Published in the SCIE Journal Clinical Nuclear Medicine
Demonstrating the Usefulness and Potential Value of SPECT/CT in Cancer Diagnosis
Cheon In-guk, head of the Department of Nuclear Medicine at the Southeast Regional Radiation Medicine Institute, simultaneously detected three different tumors using 99mTc-MIBI SPECT/CT imaging.
This study was published last August in the SCIE journal Clinical Nuclear Medicine (IF 10.0) under the title "Papillary Thyroid Cancer, Small Cell Lung Cancer, and Parathyroid Adenoma Synchronously Visualized on 99mTc-MIBI SPECT/CT in a Patient With Hyperparathyroidism: Comparison With 18F-FDG PET/CT.”
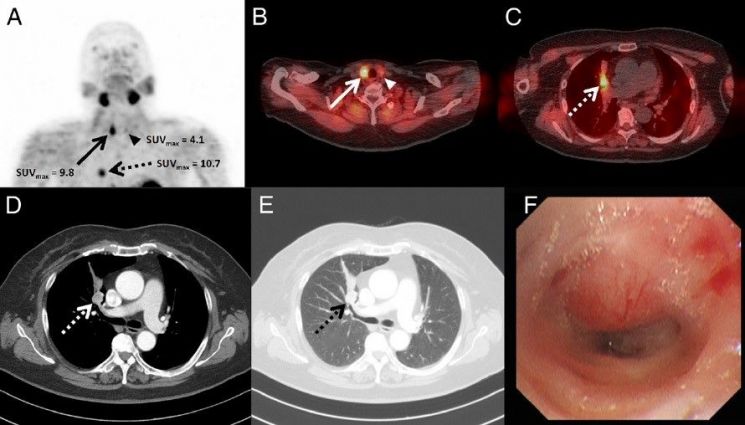 As a result of SPECT/CT imaging, the SUVmax (maximum standardized uptake value) for each tumor (Photo A) is as follows: Small cell lung cancer: 10.7, Thyroid papillary carcinoma: 9.8, Parathyroid adenoma: 4.1. In addition to thyroid papillary carcinoma and parathyroid adenoma (Photos B and C), lung nodules (Photos D and E) were identified, and a mass protruding into the airway was observed during endoscopy (Photo F). A biopsy was performed, confirming the diagnosis of small cell lung cancer.
As a result of SPECT/CT imaging, the SUVmax (maximum standardized uptake value) for each tumor (Photo A) is as follows: Small cell lung cancer: 10.7, Thyroid papillary carcinoma: 9.8, Parathyroid adenoma: 4.1. In addition to thyroid papillary carcinoma and parathyroid adenoma (Photos B and C), lung nodules (Photos D and E) were identified, and a mass protruding into the airway was observed during endoscopy (Photo F). A biopsy was performed, confirming the diagnosis of small cell lung cancer.
The 99mTc-MIBI used in this examination is a radiopharmaceutical that binds to mitochondria and accumulates within cells. After intravenous injection and a certain period, gamma rays emitted are detected externally to create images. Clinically, it is currently used to localize lesions preoperatively in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism or to assess myocardial ischemia. It is also utilized in some cases for breast cancer screening through 99mTc-MIBI mammography.
The case reported in the paper involved a 71-year-old female thyroid cancer patient suspected of having primary hyperparathyroidism who underwent parathyroid 99mTc-MIBI SPECT/CT. Besides the parathyroid adenoma, previously diagnosed thyroid cancer and an unknown lung lesion were observed, raising the possibility of lung cancer, which was later confirmed as small cell lung cancer through biopsy.
While there have been reports of detecting two different tumors simultaneously using SPECT/CT, cases identifying three tumors at the same time are extremely rare.
When this patient underwent both 99mTc-MIBI SPECT/CT and 18F-FDG PET/CT, the maximum standardized uptake values (SUVmax) for small cell lung cancer were 10.7 and 3.0, respectively, with 99mTc-MIBI SPECT/CT showing a higher value.
This demonstrates the complementary usefulness of 99mTc-MIBI SPECT/CT in diagnosing malignant tumors that are less visible on 18F-FDG PET/CT.
Dr. Cheon In-guk stated, “99mTc-MIBI is also known to be useful in evaluating multidrug resistance, so actively utilizing it for pre-treatment diagnosis, staging, and chemotherapy planning of various malignant tumors can provide valuable additional information.” He added, “In the future, alongside 18F-FDG PET/CT, 99mTc-MIBI SPECT/CT could become a new and useful imaging modality in the diagnosis of malignant tumors.”
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.

















