Chronic Inflammation of the Liver Leads to Cirrhosis and Liver Cancer
Lifestyle Improvements and Regular Checkups
Enable Complete Cure if Detected Early
Liver cancer is one of the cancers with a high mortality rate worldwide. However, liver cancer is a preventable disease.
By properly controlling inflammation, which is a major cause of liver cancer, the likelihood of developing liver cancer can be significantly reduced. So, how does inflammation affect the development of liver cancer, and how can it be prevented? We spoke with Dr. Han Sang-young, Director of the Liver Center at Centum General Hospital and former professor at Dong-A University Hospital, to learn more.
▲ The Link Between Chronic Inflammation and Liver Cancer
The most important factor in the development of liver cancer is chronic inflammation of the liver. Inflammation causes damage to liver cells, and during the repeated cycles of damage and regeneration, the likelihood of mutations occurring in liver cells increases. As these mutations accumulate, the risk of normal liver cells transforming into cancer cells also rises.
Dr. Han Sang-young explained, “Chronic inflammation especially has a high potential to cause liver cirrhosis, which is considered a state with a very high probability of progressing to liver cancer. The regenerative nodules found in liver cirrhosis create an environment where inflammation and mutations can lead to the development of liver cancer.”
There are various causes of chronic inflammation in the liver. The most common among them are hepatitis B and hepatitis C. If left untreated, these can lead to liver cirrhosis and liver cancer.
The second cause is alcoholic hepatitis. Excessive alcohol consumption induces toxicity in liver cells, causing chronic inflammation and increasing the risk of liver cancer. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis also induces chronic inflammation and is a risk factor for liver cancer. Autoimmune hepatitis is similar; that is, if liver cells are continuously attacked due to an autoimmune disease, chronic inflammation can occur.
▲ Why Inflammation Causes Liver Cancer
In a state of chronic inflammation, excessive reactive oxygen species are produced, damaging the DNA of liver cells. If the damaged DNA is not properly repaired, mutations occur, increasing the risk of transformation into cancer cells.
Cytokines (inflammatory substances) secreted during the inflammatory response promote the proliferation of cancer cells and stimulate angiogenesis, allowing cancer cells to spread rapidly. Additionally, chronic inflammation impairs the function of immune cells, preventing effective elimination of cancer cells and creating an environment conducive to liver cancer development.
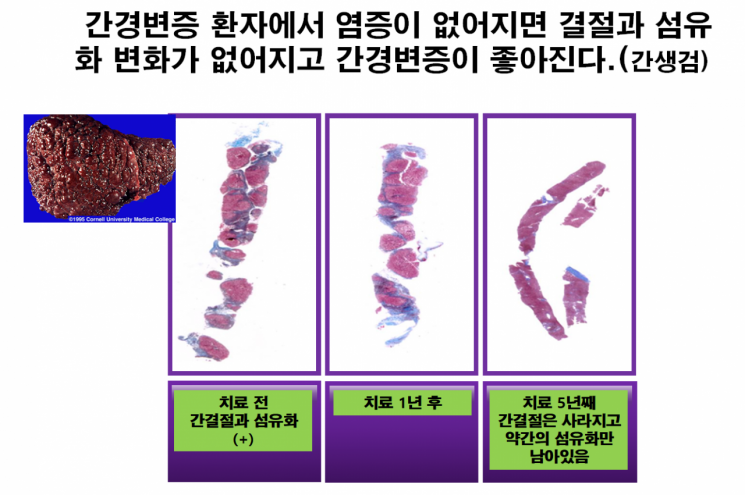 It shows the process of improvement in cirrhosis when inflammation decreases in a patient with cirrhosis (leftmost photo), leading to improvement in nodules and fibrosis. Provided by Centum General Hospital Liver Center.
It shows the process of improvement in cirrhosis when inflammation decreases in a patient with cirrhosis (leftmost photo), leading to improvement in nodules and fibrosis. Provided by Centum General Hospital Liver Center.
▲ Preventing Liver Cancer Through Inflammation Management
Dr. Han emphasized, “Reducing inflammation decreases liver cell damage and can prevent the vicious cycle leading to liver cirrhosis. Without liver cirrhosis, the likelihood of developing liver cancer is significantly lower. Ultimately, managing inflammation well is the most important method for preventing liver cancer.”
Therefore, for hepatitis B, vaccination should be administered, and hepatitis C should be actively treated. Antiviral drugs can effectively suppress hepatitis. If autoimmune hepatitis or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis is suspected, early suppression of inflammation through specialized drug treatment and management is necessary.
Improving lifestyle habits is also essential. Dr. Han advises the following specific methods.
First is a balanced diet. Consuming foods high in fructose (sugar) leads to visceral fat formation and increases protein ratios, but eating fiber-rich vegetables and whole grains can reduce inflammatory responses. Foods rich in antioxidants such as berries, green tea, and broccoli help remove reactive oxygen species and prevent liver cell damage. Regular exercise, sufficient sleep, stress management, smoking cessation, and alcohol moderation are also necessary.
▲ Importance of Regular Checkups
Dr. Han Sang-young of the Liver Center at Centum General Hospital stated, “Liver cancer has a high cure rate if detected early. However, since there are no special symptoms in the early stages, regular checkups are essential.”
He added, “Especially patients with hepatitis B or hepatitis C belong to a high-risk group for liver cancer, so it is advisable to consistently undergo liver ultrasound and blood tests every 3 to 6 months for early detection.” Since ultrasound cannot view the entire liver, it is necessary to have CT or MRI scans once every 1 to 2 years to precisely check the condition of the liver.
Dr. Han emphasized, “Treatment for early liver cancer varies depending on the patient’s condition and the location of the lesion, but if the treatment method is well chosen, it can be cured.”
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















