Korea's traditional foreign currency earning methods were severely curtailed. They had to find alternative ways to earn money. Hacking was the foreign currency procurement method North Korea turned to. According to a 2023 United Nations Panel of Experts (UNPE) report, half of North Korea's foreign currency income comes from cyber theft. North Korea's cyber theft revenue exceeds three times its exports to China. The number of North Korean cybercrime personnel increased from 6,800 in 2022 to 8,400 in 2023. Former FBI analyst Nick Carlson summarized the importance of hacking to North Korea's economy in one sentence: "A few dozen hackers are doing the work of millions of laborers."
Despite external accusations that North Korea is behind these attacks, the regime remains indifferent and continues to increase the scale of cryptocurrency theft. According to blockchain analytics firm Chainalysis, North Korean hackers stole $661 million in 2023 alone, and the amount nearly doubled to $1.34 billion in 2024. This accounts for 60% of the global virtual asset theft amount.
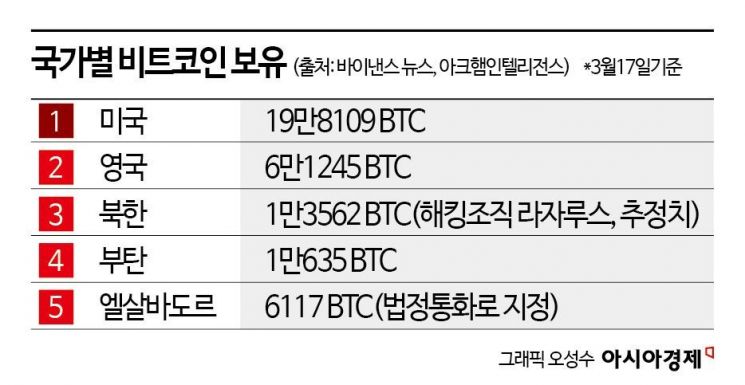
North Korea is also one of the countries holding the most Bitcoin globally, following the United States and the United Kingdom. According to Binance News, operated by the world's largest cryptocurrency exchange Binance, and cryptocurrency data provider Arkham Intelligence, North Korea's hacking group Lazarus is estimated to hold 13,562 Bitcoins (BTC), worth approximately $1.14 billion (about 1.65 trillion KRW). This ranks third worldwide, after the U.S. holding 198,109 BTC and the U.K. holding 61,245 BTC.
Ethereum Theft Hacking Group Targets South Korea’s Semiconductor, Defense, and Manufacturing Industries
The international community recognizes North Korea's cyber hacking as a serious threat. Accordingly, various countries and security agencies are collaborating to strengthen countermeasures. The United States has added North Korea-linked cryptocurrency addresses to its sanctions list and is working with financial institutions to enhance anti-money laundering measures. South Korea and Japan are also establishing systems to block North Korea-linked transactions in cooperation with cryptocurrency exchanges.
As surveillance tightens, North Korea immediately switches to new methods to evade crackdowns. Particularly, exchanges in India and Indonesia, where regulations are lax, have become new targets for North Korea. According to foreign media reports, they use artificial intelligence (AI) to craft phishing emails in multiple languages with high sophistication. They also use AI to make phishing emails appear more authentic and distribute them on a large scale. After securing employment at overseas companies adopting remote and work-from-home policies, they collude with hacking groups. The South China Morning Post (SCMP) reported, "North Korean hackers are believed to have been involved in cryptocurrency-related cybercrime for over a decade and have developed a talent pool well-versed in virtual assets," adding, "Recently, they have begun using generative AI to enhance their attacks."
With North Korea's cyber attacks intensifying, South Korea cannot feel secure. Luke McNamara, Deputy Lead Analyst of Google's Threat Intelligence Group, warned on the 19th, "Recently, APT 45 and the Lazarus group, known to be linked to North Korea, are believed to be targeting South Korea's manufacturing, automotive, defense, and semiconductor industries." There is a possibility that North Korean hacking groups infiltrate domestic companies' internal systems, acquire national technological secrets, and then threaten to leak them externally unless paid in Bitcoin.
Based on Google's cloud investigation results, he also analyzed that the industries most targeted by cyber attacks in South Korea over recent years are manufacturing, financial services, and the media and entertainment sectors.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.


![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















