Maximizing the Efficiency of Alkaline Water Electrolysis
A Breakthrough Catalyst for the Next-Generation Clean Hydrogen Economy
Hanyang University announced on the 7th that Professor Kim Byung-hyun of the Department of Chemical and Molecular Engineering at the ERICA Campus and a joint research team including Dr. Lee Young-jun and Dr. Lee Sung-ho from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) have developed a high-performance catalyst technology for carbon-free clean hydrogen production.
 (From left) Corresponding author - Professor Byung-Hyun Kim, Hanyang University ERICA, Dr. Young-Jun Lee, KIST, Dr. Sung-Ho Lee, KIST. Provided by Hanyang University
(From left) Corresponding author - Professor Byung-Hyun Kim, Hanyang University ERICA, Dr. Young-Jun Lee, KIST, Dr. Sung-Ho Lee, KIST. Provided by Hanyang University
 (From left) First author - Dr. Natarajan Logeshwaran, KIST, PhD candidate Kyuchan Kim, Hanyang University ERICA
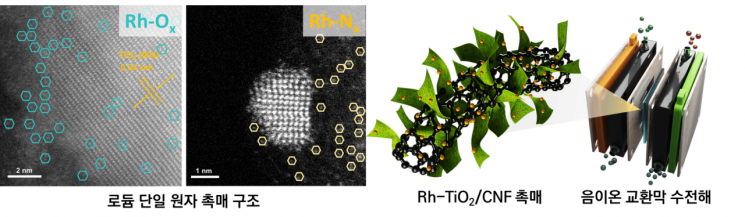
(From left) First author - Dr. Natarajan Logeshwaran, KIST, PhD candidate Kyuchan Kim, Hanyang University ERICA This research overcomes the limitations of alkaline water electrolysis and proposes a novel catalyst (Rh-TiO2/CNF) that significantly improves economic feasibility and efficiency, laying the foundation for the next-generation clean hydrogen economy.
Although conventional alkaline water electrolysis has advantages such as low equipment cost and simple structure, it has limitations due to the relatively slow rate of hydrogen ion formation and hydrogen evolution reactions during water splitting. To overcome this, the research team utilized carbon nanofibers (CNF) as a support, formed titanium oxide (TiO2) on it, and then introduced a dual fixation method of rhodium (Rh) single atoms with nitrogen (Rh-Nx) and oxygen (Rh-Ox). This approach lowers the energy barrier for water splitting on the catalyst surface and creates a synergistic effect that promotes the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER), enabling high-efficiency hydrogen production even in alkaline environments.
 Schematic diagram of the catalyst and alkaline water electrolysis system developed through this study. Provided by Hanyang University
Schematic diagram of the catalyst and alkaline water electrolysis system developed through this study. Provided by Hanyang University
Through various experiments and computational chemistry analyses, the research team demonstrated the impact of the Rh-Nx and Rh-Ox combination on hydrogen evolution and water splitting reactions. This catalyst stably maintains a current density of up to 1 A cm?² per cell area and was confirmed to operate at high power for over 225 hours. It also showed excellent stability and efficiency in a 2-cell AEMWE stack, considering industrialization stages. In particular, it is expected to greatly enhance economic competitiveness by replacing or complementing existing expensive precious metal catalysts (such as Pt and Ir).
Dr. Lee Young-jun of KIST explained, “The binary rhodium single-atom catalyst technology developed this time dramatically increases hydrogen production efficiency under alkaline conditions and will contribute to realizing the next-generation clean hydrogen economy.” Professor Kim Byung-hyun also emphasized the significance of the research, stating, “By identifying factors that improve water electrolysis catalyst performance through computational chemistry techniques, this will greatly contribute to the design of new catalysts and industrial applications in the future.”
This research achievement is evaluated as an important milestone in the development of eco-friendly energy technologies that the government and industry are focusing on, and it is expected to be applied to industrial sites such as large-scale electrolyzer systems, significantly strengthening domestic and international competitiveness in clean hydrogen production.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.

![User Who Sold Erroneously Deposited Bitcoins to Repay Debt and Fund Entertainment... What Did the Supreme Court Decide in 2021? [Legal Issue Check]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026020910431234020_1770601391.png)













