From User Personal Information to Input Data and Serial Numbers
No 'Opt-Out' Setting to Stop Data Collection
App Downloads Blocked, but Existing Users Unaffected
Web Page Remains Accessible
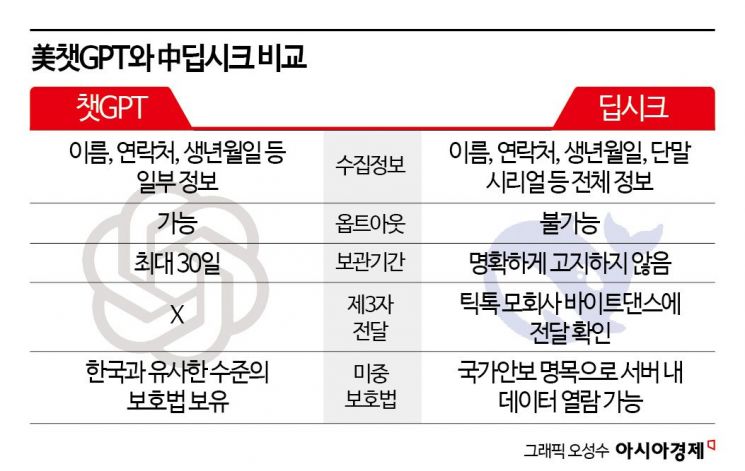
The distinguishing feature of China's generative AI DeepSeek compared to other AI services is that it collects user information "as a whole" without going through the 'tokenization' process that identifies only the necessary information.
Collecting All User Information
According to DeepSeek's privacy policy on the 18th, it can collect user input information such as 'text, chat records, uploaded files' and automatically collected information including 'device and network information, location information, payment information' as is. It also collects account information such as the name, date of birth, and email address entered at the time of registration.
In particular, there was controversy at the initial launch of DeepSeek for collecting keyboard input patterns, but this was excluded from the collection targets as of the 14th. Keyboard input patterns are classified as sensitive information because they can identify individual users and be used to infer important information entered by users, such as passwords.
This differs from information collection by other AI companies. OpenAI's ChatGPT also collects text entered by users, uploaded files, device identifiers, and so on. However, it goes through a 'tokenization' process so that it is impossible to know from whom the information was collected. 'Tokenization' is a method that allows only the necessary information to be used safely. For example, it is similar to showing only the last four digits of a card number on a convenience store receipt instead of the entire number. Through this process, user-identifying information is removed, leaving only the input data to be used for service improvement.
An AI industry insider pointed out regarding DeepSeek's privacy policy, "You can consider that all the digital information I input is handed over," and explained, "In advanced countries such as the United States, regulations on the use of specific personal data are clearly stated in privacy laws, making collection and use impossible."
No Specified Data Usage Period, No Right to Refuse
It is also problematic that DeepSeek does not provide an 'opt-out' setting to refuse the collection of information so that user input is not used for generative AI training. AI services such as ChatGPT, Gemini (Google), and ClovaX (Naver) do not use conversation content and input data for AI service improvement if users refuse. The opt-out option can be easily set in each service's settings. However, DeepSeek does not provide such service settings. This means that all information entered by users while using the service is fully utilized as data for service improvement.
The period for storing collected data is also unclear. DeepSeek's privacy policy states the data retention period as "for the period necessary to provide the service" only. The deletion deadline for collected data is also vague, described as "when no longer needed." In contrast, ChatGPT and ClovaX set the retention period for user input data to a maximum of 30 days. Gemini allows users to set the data retention period themselves, and ClovaX provides a function for users to delete previously entered data directly.
Personal Information Stored on Servers in China
Concerns also arise from the fact that DeepSeek's personal information and data are stored on servers within China. According to DeepSeek's terms, it is possible to transfer personal information to China. The terms state, "The servers are located in the People's Republic of China, and user personal data may be processed and stored on our servers within China."
However, under current Chinese law, if government agencies request information stored on domestic servers, the company must provide it. This means it is difficult to dispel concerns about information leakage. The Personal Information Protection Commission has already confirmed that DeepSeek user information has been transferred to ByteDance, the parent company of the Chinese social networking service (SNS) TikTok. Jang Dong-in, a professor at the AI Graduate School of the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), also said, "DeepSeek has notified that it will use the collected personal information as it sees fit, so caution is necessary."
Although the Personal Information Protection Commission's recommendation to DeepSeek has halted new app downloads, controversy is expected over the effectiveness of this measure. Users who have already downloaded the DeepSeek app can continue to use it, and the DeepSeek web page is excluded from this measure. According to app analysis services WiseApp and Retail, the number of DeepSeek app users in the fourth week of last month was 1.21 million, ranking second among generative AI apps after ChatGPT (4.93 million) during the same period. A Personal Information Protection Commission official explained, "For users who have already downloaded and are using the DeepSeek app, there is little the business operator can do, so users should be cautious when entering personal information," adding, "Due to the nature of the internet, blocking is not easy."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.