NVIDIA's 'RTX 50' Features GDDR7 from Samsung and Other Top Three Memory Makers
Partially Replacing HBM Demand
Expanding Applications to On-Device AI, HPC, and Data Centers
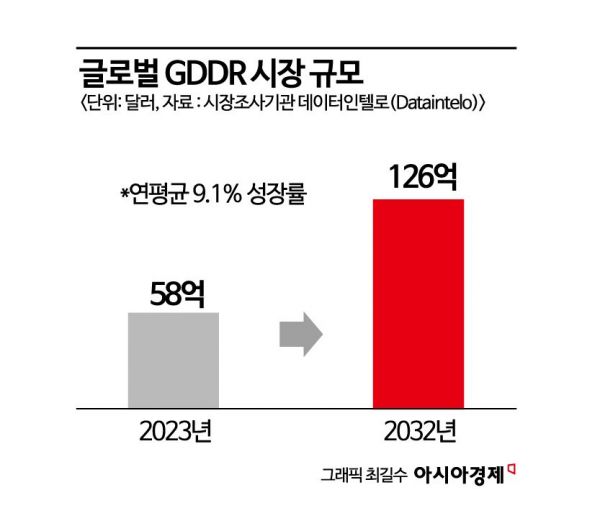
NVIDIA's newly launched graphics processing unit (GPU) 'RTX 50' has brought attention to graphics double data rate (GDDR) memory. Previously considered a niche market within DRAM, GDDR is replacing some of the demand for high bandwidth memory (HBM) and is seeing increased adoption due to growing potential demand in on-device AI, metaverse, automotive, and other sectors. The industry expects the related market size to reach $12.6 billion (approximately 18.532 trillion KRW) by 2032.
According to industry sources on the 14th, NVIDIA's newly released GeForce GPU 'RTX 50' is equipped with GDDR7 from the three major memory companies: Samsung Electronics, SK Hynix, and Micron. While the previous generation RTX 4090 only used Micron's GDDR6X, the new version has secured supply volumes from domestic companies as well.
GDDR was originally the standard specification for graphics DRAM specialized in fast graphics processing. Recently, its applications have expanded beyond traditional graphics DRAM uses such as PCs and game consoles to fields requiring high-performance products, including AI chipsets, high-performance computing (HPC), autonomous vehicles, and data centers.
Most notably, GDDR is gaining attention as a partial substitute for HBM. HBM is the mainstream memory for AI semiconductors but continues to face issues with high cost and supply shortages. While GDDR offers lower performance than HBM, it is praised for lower power consumption and better cost-effectiveness. GDDR features a circuit design that is parallelized to process large amounts of data simultaneously. Although its figures are lower than HBM, the data transfer speed per pin surpasses that of HBM, indicating significant potential for utilization.
In particular, AI accelerators are divided into 'training' for acquiring large-scale data and 'inference' for providing the acquired data as a service. Until now, most big tech companies have used NVIDIA's AI accelerators with HBM-attached GPUs without distinguishing between training and inference. However, as criticisms arise that GPU-based AI accelerators are inefficient for inference, the number of companies using GDDR is increasing. Canadian AI semiconductor startup Tenstorrent, led by CEO Jim Keller, attracted industry attention by unveiling its accelerator Wormhole, which uses GDDR (6th generation) instead of HBM.
GDDR is regarded as highly versatile, being used mostly in graphics cards for personal devices such as laptops and gaming consoles, beyond just being an 'HBM alternative.' The market is also expanding to include extended reality (XR) centered on the metaverse, automotive sectors focusing on vehicle infotainment and autonomous driving systems. Market research firm Dataintelo predicts the global GDDR market size will grow from about $5.8 billion in 2023 to approximately $12.6 billion by 2032.
An industry insider said, "Since GDDR is considered a universal alternative to GPUs with limited supply, it is expected to align well with artificial general intelligence (AGI) chips, suggesting that the share of GDDR will likely increase rapidly."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.