A Woman in Her 60s Loses Consciousness Due to Ruptured Cerebral Aneurysm and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Centum General Hospital Performs Coil Embolization, Patient Discharged Walking After Three Weeks
Minimally Invasive Technique Enables Fast Recovery Without Craniotomy
‘Subarachnoid hemorrhage’ is extremely dangerous, with a mortality rate reaching as high as 50%.
Therefore, rapid diagnosis and treatment after the onset of symptoms are essential to increase the patient’s chances of survival and minimize physical sequelae.
In this regard, there was a recent case of surgical treatment for a patient who suffered a brain hemorrhage.
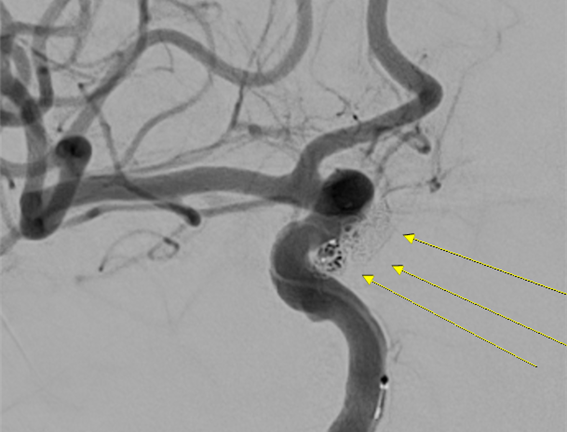
According to Centum General Hospital, a 68-year-old woman, A, was transported to the emergency room due to decreased consciousness. Medical staff performed a brain CT scan, which confirmed subarachnoid hemorrhage. Additional CT angiography revealed that the cause was a ruptured aneurysm in the right carotid artery.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage occurs when the blood vessel wall weakens and balloons like a balloon before bursting, causing acute brain hemorrhage that can lead to fatal outcomes. Ms. A was in a condition where rebleeding could occur from the ruptured aneurysm, and if rebleeding happened, it could cause brain damage and increase the risk of death.
In response, Dr. Donghyuk Lee, head of the Neurosurgery Department at Centum General Hospital, immediately performed an emergency ‘coil embolization’ on Ms. A.
Coil embolization is a minimally invasive surgical method that treats brain aneurysms through endovascular access without craniotomy (surgery involving direct incision of the head). A fine catheter is inserted through blood vessels in the femoral artery or arm, positioned in the cerebral blood vessels, and special metal coils are filled inside the aneurysm.
This surgical method not only blocks blood flow to prevent further bleeding but also has the advantage of a faster recovery due to its minimally invasive nature and allows for additional embolization procedures if necessary.
Before surgery, Ms. A was in a confused state of consciousness, but after the surgery, her condition improved to a drowsy state. She then received intensive care in the intensive care unit for one week, was transferred to a general ward, and underwent rehabilitation therapy. She was discharged walking three weeks after admission. In cases of subarachnoid hemorrhage, only 5 to 10% of patients return to their pre-bleeding state without sequelae.
Dr. Donghyuk Lee, head of the Neurosurgery Department at Centum General Hospital, explained, “Subarachnoid hemorrhage occurs when weakened blood vessels balloon like a berry aneurysm and rupture, causing brain hemorrhage. Coil embolization is a treatment that blocks the weakened part of the vessel with metal coils. This prevents rebleeding and protects the brain from damage.”
As shown in the above case, subarachnoid hemorrhage is a condition where early treatment can determine the patient’s survival and the extent of physical sequelae.
Dr. Lee emphasized, “Therefore, if symptoms such as severe headache, decreased or confused consciousness, vomiting, dizziness, visual disturbances, unilateral paralysis, or sensory abnormalities suddenly appear, you must immediately visit a hospital.”
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.