Hot Hole Photocurrent Enhancement Mechanism Unveiled by KAIST and Inha University Research Team
Accelerating Commercialization of Next-Generation High-Efficiency Photoenergy Conversion Technologies
Domestic researchers have developed a technology that maintains 'hot holes' longer and amplifies their flow, potentially accelerating the commercialization of next-generation high-efficiency photoenergy conversion technologies.
When light hits a metal nanostructure, plasmonic hot carriers are instantaneously generated. These carriers are crucial mediators that convert light energy into high value-added energy sources such as electrical and chemical energy.
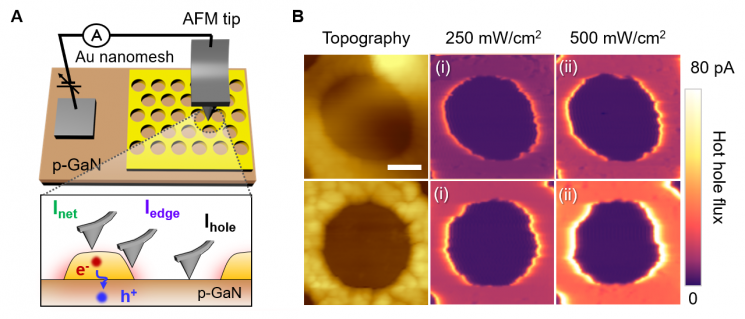 Schematic diagram of real-time hot hole flow observation using atomic force microscopy. Provided by KAIST
Schematic diagram of real-time hot hole flow observation using atomic force microscopy. Provided by KAIST
Among the 'holes'?empty spaces created when electrons move upon light hitting a metal surface?hot holes with high energy amplify the efficiency of photoelectrochemical reactions. However, hot holes typically occur and vanish within a fleeting moment of one quadrillionth of a second (femtoseconds), making practical applications difficult.
The research team led by Professor Jung-Young Park, a distinguished professor in the Department of Chemistry at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), in collaboration with Professor Moon-Sang Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at Inha University, announced on the 12th that they successfully amplified hot hole flow and elucidated the mechanism for enhancing photocurrent.
The team designed a nano-diode structure by placing a metal nanomesh on a special semiconductor substrate (p-type gallium nitride), engineering the substrate surface to promote hot hole extraction. In the gallium nitride substrate aligned with the hot hole extraction direction, the hot hole flow amplification effect was approximately twice that of substrates oriented in other directions.
Using a photocurrent mapping system based on photoconductive atomic force microscopy (pc-AFM), they analyzed hot hole flow in real time at the nanometer scale (one hundred thousandth the thickness of a human hair). They confirmed that hot hole flow is strongly activated mainly at 'hot spots' where light is locally concentrated on the gold nanomesh, but by changing the growth direction of the gallium nitride substrate, hot hole flow was also activated in areas outside the hot spots.
Through this research, the team found an efficient method to convert light into electrical and chemical energy, which could significantly advance next-generation solar cells, photocatalysts, and hydrogen production technologies.
Professor Jung-Young Park of KAIST stated, "We were able to control hot hole flow for the first time using the nano-diode technique, which can make revolutionary contributions to various photoelectric devices and photocatalyst applications. It can be applied to energy conversion technologies using solar power (solar cells, hydrogen generation, etc.) and the development of ultra-small photoelectric devices (photo sensors, nano semiconductor devices)."
Dr. Hyun-Hwa Lee from KAIST's Department of Chemistry and Dr. Yoo-Jin Park, a postdoctoral researcher in the Department of Chemical Engineering at the University of Texas at Austin, participated as first authors. Professor Moon-Sang Lee of Inha University and Professor Jung-Young Park of KAIST's Department of Chemistry served as co-corresponding authors. The research results were published online on the 7th in the international journal Science Advances. (Paper title: Reconfiguring hot-hole flux via polarity modulation of p-GaN in plasmonic Schottky architectures)
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.