Major financial holding companies and banks are busy submitting their accountability structure charts early in response to the so-called 'Financial Sector Serious Accident Punishment Act.' This marks a complete turnaround from the initially lukewarm attitude toward submitting these charts. The financial authorities are incentivizing financial companies that apply for the pilot operation by the end of this month with 'carrots' such as reduced penalties. Financial companies plan to strengthen their internal control commitment against frequent financial accidents by submitting the accountability structure charts early.
On the 30th, KB Financial Group and KB Kookmin Bank submitted their accountability structure charts to the Financial Supervisory Service (FSS) in accordance with the 'Act on the Governance of Financial Companies' and are participating in the pilot operation. Major financial holding companies also plan to submit their accountability structure charts to the FSS by the end of this month to participate in the pilot operation. All major financial holding companies are reportedly in the final review stage.
Yang Jong-hee, Chairman of KB Financial Group, said, "The operation of the accountability structure chart is a fundamental task for employees themselves and customer protection, and an internal control device that supports the financial company to perform its essential duties." He added, "KB Financial will do its best to establish a basic system for preventing financial accidents and securing customer trust through faithful operation of the accountability structure chart."
Among the five major banks, Shinhan Bank was the first to submit the accountability structure chart. Following Shinhan Bank's submission last month, DGB Financial Group and iM Bank simultaneously submitted theirs on the 21st. This is the first time a holding company and its bank have submitted simultaneously. Hana Bank submitted on the 25th, and Woori Bank completed submission on the 28th. NH Nonghyup Bank also plans to complete submission by the end of this month to participate in the pilot operation.
The accountability structure chart is a document that pre-designates the specific responsibilities and internal control areas of financial company executives, clarifying accountability in the event of financial accidents such as embezzlement. It is called the 'Financial Sector Serious Accident Punishment Act' because it serves as grounds for disciplining executives such as the CEO.
Earlier, the financial authorities announced in July the enforcement of the governance law, which includes the introduction of the accountability structure chart, and stated that a pilot operation would be conducted from early November until early January next year before full implementation. Accordingly, banks and financial holding companies must submit their accountability structure charts by January 2 next year at the latest, while financial investment and insurance companies (with total assets of 5 trillion KRW or more) and savings banks (with total assets of 700 billion KRW or more) must submit by July 2 next year.
Initially, financial companies were reluctant to submit the accountability structure charts. However, the financial authorities encouraged participation by offering incentives such as reduced or waived penalties if employees self-detect or correct legal violations during the pilot operation period for companies applying by the 31st of this month, which changed the atmosphere.
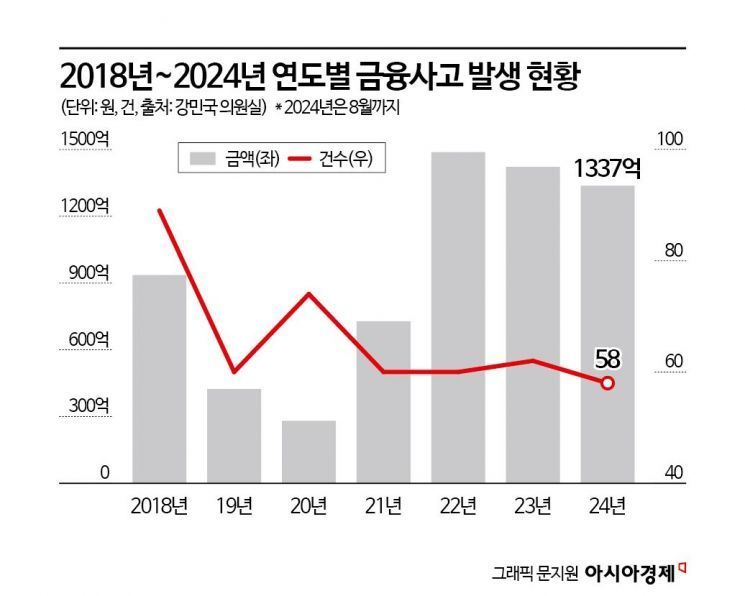
The financial authorities took this bold step to introduce the accountability structure chart due to the frequent occurrence of financial accidents such as embezzlement. According to the 'Domestic Financial Sector Accident Occurrence Status' submitted by the Financial Supervisory Service to Kang Min-guk, a member of the National Assembly's Political Affairs Committee from the People Power Party, a total of 463 financial accidents occurred from 2018 to August this year, amounting to 661.673 billion KRW.
By sector, banks accounted for the largest amount at 409.75 billion KRW (264 cases). Among banks, Woori Bank had the highest amount at 142.113 billion KRW (30 cases), followed by KB Kookmin Bank with 68.32 billion KRW (36 cases), and Kyongnam Bank with 60.158 billion KRW (6 cases).
A financial industry insider said, "The accountability structure chart means that if an accident occurs, you have to step down from your position, so initially, no financial company was willing to step forward and participate." He added, "However, with financial accidents continuing and more companies joining the pilot operation one by one, it has now become difficult not to participate."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.